Tanchangya or Tongchangya may refer to:
- Tanchangya people, a tribal people of Bangladesh, India and Myanmar
- Tanchangya language, their Indo-Aryan language
- Tanchangya script, an abugida script for the language
Tanchangya or Tongchangya may refer to:
Chinese can refer to:
Tamil may refer to:
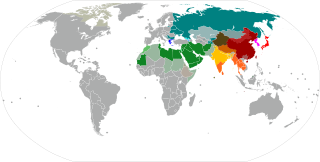
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used by various languages in several language families in South, East and Southeast Asia: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolic, Austroasiatic, Austronesian, and Tai. They were also the source of the dictionary order (gojūon) of Japanese kana.
Marathi may refer to:
Armenian may refer to:
Gujarati may refer to:
Persian may refer to:
Sinhala may refer to:
Khitan or Khitai may refer to:

There are approximately a hundred languages spoken in Myanmar. Burmese, spoken by two-thirds of the population, is the official language.
Chakma language is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Chakma and Daingnet people. The language has common features with other languages in the region like the Chittagonian, Tanchangya, Arakanese and others. It is spoken by around 380,000 people. 150,000 of these are in southeast Bangladesh, primarily the Chittagong Hill Tracts, and another 230,000 in India, including 97,000 in Mizoram, Tripura and Arunachal Pradesh. It is written using the Chakma script, but literacy in this script is low.
The tribal people of Bangladesh are ethnic minorities in Chittagong Hill Tracts (southeastern), Sylhet Division (northeastern), Rajshahi Division (west), and Mymensingh Division (north-central) areas of the country. They are indigenous and the tribal races, total population of ethnic minorities in Bangladesh was estimated to be over 2 million in 2010. They are diverse ethnic communities including Tibeto-Burman, Austric and Dravidian people.
Telugu may refer to:

The Tanchangya people or Tanchangyas are an indigenous ethnic group living in the Chittagong Hill Tracts (CHT) of Bangladesh, Indian states of Tripura and Mizoram, and Rakhine state of Myanmar.
TNV may refer to:
Tagalog may refer to:

Bangladeshis are the citizens of Bangladesh, a South Asian country centered on the transnational historical region of Bengal along the eponymous bay.
The Tanchangya language is one of the eleven indigenous languages in Chittagong Hill Tracts in present-day Bangladesh, and an ethnic group in the Indian states of Tripura and Mizoram, as well as Rakhine State in Myanmar. It is categorized as an Indo-Aryan language, despite some scholars having the opinion of it being Tibeto-Burman language. It is closely related to Chakma and Chittagonian.

The Daingnet people, also known as the Thetkama people are an ethnic group indigenous to northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. According to their own internal census in 1995 they numbered about 60,000. In 2011, the number is estimated to be around 80,000. From appearance they are indistinguishable from the Rakhine people; however, the Daingnet people have a distinct language and culture. Ethnically, they are closely related to the Chakma people of Bangladesh and Northeast India. The languages of the Daingnet and Chakma people are mutually intelligible. Daingnet people are one of 135 ethnic groups officially recognized by the Myanmar government as indigenous to Myanmar. Daingnets are one of the Tibeto-Burman tribes. Genetically they are closely related to the Tibetans, Burmans and Rakhines.
The Tanchangya script, also known as Ka-Pat, is an abugida used to write the Tanchangya language. It is in the southern Brahmic family of scripts. Due to its script family, it has similarities to the Burmese alphabet, Mon alphabet, and Chakma script.