See also
- Tecovasaurus, an extinct Late Triassic amniote genus
Tecovas may refer to:

Palo Duro Canyon is a canyon system of the Caprock Escarpment located in the Texas Panhandle near the cities of Amarillo and Canyon. As the second-largest canyon in the United States, it is roughly 120 mi (190 km) long and has an average width of 6 mi (9.7 km), but reaches a width of 20 mi (32 km) at places. Its depth is around 820 ft (250 m), but in some locations, it increases to 1,000 ft (300 m). Palo Duro Canyon has been named "The Grand Canyon of Texas" both for its size and for its dramatic geological features, including the multicolored layers of rock and steep mesa walls, which are similar to those in the Grand Canyon.
Bailey may refer to:

Cistercian Preparatory School is a private school for young men located in Irving, Texas, in the Roman Catholic Diocese of Dallas. Serving grades five through twelve, the school has a population of about 350 boys. Each grade is assigned a priest or a dedicated teacher as a "Form Master," who follows the class over the years and is responsible for building a feeling of community.

Adelobasileus is a genus of mammaliamorph cynodonts from the Late Triassic (Carnian), about 225 million years ago. It is known only from a partial skull recovered from the Tecovas formation in western Texas, southern United States, referred to the species Adelobasileus cromptoni.
Caseosaurus is a dubious genus of saurischian dinosaur that lived approximately 237 to 227 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period in what is now Texas, in North America. It was a small, lightly-built, bipedal, ground-dwelling carnivore, and could grow up to 2 m (6.6 ft) long.
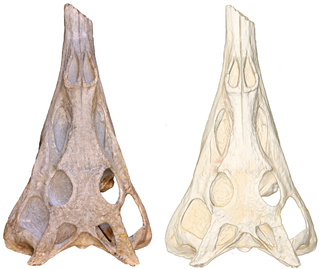
Paleorhinus is an extinct genus of basal phytosaur known from the Late Triassic of Texas and Wyoming, United States, Bavaria, Germany and possibly Poland. It contains two valid species, the type species: Paleorhinus bransoni and Paleorhinus angustifrons. Paleorhinus had a length of about 2.5 meters.
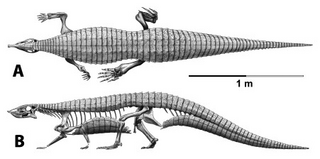
Stagonolepis is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland, the Chinle Formation of Arizona and Utah and the Bluewater Creek Formation of New Mexico.
Crockett may refer to:

The Dockum is a Late Triassic geologic group found primarily on the Llano Estacado of western Texas and eastern New Mexico with minor exposures in southwestern Kansas, eastern Colorado, and Oklahoma panhandle. The Dockum reaches a maximum thickness of slightly over 650 m but is usually much thinner. The Dockum rests on an unconformity over the Anisian aged Anton Chico Formation.
Moran may refer to:

Triodus is an extinct genus of xenacanthidan shark that lived from the Carboniferous to the Triassic. It was a freshwater shark, and fossils have been found in the Chinle Formation and Black Prince Limestone of Arizona, the Petrified Forest Member of New Mexico and the Tecovas Formation of Texas, United States. In 2017, a new species Triodus richterae was described from the Rio do Rasto Formation of Brazil.

Angistorhinus is an extinct genus of phytosaur known from the Late Triassic period of Texas and Wyoming, United States. It was first named by Mehl in 1913 and the type species is Angistorhinus grandis. Other species from Texas and Wyoming, A. alticephalus, A. gracilis and A. maximus, are cospecific with the type species. Angistorhinus is known from the holotype UC 631, partial skull and lower jaws recovered from the Popo Agie Formation, Chugwater Group, Wyoming and from the associated paratype UM 531, a partial skull, TMM 31098-1, skull and lower jaws and ROM 7977, partial skull and lower jaws, recovered from the 'Pre-Tecovas Horizon' in the Dockum Group, Texas. A possible second species, A. talainti is known from the Triassic of Morocco. In 1995, Long and Murry created the new combination, Angistorhinus megalodon by synonymy for Brachysuchus. Hungerbühler and Sues (2001) hypothesised that Angistorhinus is a junior synonym of Rutiodon. However, in 2010 Michelle R. Stocker retained the validity of Brachysuchus and of A. grandis.
Lucasuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Bull Canyon Formation of the Dockum Group outcropping in the Revuelto Creek locality in Quay County, New Mexico. All specimens date back to the Norian stage of the Late Triassic. The genus was named in 1995 after the American paleontologist Spencer G. Lucas.
Tecovasuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur. It is known primarily from osteoderms found from the Tecovas Formation in Texas, which is Late Triassic in age, dating back to the upper Carnian. Material is also known from several other localities of the Chinle Group in New Mexico and Arizona. Specimens of Tecovasuchus have been collected from the Tecovas Formation, the Bluewater Creek Formation, and the Los Esteros Member of the Santa Rosa Formation.

The Garita Creek Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico that contains vertebrate fossils characteristic of the Carnian Age of the late Triassic.
Colognathus is a genus of extinct reptile from Late Triassic rocks of the southwestern United States. It was described in 1928 from a jaw fragment by Case, who interpreted the new taxon as a fish. The type species is C. obscurus.
Sierritasuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur in the subfamily Desmatosuchinae. It is known from a small holotype skeleton from the Late Triassic Tecovas Formation of Texas. This skeleton was discovered in 1939 and was originally assigned to the genus Desmatosuchus. It was placed in its own genus in 2008 after having been in the collections of the University of Michigan Museum of Paleontology, with the type species being S. macalpini. The generic name refers to Sierrita de la Cruz Creek where the holotype was found, and the specific name refers to Archie MacAlpin, who discovered the skeleton. Based on the histology of the scutes of the holotype, the individual was a subadult that was not fully grown.

The Trujillo Formation is a geologic formation in Texas and New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the upper Triassic period.
Tecovas Creek is a creek in Potter County, Texas, USA. Its source is in Bushland, Texas, and it flows into the Canadian River. It is crossed by Farm Road 1061. It is located on the Frying Pan Ranch. The name comes from "techados," which means "roofed" in Spanish.
The Frying Pan Ranch is a historic ranch in Potter County, Texas. Tecovas Creek, a tributary of the Canadian River, flows through the ranch.