Related Research Articles
A television channel is a terrestrial frequency or virtual number over which a television station or television network is distributed. For example, in North America, "channel 2" refers to the terrestrial or cable band of 54 to 60 MHz, with carrier frequencies of 55.25 MHz for NTSC analog video (VSB) and 59.75 MHz for analog audio (FM), or 55.31 MHz for digital ATSC (8VSB). Channels may be shared by many different television stations or cable-distributed channels depending on the location and service provider

Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).

The VRT, is the national public-service broadcaster for the Flemish Community of Belgium.

News broadcasting is the medium of broadcasting various news events and other information via television, radio, or the internet in the field of broadcast journalism. The content is usually either produced locally in a radio studio or television studio newsroom, or by a broadcast network. It may include material such as sports coverage, weather forecasts, traffic reports, political commentary, expert opinions, editorial content, and other material that the broadcaster feels is relevant to their audience. An individual news program is typically reported in a series of individual stories that are presented by one or more anchors. A frequent inclusion is live or recorded interviews by field reporters.
Community television in Australia is a form of free-to-air non-commercial citizen media in which a television station is owned, operated and/or programmed by a community group to provide local programming to its broadcast area. In principle, community television is another model of facilitating media production and involvement by private citizens and can be likened to public-access television in the United States and community television in Canada.
Television in Germany began in Berlin on 22 March 1935, broadcasting for 90 minutes three times a week. It was home to the first public television station in the world, named Fernsehsender Paul Nipkow.
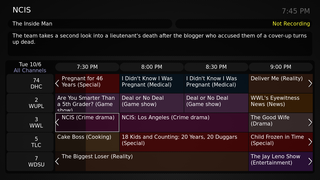
Guide Plus+, TV Guide On Screen, TV Guide Daily, TV Guide Plus+ and Guide Plus+ Gold or G-Guide are brand names for an interactive electronic program guide (EPG) system that is used in consumer electronics products, such as television sets, DVD recorders, personal video recorders, and other digital television devices. It offers interactive on-screen program listings that enable viewers to navigate, sort, select and schedule television programming for viewing and recording. The differing names are only used for marketing purposes – the entire system is owned by Rovi Corporation, the successor to Gemstar-TV Guide International. In 2016, Rovi acquired digital video recorder maker TiVo Inc., and renamed itself TiVo Corporation.

The Moel-y-Parc transmitting station is situated on Moel y Parc, a hill in north-east Wales at the northern end of the Clwydian range, close to the town of Caerwys and several miles (kilometres) north-east of Denbigh. It was built in 1962/1963 by the IBA to bring 405-line VHF ITV television to North Wales and it has been on the air since 1963. Its original height of 229 metres (751 ft) made it the tallest structure in North Wales and it stands on land that is itself about 335 metres (1,099 ft) above sea level. In 1965, VHF television transmissions from the BBC commenced from the site.
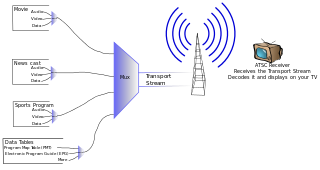
An ATSCtuner, often called an ATSC receiver or HDTV tuner, is a type of television tuner that allows reception of digital television (DTV) television channels that use ATSC standards, as transmitted by television stations in North America, parts of Central America, and South Korea. Such tuners are usually integrated into a television set, VCR, digital video recorder (DVR), or set-top box which provides audio/video output connectors of various types.
Radio Alice was an Italian free radio broadcasting from Bologna at the end of the 1970s. It started transmitting on 9 February 1976 using an ex-military transmitter on a frequency of 100.6 MHz. The station founders were associated with the Italian counter-culture movement of 1977 and drew inspiration from the Situationists and Dada. Franco "Bifo" Berardi, one of the founders, described Radio Alice as a "mix between a classical medium of militant information and a sort of art experiment in media sabotage."
A pirate television station is a broadcast television station that operates without a broadcast license. Like its counterpart pirate radio, the term pirate TV lacks a specific universal interpretation. It implies a form of broadcasting that is unwelcome by the licensing authorities within the territory where its signals are received, especially when the country of transmission is the same as the country of reception. When the area of transmission is not a country, or when it is a country and the transmissions are not illegal, those same broadcast signals may be deemed illegal in the country of reception. Pirate television stations may also be known as "bootleg TV", or confused with licensed low-power broadcasting (LPTV) or amateur television (ATV) services.
The television industry in Turkey includes high-tech program production, transmission and coverage. Turkish Radio and Television Corporation is Turkey's largest and most powerful national television station. As of 1 August 2019, RTÜK states that there a total of 536 television channels in Turkey. Turkey is the world's fastest growing television series exporter and has currently overtaken both Mexico and Brazil as the world's second highest television series exporter after the United States. Turkish television drama has grown in since the early 2000s.
In broadcasting, digital subchannels are a method of transmitting more than one independent program stream simultaneously from the same digital radio or television station on the same radio frequency channel. This is done by using data compression techniques to reduce the size of each individual program stream, and multiplexing to combine them into a single signal. The practice is sometimes called "multicasting".

Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter.

TV3 Lithuania is a Lithuanian free-to-air television channel that was launched on 11 April 1993. It was owned by Modern Times Group (MTG) until 2017, when it was acquired by Providence Equity Partners for €115 million.

Sun Direct is an Indian Satellite television service provider, It was launched in December 2007. It transmits digital satellite television and audio to households in India. Sun Direct uses MPEG-4 digital compression, transmitting HD Channels on GSAT-15 at 93.5°E and SD Channels on MEASAT-3 at 91.5°E. Sun Direct currently offers total 480+ channels and services, along with many other active services. It is the first service provider to launch HD Counterpart.
Television in Italy was introduced in 1939, when the first experimental broadcasts began. However, this lasted for a very short time: when fascist Italy entered World War II in 1940 all transmissions were interrupted, and were resumed in earnest only nine years after the end of the conflict, on January 3, 1954.
High-definition television describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs.
The digital transition in the United States was the switchover from analog to exclusively digital broadcasting of terrestrial television programming. According to David Rehr, then president and CEO of the National Association of Broadcasters, this transition represented "the most significant advancement of television technology since color TV was introduced." For full-power TV stations, the transition went into effect on June 12, 2009, with stations ending regular programming on their analog signals no later than 11:59 p.m. local time that day.

CMQ was a Cuban radio and television station located in Havana, Cuba, reaching an audience in the 1940s and 1950s, attracting viewers and listeners with a program that ranged from music and news dissemination. It later expanded into radio and television networks. As a radio network it was a heated competitor of the RHC-Cadena Azul network.
References
- ↑ And_ / Tim Parish (2005), Telestreet: The Italian Media Jacking Movement , retrieved 2021-01-14