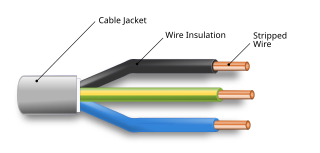
Category 5 cable, commonly referred to as Cat 5, is a twisted pair cable for computer networks. Since 2001, the variant commonly in use is the Category 5e specification (Cat 5e). The cable standard provides performance of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for most varieties of Ethernet over twisted pair up to 1000BASE-T. Cat 5 is also used to carry other signals such as telephony and video.

The BNC connector is a miniature quick connect/disconnect radio frequency connector used for coaxial cable. The interface specifications for the BNC and many other connectors are referenced in MIL-STD-348. It features two bayonet lugs on the female connector; mating is fully achieved with a quarter turn of the coupling nut. BNC connectors are used with miniature-to-subminiature coaxial cable in radio, television, and other radio-frequency electronic equipment, test instruments, and video signals. The BNC was commonly used for early computer networks, including ARCnet, the IBM PC Network, and the 10BASE2 variant of Ethernet. BNC connectors are made to match the characteristic impedance of cable at either 50 ohms or 75 ohms. They are usually applied for frequencies below 4 GHz and voltages below 500 volts.

An electrical connector is an electro-mechanical device used to join electrical terminations and create an electrical circuit. Electrical connectors consist of plugs (male-ended) and jacks (female-ended). The connection may be temporary, as for portable equipment, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices. An adapter can be used to effectively bring together dissimilar connectors.

An RCA connector, sometimes called a phono connector or Cinch connector, is a type of electrical connector commonly used to carry audio and video signals. The name RCA derives from the Radio Corporation of America, which introduced the design by the early 1940s for internal connection of the pickup to the chassis in home radio-phonograph consoles. It was originally a low-cost, simple design, intended only for mating and disconnection when servicing the console. Refinement came with later designs, although they remained compatible.

The XLR connector is a style of electrical connector, primarily found on professional audio, video, and stage lighting equipment. The connectors are circular in design and have between three and seven pins. They are most commonly associated with balanced audio interconnection, including AES3 digital audio, but are also used for lighting control, low-voltage power supplies, and other applications. XLR connectors are available from a number of manufacturers and are covered by an international standard for dimensions, IEC 61076-2-103. They are superficially similar to the smaller DIN connector range, but are not physically compatible with them.

A registered jack (RJ) is a standardized telecommunication network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. Registration interfaces were first defined in the Universal Service Ordering Code (USOC) system of the Bell System in the United States for complying with the registration program for customer-supplied telephone equipment mandated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the 1970s. They were subsequently codified in title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 68.

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.

The 25-pair color code, originally known as even-count color code, is a color code used to identify individual conductors in twisted-pair wiring for telecommunications.

An audio multicore cable is a thick cable which contains from four to 64 individual audio cables inside a common, sturdy outer jacket. Audio multicore cables are widely used whenever multiple audio signals, for example from a number of microphones, need to be conveyed between common locations. Typical professional audio applications include audio recording, sound reinforcement, PA systems and broadcasting. The "snake" is typically used to make it easier to route many signals from the microphones or other input transducers, to the audio console or sound equipment.

A telephone plug is a type of connector used to connect a telephone set to the telephone wiring inside a building, establishing a connection to a telephone network. It is inserted into its counterpart, a telephone jack, commonly affixed to a wall or baseboard. The standard for telephone plugs varies from country to country, though the RJ11 modular connector has become by far the most common.

In telecommunications, structured cabling is building or campus cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements called subsystems.

A 66 block is a type of punchdown block used to connect sets of wires in a telephone system. They have been manufactured in three sizes, A, B, and M. A and B have six clips in each row while M has only 4. The A blocks have the rows spaced farther apart and have been obsolete for many years. The B style is used mainly in distribution panels where several destinations need to connect to the same source. The M blocks are often used to connect a single instrument to such a distribution block. 66 blocks are designed to terminate 22 through 26 AWG solid copper wire. The 66 series connecting block, introduced in the Bell System in 1962, was the first terminating device with insulation displacement connector technology. The term 66 block reflects its Western Electric model number.

The micro ribbon or miniature ribbonconnector is a common type of electrical connector for a variety of applications, such as in computer and telecommunications equipment having many contacts.

The 1A2 Key Telephone System is a business telephone system developed and distributed by the Western Electric Company for the Bell System.

A modular connector is an electrical connector that was originally designed for use in telephone wiring, but has since been used for many other purposes. Many applications that originally used a bulkier, more expensive connector have converted to modular connectors. Probably the best known applications of modular connectors are for telephone and Ethernet.
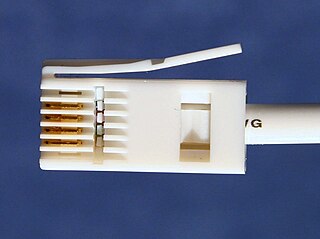
British telephone sockets were introduced in their current plug and socket form on 19 November 1981 by British Telecom to allow subscribers to connect their own telephones. The connectors are specified in British Standard BS 6312. Electrical characteristics of the telephone interface are specified by individual network operators, e.g. in British Telecom's SIN 351. Electrical characteristics required of British telephones used to be specified in BS 6305.
Many different electrical connectors have been used to connect microphones to audio equipment—including PA systems, radios, tape recorders, and numerous other devices.
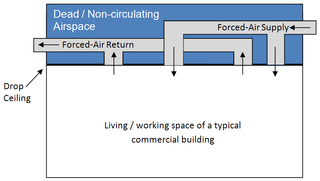
A plenum space is a part of a building that can facilitate air circulation for heating and air conditioning systems, by providing pathways for either heated/conditioned or return airflows, usually at greater than atmospheric pressure. Space between the structural ceiling and the dropped ceiling or under a raised floor is typically considered plenum; however, some drop-ceiling designs create a tight seal that does not allow for airflow and therefore may not be considered a plenum air-handling space.
ANSI/TIA-568 is a set of telecommunications standards from the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA). The standards address commercial building cabling for telecommunications products and services.