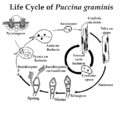
Telium, plural telia, are structures produced by rust fungi as part of the reproductive cycle. [1] They are typically yellow or orange drying to brown or black and are exclusively a mechanism for the release of teliospores which are released by wind or water to infect the alternate host in the rust life-cycle. The telial stage provides an overwintering strategy in the life cycle of a parasitic heteroecious fungus by producing teliospores; this occurs on cedar trees. A primary aecial stage is spent parasitizing a separate host plant which is a precursor in the life cycle of heteroecious fungi. Teliospores are released from the telia in the spring. The spores can spread many kilometers through the air, however most are spread near the host plant. [2]