
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is the genetic material of an organism. It consists of DNA. The genome includes both the genes and the noncoding DNA, as well as mitochondrial DNA and chloroplast DNA. The study of the genome is called genomics.
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.
An inverted repeat is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. The intervening sequence of nucleotides between the initial sequence and the reverse complement can be any length including zero. When the intervening length is zero, the composite sequence is a palindromic sequence. For example, 5'---TTACGnnnnnnCGTAA---3' is an inverted repeat sequence.
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a supersecondary structure, which also appears in a variety of other molecules. Motifs do not allow us to predict the biological functions: they are found in proteins and enzymes with dissimilar functions.
A minisatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are typically repeated 5-50 times. Minisatellites occur at more than 1,000 locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Minisatellites are prominent in the centromeres and telomeres of chromosomes, the latter protecting the chromosomes from damage. The name "satellite" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. Minisatellites are small sequences of DNA that do not encode proteins but appear throughout the genome hundreds of times, with many repeated copies lying next to each other.
Satellite DNA consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating, non-coding DNA. Satellite DNA is the main component of functional centromeres, and form the main structural constituent of heterochromatin.
Repeated sequences are patterns of nucleic acids that occur in multiple copies throughout the genome. Repetitive DNA was first detected because of its rapid re-association kinetics. In many organisms, a significant fraction of the genomic DNA is highly repetitive, with over two-thirds of the sequence consisting of repetitive elements in humans.

A variable number tandem repeat is a location in a genome where a short nucleotide sequence is organized as a tandem repeat. These can be found on many chromosomes, and often show variations in length among individuals. Each variant acts as an inherited allele, allowing them to be used for personal or parental identification. Their analysis is useful in genetics and biology research, forensics, and DNA fingerprinting.
A Y-STR is a short tandem repeat (STR) on the Y-chromosome. Y-STRs are often used in forensics, paternity, and genealogical DNA testing. Y-STRs are taken specifically from the male Y chromosome. These Y-STRs provide a weaker analysis than autosomal STRs because the Y chromosome is only found in males, which are only passed down by the father, making the Y chromosome in any paternal line practically identical. This causes a significantly smaller amount of distinction between Y-STR samples. Autosomal STRs provide a much stronger analytical power because of the random matching that occurs between pairs of chromosomes during the zygote making process.
Slipped strand mispairing (SSM),, is a mutation process which occurs during DNA replication. It involves denaturation and displacement of the DNA strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Slipped strand mispairing is one explanation for the origin and evolution of repetitive DNA sequences.
A Short Tandem Repeat (STR) analysis is one of the most useful methods in molecular biology which is used to compare specific loci on DNA from two or more samples. A short tandem repeat is a microsatellite, consisting of a unit of two to thirteen nucleotides repeated several to dozens of times in a row on the DNA strand. STR analysis measures the exact number of repeating units. This method differs from restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis (RFLP) since STR analysis does not cut the DNA with restriction enzymes. Instead, probes are attached to desired regions on the DNA, and a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is employed to discover the lengths of the short tandem repeats.

A HEAT repeat is a protein tandem repeat structural motif composed of two alpha helices linked by a short loop. HEAT repeats can form alpha solenoids, a type of solenoid protein domain found in a number of cytoplasmic proteins. The name "HEAT" is an acronym for four proteins in which this repeat structure is found: Huntingtin, elongation factor 3 (EF3), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and the yeast kinase TOR1. HEAT repeats form extended superhelical structures which are often involved in intracellular transport; they are structurally related to armadillo repeats. The nuclear transport protein importin beta contains 19 HEAT repeats.
STRBase is a database of Short Tandem Repeats

The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) is the United States national DNA database created and maintained by the Federal Bureau of Investigation. CODIS consists of three levels of information; Local DNA Index Systems (LDIS) where DNA profiles originate, State DNA Index Systems (SDIS) which allows for laboratories within states to share information, and the National DNA Index System (NDIS) which allows states to compare DNA information with one another.
ProRepeat is a database of protein repeats.
Multiple loci VNTR analysis (MLVA) is a method employed for the genetic analysis of particular microorganisms, such as pathogenic bacteria, that takes advantage of the polymorphism of tandemly repeated DNA sequences. A "VNTR" is a "variable-number tandem repeat". This method is well known in forensic science since it is the basis of DNA fingerprinting in humans. When applied to bacteria, it contributes to forensic microbiology through which the source of a particular strain might eventually be traced back, making it a useful technique for outbreak surveillance. In a typical MLVA, a number of well-selected and characterised loci are amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), so that the size of each locus can be measured, usually by electrophoresis of the amplification products together with reference DNA fragments. Different electrophoresis equipment can be used depending on the required size estimate accuracy, and the local laboratory set-up, from basic agarose gel electrophoresis up to the more sophisticated and high-throughput capillary electrophoresis devices. From this size estimate, the number of repeat units at each locus can be deduced. The resulting information is a code which can be easily compared to reference databases once the assay has been harmonised and standardised. MLVA has become a major first line typing tool in a number of pathogens where such an harmonisation could be achieved, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Bacillus anthracis, Brucella.
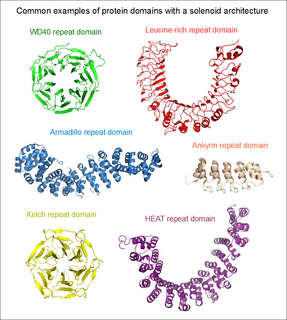
An array of protein tandem repeats is defined as several adjacent copies having the same or similar sequence motifs. These periodic sequences are generated by internal duplications in both coding and non-coding genomic sequences. Repetitive units of protein tandem repeats are considerably diverse, ranging from the repetition of a single amino acid to domains of 100 or more residues.




