History and criteria
The Tank Badge was instituted by the Minister of Defence Otto Gessler on 13 Jul 1921 and laid down in the Heeres-Verordnungsblatt Nr. 41 of 15 July 1921. [1] [2] It was to be issued to veterans of World War I who qualified by: being a crewman (commander, driver, gunner, loader, mechanic, signaller or messenger) of a tank; either an A7V or a Beutepanzer (captured tank), and either participated in three armored assaults or being wounded during an armored assault. [2]
Potential recipients had to apply to the Inspectorate of Motorized Troops to receive a certificate; the actual badge had to be obtained privately. Because of this unusual method of application the badge was officially certified in only 99 cases. [3] [4]

The 8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41 is a German 88 mm anti-aircraft and anti-tank artillery gun, developed in the 1930s. It was widely used by Germany throughout World War II and is one of the most recognized German weapons of the conflict. Development of the original model led to a wide variety of guns.

Philipp Freiherr von Boeselager was the second-last surviving member of the 20 July Plot, a conspiracy of Wehrmacht officers to assassinate the German dictator Adolf Hitler in 1944.
Awards and decorations of Nazi Germany were military, political and civilian decorations that were bestowed between 1923 and 1945, first by the Nazi Party and later the state of Nazi Germany.

The Battle of Debrecen, called by the Red Army the Debrecen Offensive Operation, was a battle taking place from 6 to 29 October 1944 on the Eastern Front in Hungary during World War II.

The Infantry Assault Badge was a German military decoration awarded to Waffen-SS and Wehrmacht Heer soldiers during the Second World War. This decoration was instituted on 20 December 1939 by the Commander-in-Chief (Oberbefehlshaber) of the German Army, Generalfeldmarschall Walther von Brauchitsch. It could be awarded to members of infantry and Gebirgsjäger units that had participated in infantry assaults, with light infantry weapons, on at least three separate days of battle in the front line on or after 1 January 1940. When a counter-offensive led to fighting, it could also apply. Award of the Infantry Assault Badge was authorized at regimental command level, and mechanized or motorized infantry were not eligible for the original badge. A bronze variant of the Infantry Assault Badge was created in June 1940, authorized for motorized and mechanized infantry units, using similar requirements for award as the original silver variant. Non-infantry personnel were not eligible for either grade of the Infantry Assault Badge, but were eligible for other combat recognition badges, usually the General Assault Badge, Close Combat Clasp, or the Panzer Badge. The Luftwaffe would develop its own ground combat badge in 1942, the Ground Assault Badge.

The Pak 43 was a German 88 mm anti-tank gun developed by Krupp in competition with the Rheinmetall 8.8 cm Flak 41 anti-aircraft gun and used during World War II. The Pak 43 was the most powerful anti-tank gun of the Wehrmacht to see service in significant numbers, also serving in modified form as the 8.8 cm KwK 43 main gun on the Tiger II tank, the open-top Nashorn and fully enclosed, casemate-hulled Elefant and Jagdpanther tank destroyers.
The Danzig Cross was a Nazi decoration of the Free City of Danzig. The Cross was instituted on 31 August 1939 as a two grade decoration by Danzig Gauleiter Albert Forster. It was awarded to those, both in Danzig and in the wider Reich, who contributed to building up the Nazi Party in the Free City prior to its incorporation into Germany on 1 September 1939.
The 41st Division was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. It was established on October 1, 1912, in Deutsch Eylau. The division was subordinated in peacetime to the XX Army Corps. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. It was mainly recruited in the Prussian province of West Prussia.
The 21st Reserve Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed on mobilization of the German Army in August 1914 as part of XVIII Reserve Corps. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was raised primarily in the Prussian Province of Hesse-Nassau, but one battalion of the 88th Reserve Infantry Regiment came from the Grand Duchy of Hesse and some other troops of the division came from Westphalia and the Rhine Province.

The Tank Destruction Badge was a World War II German military decoration awarded to individuals of the Wehrmacht who had single-handedly destroyed an enemy tank or an armored combat vehicle using a hand-held weapon. Anti-tank units were ineligible for this award. It was established on 9 March 1942, but could be awarded for actions dating back to 22 June 1941. Prior to the introduction of this award, the soldier would be awarded the General Assault Badge for the action.

The General Assault Badge was a military decoration awarded during World War II to personnel of the German Army, Waffen-SS and Ordnungspolizei who supported an infantry attack but were not part of specific infantry units and therefore did not qualify for the Infantry Assault Badge. It was instituted by General Walther von Brauchitsch on 1 June 1940.

Ernst Volckheim was one of the founders of armored and mechanized warfare. A German officer in the First and Second World War, Volkheim rose to the rank of colonel, during World War II in the German Army. Little known outside of professional military and historical circles, Volkheim is considered the foremost military academic influence on German tank war proponent, Heinz Guderian, because both Volkheim's teaching as well as his 1924 professional military articles place him as one of the very earliest theorists of armored warfare and the use of German armored formations including independent tank corps.
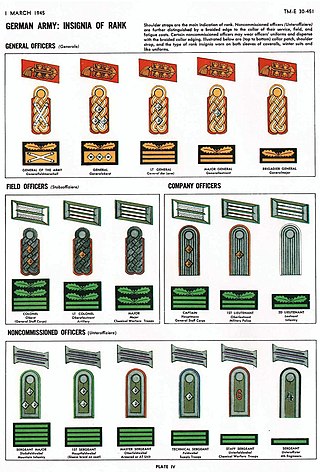
The Heer as the German army and part of the Wehrmacht inherited its uniforms and rank structure from the Reichsheer of the Weimar Republic (1921–1935). There were few alterations and adjustments made as the army grew from a limited peacetime defense force of 100,000 men to a war-fighting force of several million men.

The Awards and decorations of the German Armed Forces are decorations awarded by the German Bundeswehr, the German government, and other organizations to the German military and allied forces. Modern era German military awards have been presented since the establishment of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.

The Ground Assault Badge of the Luftwaffe was a World War II German military decoration awarded to Luftwaffe personnel for achievement in ground combat. It was instituted on 31 March 1942 by the commander-in-chief Hermann Göring.

Karl Eduard August Rothenburg was a higly decorated German officer in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of both the Pour le Mérite and the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Between wars he served as a commander in the police force, before returning to the Wehrmacht in 1934. During World War II he was the commander of a Panzer Regiment of the 7th Panzer Division. Rothenburg was killed six days into the invasion of the Soviet Union on 28 June 1941 near Minsk, Belarus and was posthumously promoted to Generalmajor.

Willy Martin Ernst Rohr was a German Army officer who was a major contributor to the development of infantry tactics in World War I, particularly for the system of Storm Battalions.

The Condor Legion Tank Badge was a German military decoration awarded to tank crews who served with the German Condor Legion during the Spanish Civil War, 1936–1939.
The 43M Turán III or 44M Turán III was a Hungarian medium tank of World War II. It was based on the 41M Turán II medium tank but was equipped with a significantly larger turret and a much more powerful long-barreled 75 mm gun.















