CollabNet VersionOne is a software company founded by Tim O’Reilly, Brian Behlendorf, and Bill Portelli, headquartered in Alpharetta, Georgia, United States. CollabNet focuses on value stream management, DevOps, agile management, application lifecycle management (ALM), and enterprise version control.
The International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) is a software testing certification board that operates internationally. Founded in Edinburgh in November 2002, the ISTQB is a non-profit association legally registered in Belgium.
Azure DevOps Server, formerly known as Team Foundation Server (TFS) and Visual Studio Team System (VSTS), is a Microsoft product that provides version control, reporting, requirements management, project management, automated builds, testing and release management capabilities. It covers the entire application lifecycle and enables DevOps capabilities. Azure DevOps can be used as a back-end to numerous integrated development environments (IDEs) but is tailored for Microsoft Visual Studio and Eclipse on all platforms.
Dr. David Gelperin chaired the working groups developing the IEEE 829-1989 software testing documentation standard. With Jerry E. Durant he went on to develop the High Impact Inspection Technology that builds upon traditional inspections but utilizes a test driven additive.
Rex Black is a software engineer, entrepreneur and an author in the field of software testing. Black graduated from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) in 1990 with a bachelors of science in computer science and engineering. In 1983, Black started work in the software engineering field and has spent more than 20 years in software testing.
DevOps is a methodology integrating and automating the work of software development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops). It serves as a means for improving and shortening the systems development life cycle. DevOps is complementary to agile software development; several DevOps aspects came from the agile approach.
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate. Continuous testing was originally proposed as a way of reducing waiting time for feedback to developers by introducing development environment-triggered tests as well as more traditional developer/tester-triggered tests.
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery.
Disciplined agile delivery (DAD) is the software development portion of the Disciplined Agile Toolkit. DAD enables teams to make simplified process decisions around incremental and iterative solution delivery. DAD builds on the many practices espoused by advocates of agile software development, including scrum, agile modeling, lean software development, and others.
Performance management work (PMW) describes all activities that are necessary to ensure that performance requirements of application systems (AS) can be met. Therefore, PMW integrates software performance engineering (SPE) and application performance management (APM) activities. SPE and APM are part of different lifecycle phases of an AS, namely systems development and IT operations. PMW supports a comprehensive coordination of all SPE and APM activities, which is inevitable due to an increased complexity of AS architectures.
Shift-left testing is an approach to software testing and system testing in which testing is performed earlier in the lifecycle. It is the first half of the maxim "test early and often". It was coined by Larry Smith in 2001.
Perforce Software, Inc. is an American developer of software used for developing and running applications, including version control software, web-based repository management, developer collaboration, application lifecycle management, web application servers, debugging tools, platform automation, and agile planning software.

Better Software magazine was a quarterly digital magazine published by TechWell Corporation. It covered topics of interest to software testers, developers, project managers, and business analysts. Better Software was originally published in 1996 as Software QA magazine, focusing primarily on software QA and testing. Software QA was renamed Better Software magazine in 2004.
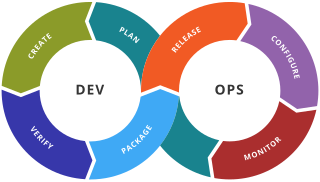
A DevOps toolchain is a set or combination of tools that aid in the delivery, development, and management of software applications throughout the systems development life cycle, as coordinated by an organisation that uses DevOps practices.

Tricentis is a software testing company founded in 2007 and headquartered in Austin, Texas. It provides software testing automation and software quality assurance products for enterprise software.

MLOps or ML Ops is a paradigm that aims to deploy and maintain machine learning models in production reliably and efficiently. The word is a compound of "machine learning" and the continuous delivery practice (CI/CD) of DevOps in the software field. Machine learning models are tested and developed in isolated experimental systems. When an algorithm is ready to be launched, MLOps is practiced between Data Scientists, DevOps, and Machine Learning engineers to transition the algorithm to production systems. Similar to DevOps or DataOps approaches, MLOps seeks to increase automation and improve the quality of production models, while also focusing on business and regulatory requirements. While MLOps started as a set of best practices, it is slowly evolving into an independent approach to ML lifecycle management. MLOps applies to the entire lifecycle - from integrating with model generation, orchestration, and deployment, to health, diagnostics, governance, and business metrics.
CivicActions, Inc. is a services firm that provides technological support with a focus on free and open-source software to agencies.
Angie Jones is a software engineer and automation architect who specializes in software testing and development. Jones has contributed to several open-source testing tools and libraries, including Selenium and Appium.
TestOps refers to the discipline of managing the operational aspects of testing within the software delivery lifecycle.



