
USS Icefish (SS-367), a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the icefish, any member of the family Salangidae, small smeltlike fishes of China and Japan. These fish are also collectively known as whitebait.

USS Pilotfish (SS-386), a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named after the pilot fish, a carangoid fish, often seen in warm latitudes in company with sharks.

The Diocese of Chalan Kanoa is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in the United States. It comprises the territory of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and is a suffragan of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Agaña. The diocese was canonically erected on 8 November 1984 by Pope John Paul II. Its territories were taken from the archdiocese based in Guam.

Garapan is the largest village and the center of the tourism industry on the island of Saipan, which is a part of the United States Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI). Garapan, as a census-designated place, has an area of 1.2 km2 (0.46 sq mi) and a population of 3,588.

USS Muliphen (AKA-61/LKA-61) was an Andromeda-class attack cargo ship in service with the United States Navy from 1944 to 1970. She was sunk as an artificial reef in 1989.

USS Keokuk (AN-5/CM-8/CMc-6/AKN-4) was a mine and net laying ship of the United States Navy during World War II.
USS Valve (ARS-28) was a Diver-class rescue and salvage ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy during World War II. Her task was to come to the aid of stricken vessels.

USNS General Hoyt S. Vandenberg (T-AGM-10) was a General G. O. Squier-class transport ship in the United States Navy in World War II named in honor of U.S. Army Chief of Engineers Harry Taylor. She served for a time as army transport USAT General Harry Taylor, and was reacquired by the navy in 1950 as USNS General Harry Taylor (T-AP-145).

Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands Public School System is a school district serving the Northern Mariana Islands, a United States territory.

USS LST-340 - later known as USS Spark (IX-196) - was a LST-1-class tank landing ship that served with the U.S. Navy during World War II. LST-340 served in the Pacific theatre and, despite suffering severe damage from the enemy, was awarded three battle stars for her action in dangerous areas. She was declared too damaged to return to the United States, so she was then reassigned as a barracks ship at Saipan.
San Vicente is a village on Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is located on the eastern side close to the shore of Magicienne Bay, to the south of the island's highest point, Mount Tapochau. It is connected via the cross-island road to Susupe in the west and with Capitol Hill and Tanapag to the north.
Tanapag is a settlement on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is located close to Tanapag Beach on the northwest coast, just to the north of Capital Hill, the island group's center of government. It lies on the Marpi Road, which stretches the length of the island's northwest coast.
San Roque is a settlement in Saipan, in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is located to the north of Tanapag on the island's northwest coast, close to the point where the barrier reef protecting the Tanapag Harbor joins to the island. It is connected to Tanapag by the Marpi Road, which runs the length of the northwestern coast.
The Maritime Heritage Trail – Battle of Saipan is located within the protected waters of Saipan lagoon in the Northern Marianas archipelago. The majority of the dive sites including two Japanese shipwrecks, two Japanese aircraft, two US aircraft, a US landing vehicle and two Japanese landing craft can be found in the clear waters between Garapan, Tanapag Harbor, and Mañagaha Island while further south in Chalan Kanoa Lagoon there are three US tanks.

The Japanese Lighthouse is an old lighthouse situated atop Navy Hill in Garapan, Saipan, in the Northern Mariana Islands. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974. The lighthouse is one of the few surviving pre-World War II, civilian structures originally built by the Japanese.

VPB-18 was a Patrol Bombing Squadron of the U.S. Navy, flying the PBM-3D Mariner. The squadron was established as Patrol Squadron 18 (VP-18) on 15 January 1944 and redesignated as VPB-18 on 1 October 1944. It was disestablished on 23 November 1945. The squadron had a distinguished combat history in the Pacific War.

Ulithi Civil Airfield is a public airport serving the island of Falalop, located in the Ulithi Atoll in the Caroline Islands, Federated States of Micronesia. It was previously Falalop Airfield or Naval Air Base Ulithi, when used as a World War II airfield.

Kizugawa Maru, or Kitsugawa Maru, is a World War II-era Japanese water tanker sunk in Apra Harbor, Guam. Damaged by a submarine torpedo attack off Guam on April 8, 1944, she was towed into port for repairs. In port, she was further damaged in three separate U.S. air attacks during the Mariana and Palau Islands campaign. Deemed irreparable, Kizugawa Maru was scuttled by shore guns on June 27, 1944. The shipwreck is now a deep recreational diving site.

Naval Base Saipan or Naval Advance Base Saipan or Naval Air Base Saipan was a United States Navy Naval base built during World War II to support Pacific Ocean theater of war and the many warships and troops fighting the war. The base was on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. The base was part of the Pacific island hopping campaign. The base construction started after the Battle of Saipan ended on July 9, 1944. US Naval Advance Base Saipan was constructed by the Seabees Naval Mobile Construction Battalions. The base was under the Commander Naval Forces Marianas. Saipan is 12 miles (19 km) long and 5 miles (8.0 km) wide. About 70% of the island was sugarcane cultivation at the start of the base construction. At the start of the Battle of Saipan, the island's population had about 30,000 Japanese troops and about 20,000 Japanese civilians. The city of Garapan was the administrative center for the Saipan governmental district.
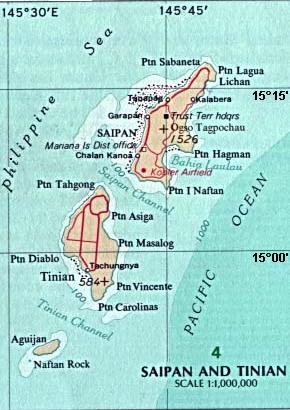
Tinian Naval Base and Naval Air Facility Tinian was a major United States Navy sea and air base on Tinian Island, part of the Northern Mariana Islands on the east side of the Philippine Sea in the Pacific Ocean. The base was built during World War II to support the many bombers and aircraft fighting and patrolling in the South West Pacific theatre of the Pacific War. Numerous naval facilities were built on the entire island of 101.22 km. The main port was built at the city and port of San Jose, also called Tinian Harbor. All construction was done by the Navy's Seabees Sixth Construction Brigade with minor help from the 64th Army Engineers, including the main two airports: West Field and North Field. United States Army Air Forces operated long-range bombers out of the air base built and maintained by the Seabees. The base was decommissioned on 1 June 1947.















