
In Sabine and ancient Roman religion and myth, Luna is the divine embodiment of the Moon. She is often presented as the female complement of the Sun, Sol, conceived of as a god. Luna is also sometimes represented as an aspect of the Roman triple goddess, along with Diana and either Proserpina or Hecate. Luna is not always a distinct goddess, but sometimes rather an epithet that specializes a goddess, since both Diana and Juno are identified as moon goddesses.

The Capitolium or Capitoline Hill, between the Forum and the Campus Martius, is one of the Seven Hills of Rome.
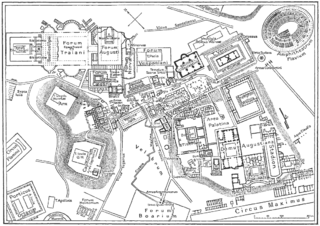
Vicus Tuscus was an ancient street in the city of Rome, running southwest out of the Roman Forum between the Basilica Julia and the Temple of Castor and Pollux towards the Forum Boarium and Circus Maximus via the west side of the Palatine Hill and Velabrum.
Festivals in ancient Rome were a very important part in Roman religious life during both the Republican and Imperial eras, and one of the primary features of the Roman calendar. Feriae were either public (publicae) or private (privatae). State holidays were celebrated by the Roman people and received public funding. Games (ludi), such as the Ludi Apollinares, were not technically feriae, but the days on which they were celebrated were dies festi, holidays in the modern sense of days off work. Although feriae were paid for by the state, ludi were often funded by wealthy individuals. Feriae privatae were holidays celebrated in honor of private individuals or by families. This article deals only with public holidays, including rites celebrated by the state priests of Rome at temples, as well as celebrations by neighborhoods, families, and friends held simultaneously throughout Rome.

The Campus Martius was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about 2 square kilometres in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome. The IV rione of Rome, Campo Marzio, which covers a smaller section of the original area, bears the same name.

The Temple of Portunus is an ancient Roman temple located in Rome, Italy. It was built beside the Forum Boarium, the Roman cattle market associated with Hercules, which was adjacent to Rome's oldest river port and the oldest stone bridge across the Tiber River, the Pons Aemilius. It was probably dedicated to the gateway god Portunus although the precise dedication remains unclear as there were several other temples in the area besides his. It was misidentified as the Temple of Fortuna Virilis from the Renaissance and remains better known by this name. The temple is one of the best preserved of all Roman temples.

Lanuvium, modern Lanuvio, is an ancient city of Latium vetus, some 32 kilometres (20 mi) southeast of Rome, a little southwest of the Via Appia.

Juno was an ancient Roman goddess, the protector and special counsellor of the state. She was equated to Hera, queen of the gods in Greek mythology and a goddess of love and marriage. A daughter of Saturn and Ops, she was the sister and wife of Jupiter and the mother of Mars, Vulcan, Bellona, Lucina and Juventas. Like Hera, her sacred animal was the peacock. Her Etruscan counterpart was Uni, and she was said to also watch over the women of Rome. As the patron goddess of Rome and the Roman Empire, Juno was called Regina ("Queen") and was a member of the Capitoline Triad, centered on the Capitoline Hill in Rome, and also including Jupiter, and Minerva, goddess of wisdom.

Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete state. Today they remain "the most obvious symbol of Roman architecture". Their construction and maintenance was a major part of ancient Roman religion, and all towns of any importance had at least one main temple, as well as smaller shrines. The main room (cella) housed the cult image of the deity to whom the temple was dedicated, and often a table for supplementary offerings or libations and a small altar for incense. Behind the cella was a room, or rooms, used by temple attendants for storage of equipment and offerings. The ordinary worshiper rarely entered the cella, and most public ceremonies were performed outside of the cella where the sacrificial altar was located, on the portico, with a crowd gathered in the temple precinct.

The Forum Boarium was the cattle market or forum venalium of ancient Rome. It was located on a level piece of land near the Tiber between the Capitoline, the Palatine and Aventine hills. As the site of the original docks of Rome and adjacent to the Pons Aemilius, the earliest stone bridge across the Tiber, the Forum Boarium experienced intense commercial activity.
The Capitoline Triad was a group of three deities who were worshipped in ancient Roman religion in an elaborate temple on Rome's Capitoline Hill. It comprised Jupiter, Juno and Minerva. The triad held a central place in the public religion of Rome.

The lectisternium was an ancient Roman propitiatory ceremony, consisting of a meal offered to gods and goddesses. The word derives from lectum sternere, "to spread a couch." The deities were represented by their busts or statues, or by portable figures of wood, with heads of bronze, wax or marble. It has also been suggested that the divine images were bundles of sacred herbs tied together in the form of a head, covered by a waxen mask so as to resemble a kind of bust, rather like the straw figures called Argei. A couch (lectus) was prepared by draping it with fabric. The figures or sacred objects pertaining to the deity were laid upon it. Each couch held a pair of deities, sometimes male with female equivalent. If the image was anthropomorphic, the left arms were rested on a cushion (pulvinus) in the attitude of reclining to eat. The couches (pulvinar) were set out in the open street, or a temple forecourt, or in the case of ludi, in the pulvinar or viewing box, and a meal was served on a table before the couch.

The Porticus Octaviae is an ancient structure in Rome. The colonnaded walks of the portico enclosed the Temples of Juno Regina (north) and Jupiter Stator (south), as well as a library. The structure was used as a fish market from the medieval period up to the end of the 19th century.

The Temple of Jupiter Stator, also known to the ancient Romans as the Temple of Jove Metellina and Metellus's Temple, was a temple dedicated to the Roman god Jupiter Stator. It was located beside the Temple of Juno Regina in the Porticus Octaviae in the southern Campus Martius before its destruction in the AD 64 Great Fire of Rome.

Tas-Silġ is a rounded hilltop on the south-east coast of the island of Malta, overlooking Marsaxlokk Bay, and close to the town of Żejtun. Tas-Silġ is a major multi-period sanctuary site with archaeological remains covering four thousand years, from the neolithic to the ninth century AD. The site includes a megalithic temple complex dating from the early third millennium BC, to a Phoenician and Punic sanctuary dedicated to the goddess Astarte. During the Roman era, the site became an international religious complex dedicated to the goddess Juno, helped by its location along major maritime trading routes, with the site being mentioned by first-century BC orator Cicero.

Fortuna Huiusce Diei was an aspect of the goddess Fortuna, known primarily for her temple in the Area Sacra di Largo Argentina at Rome. Cicero lists her among the deities who should be cultivated in his ideal state, because "she empowers each day". She thus embodies an important aspect of time as it figures in Roman religion: every day of the year had a distinct and potent nature, which the public priests were responsible for knowing and aligning the community with by means of the religious calendar.
The Temple of Fortuna Equestris was a temple dedicated to the goddess Fortuna in ancient Rome. Its precise location is unknown, though Vitruvius states it stood near the Theatre of Pompey. No evidence of it remains after 22 AD, meaning it was probably lost in the fire of 21 AD, which also damaged the Theatre of Pompey.
The Temple of Juno Regina was a temple on the Aventine Hill in Rome. A temple was vowed to "Juno, Queen of Veii" by Marcus Furius Camillus on his conquest of Veii. It was built in 396 BCE and dedicated on September 1. It held a statue of the goddess brought from Veii by Camillus - the temple was later noted for its gifts, sacrifices and miracles and was restored by Augustus, but is not mentioned in any post-Augustan sources. It was on the upper part of the clivus Publicius - two inscriptions relating to the lustral procession of 207 BC are preserved in the Santa Sabina basilica.














