Related Research Articles

Tindari, ancient Tyndaris or Tyndarion, is a small town, frazione in the comune of Patti and a Latin Catholic titular see.

Crotone is a city and comune in Calabria, Italy.

Ostia Antica is an ancient Roman city and the port of Rome located at the mouth of the Tiber. It is near modern Ostia, 25 km (16 mi) southwest of Rome. Due to silting and the invasion of sand, the site now lies 3 km (2 mi) from the sea. The name Ostia derives from Latin os 'mouth'.

Cumae was the first ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia on the mainland of Italy and was founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BC. It became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of Cuma, a frazione of the comune Bacoli and Pozzuoli in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, Italy.

The Temple of Portunus is an ancient Roman temple located in Rome, Italy. It was built beside the Forum Boarium, the Roman cattle market associated with Hercules, which was adjacent to Rome's oldest river port and the oldest stone bridge across the Tiber River, the Pons Aemilius. It was probably dedicated to the gateway god Portunus although the precise dedication remains unclear as there were several other temples in the area besides his. It was misidentified as the Temple of Fortuna Virilis from the Renaissance and remains better known by this name. The temple is one of the best preserved of all Roman temples.

In ancient Roman religion and mythology, Tellus Mater or Terra Mater is the personification of the Earth. Although Tellus and Terra are hardly distinguishable during the Imperial era, Tellus was the name of the original earth goddess in the religious practices of the Republic or earlier. The scholar Varro (1st century BC) lists Tellus as one of the di selecti, the twenty principal gods of Rome, and one of the twelve agricultural deities. She is regularly associated with Ceres in rituals pertaining to the earth and agricultural fertility.

The Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, also known as the Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus, was the most important temple in Ancient Rome, located on the Capitoline Hill. It was surrounded by the Area Capitolina, a precinct where numerous shrines, altars, statues and victory trophies were displayed.

The Theatre of Pompey, also known by other names, was a structure in Ancient Rome built during the latter part of the Roman Republican era by Pompey the Great. Completed in 55 BC, it was the first permanent theatre to be built in Rome. Its ruins are located at Largo di Torre Argentina.

Terracina is an Italian city and comune of the province of Latina, located on the coast 56 km (35 mi) southeast of Rome on the Via Appia. The site has been continuously occupied since antiquity.

The Temple of Vesta, or the aedes, is an ancient edifice in Rome, Italy. It is located in the Roman Forum near the Regia and the House of the Vestal Virgins. The Temple of Vesta housed Vesta's holy fire, which was a symbol of Rome's safety and prosperity. The temple has a circular footprint, making it a tholos.

Metapontum or Metapontium was an important city of Magna Graecia, situated on the gulf of Tarentum, between the river Bradanus and the Casuentus. It was distant about 20 km from Heraclea and 40 from Tarentum. The ruins of Metapontum are located in the frazione of Metaponto, in the comune of Bernalda, in the Province of Matera, Basilicata region, Italy.

The Temple of Mars Ultor was a sanctuary erected in Ancient Rome by the Roman Emperor Augustus in 2 BCE and dedicated to the god Mars in his guise as avenger. The centerpiece of the Forum of Augustus, it was a peripteral style temple, on the front and sides, but not the rear, raised on a platform and lined with eight columns in the Corinthian order style.

The Temple of Apollo Palatinus, sometimes called the Temple of Actian Apollo, was a temple of the god Apollo in Rome, constructed on the Palatine Hill on the initiative of Augustus between 36 and 28 BCE. It was the first temple to Apollo within the city's ceremonial boundaries, and the second of four temples constructed by Augustus. According to tradition, the site for the temple was chosen when it was struck by lightning, which was interpreted as a divine portent. Augustan writers situated the temple next to Augustus's personal residence, which has been controversially identified as the structure known as the domus Augusti.

The Temple of Minerva Medica is a ruined nymphaeum of Imperial Rome which dates to the 4th century CE. It is located between the Via Labicana and Aurelian Walls and just inside the line of the Anio Vetus. Once part of the Horti Liciniani on the Esquiline Hill, it now faces the modern Via Giolitti. It was once thought to be the temple to Minerva Medica mentioned by Cicero and other sources.

Ietas, was an ancient town of the interior of Sicily, in the northwest of the island, not very far from Panormus, in the modern comune of San Giuseppe Jato, whose name reflects the ancient town's.

The Temple of Juno Moneta was an ancient Roman temple that stood on the Arx or the citadel on the Capitoline Hill overlooking the Roman Forum. Located at the center of the city of Rome, it was next to the place where Roman coins were first minted, and probably stored the metal and coins involved in this process, thereby initiating the ancient practice of associating mints with temples. In addition, it was the place where the books of the magistrates were deposited.

The Regio III Isis et Serapis was the third regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio III took its name from the double sanctuary of Isis and Serapis, in the area of the Via Praenestina, containing the valley that was to be the future site of the Colosseum, and parts of the Oppian and Esquiline hills.

The Regio IV Templum Pacis is the fourth regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio IV took its name from the Temple of Peace built in the region by the emperor Vespasian. It includes the valley between the Esquiline and the Viminal hills, the popular area of the Suburra, and the Velian Hill.
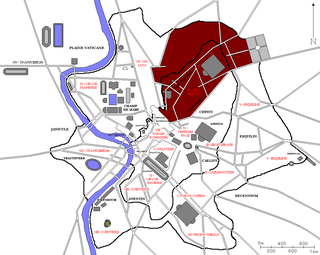
The Regio VI Alta Semita is the sixth regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio VI took its name from the street passing over the Quirinal Hill. It was a large regio that also encompassed the Viminal Hill, the lower slopes of the Pincian, and the valleys in-between.

The Regio VIII Forum Romanum Magnum is the eighth regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio VIII took its name from the Roman Forum, the political centre of Ancient Rome.
References
- Platner, Samuel Ball, A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome, Oxford University Press (1929) (online version)