Related Research Articles

Irssi is an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) client program for Linux, FreeBSD, macOS and Microsoft Windows. It was originally written by Timo Sirainen, and released under the terms of the GNU GPL-2.0-or-later in January 1999.
The Single UNIX Specification (SUS) is a standard for computer operating systems, compliance with which is required to qualify for using the "UNIX" trademark. The standard specifies programming interfaces for the C language, a command-line shell, and user commands. The core specifications of the SUS known as Base Specifications are developed and maintained by the Austin Group, which is a joint working group of IEEE, ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 15 and The Open Group. If an operating system is submitted to The Open Group for certification, and passes conformance tests, then it is deemed to be compliant with a UNIX standard such as UNIX 98 or UNIX 03.
In computing, traceroute and tracert are diagnostic command-line interface commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network.

A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to control the execution of the system using shell scripts.
Darwin is the core Unix-like operating system of macOS, iOS, watchOS, tvOS, iPadOS, audioOS, visionOS, and bridgeOS. It previously existed as an independent open-source operating system, first released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code derived from NeXTSTEP, FreeBSD, other BSD operating systems, Mach, and other free software projects' code, as well as code developed by Apple.
In computing, tar is a computer software utility for collecting many files into one archive file, often referred to as a tarball, for distribution or backup purposes. The name is derived from "tape archive", as it was originally developed to write data to sequential I/O devices with no file system of their own, such as devices that use magnetic tape. The archive data sets created by tar contain various file system parameters, such as name, timestamps, ownership, file-access permissions, and directory organization. POSIX abandoned tar in favor of pax, yet tar sees continued widespread use.

Portage is a package management system originally created for and used by Gentoo Linux and also by ChromeOS, Calculate, Sabayon, and Funtoo Linux among others. Portage is based on the concept of ports collections. Gentoo is sometimes referred to as a meta-distribution due to the extreme flexibility of Portage, which makes it operating-system-independent. The Gentoo/Alt project was concerned with using Portage to manage other operating systems, such as BSDs, macOS and Solaris. The most notable of these implementations is the Gentoo/FreeBSD project.

fdisk is a command-line utility for disk partitioning. It has been part of DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and early versions of Microsoft Windows, as well as certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. Windows 2000 and its successors have replaced fdisk with a more advanced tool called diskpart.

chroot is an operation on Unix and Unix-like operating systems that changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and its children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot name files outside the designated directory tree. The term "chroot" may refer to the chroot(2) system call or the chroot(8) wrapper program. The modified environment is called a chroot jail.
These tables provide a comparison of operating systems, of computer devices, as listing general and technical information for a number of widely used and currently available PC or handheld operating systems. The article "Usage share of operating systems" provides a broader, and more general, comparison of operating systems that includes servers, mainframes and supercomputers.

ifconfig is a system administration utility in Unix-like operating systems for network interface configuration.
Ecasound is a hard-disk recording and audio processing tool for Unix-like computer operating systems including Linux, Mac OS X, and FreeBSD.
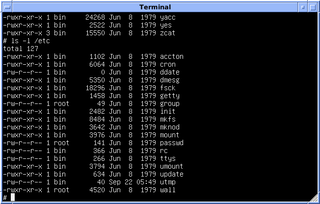
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1.
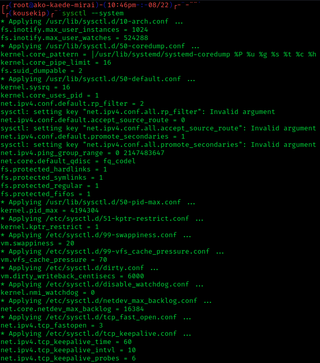
sysctl is a software mechanism in some Unix-like operating systems that reads and modifies the attributes of the system kernel such as its version number, maximum limits, and security settings. It is available both as a system call for compiled programs, and an administrator command for interactive use and scripting. Linux additionally exposes sysctl as a virtual file system.
BioLinux is a term used in a variety of projects involved in making access to bioinformatics software on a Linux platform easier using one or more of the following methods:
In computing, a dynamic linker is the part of an operating system that loads and links the shared libraries needed by an executable when it is executed, by copying the content of libraries from persistent storage to RAM, filling jump tables and relocating pointers. The specific operating system and executable format determine how the dynamic linker functions and how it is implemented.
chattr is the command in Linux that allows a user to set certain attributes of a file. lsattr is the command that displays the attributes of a file.

A Unix-like operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-like application is one that behaves like the corresponding Unix command or shell. Although there are general philosophies for Unix design, there is no technical standard defining the term, and opinions can differ about the degree to which a particular operating system or application is Unix-like.
ptrace is a system call found in Unix and several Unix-like operating systems. By using ptrace one process can control another, enabling the controller to inspect and manipulate the internal state of its target. ptrace is used by debuggers and other code-analysis tools, mostly as aids to software development.
References
- 1 2 John Ousterhout. "History of Tcl" . Retrieved 2009-05-27.
- ↑ "Mac OS X Manual Page for TclX" . Retrieved 2010-03-22.
- ↑ "RPM resource TclX" . Retrieved 2009-05-27.
- ↑ "TclX FreeBSD".