
A single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a camera that typically uses a mirror and prism system that permits the photographer to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. With twin lens reflex and rangefinder cameras, the viewed image could be significantly different from the final image. When the shutter button is pressed on most SLRs, the mirror flips out of the light path, allowing light to pass through to the light receptor and the image to be captured.
Robot was a German imaging company known originally for clockwork cameras, later producing surveillance (Traffipax) and bank security cameras. Originally created in 1934 as a brand of Otto Berning, it became part of the Jenoptik group of optical companies in 1999, and specializes in traffic surveillance today.

Carl Zeiss AG, branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe and Otto Schott he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide.
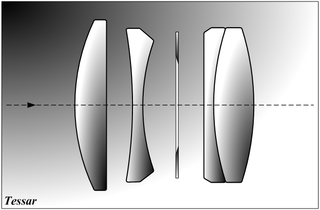
The Tessar is a photographic lens design conceived by the German physicist Paul Rudolph in 1902 while he worked at the Zeiss optical company and patented by Zeiss in Germany; the lens type is usually known as the Zeiss Tessar.

Zorki is the name of a series of 35mm rangefinder cameras manufactured in the Soviet Union between 1948 and 1978.

Rollei was a German manufacturer of optical instruments founded in 1920 by Paul Franke and Reinhold Heidecke in Braunschweig, Lower Saxony, and maker of the Rolleiflex and Rolleicord series of cameras. Later products included specialty and nostalgic type films for the photo hobbyist market.

Rolleiflex is the name of a long-running and diverse line of high-end cameras originally made by the German company Franke & Heidecke, and later Rollei-Werke.
Kiev is a Soviet and Ukrainian brand of photographic equipment including cameras manufactured by the Arsenal Factory in Kiev, Ukraine. The camera nameplates show the name "KIEV", with older cameras using "КИЕВ" or "КИЇВ" in Cyrillic.

Contax began as a camera model in the Zeiss Ikon line in 1932, and later became a brand name. The early cameras were among the finest in the world, typically featuring high quality Zeiss interchangeable lenses. The final products under the Contax name were a line of 35 mm, medium format, and digital cameras engineered and manufactured by Japanese multinational Kyocera, and featuring modern Zeiss optics. In 2005, Kyocera announced that it would no longer produce Contax cameras. The rights to the brand are currently part of Carl Zeiss AG, but no Contax cameras are currently in production, and the brand is considered dormant.

Retina was the brand-name of a long-running series of German-built Kodak 35mm cameras, produced from 1934 until 1969. Kodak Retina cameras were manufactured in Stuttgart-Wangen by the Kodak AG Dr. Nagel Werk which Kodak had acquired in December 1931.

C. P. Goerz was founded in 1886 by Carl Paul Goerz. Originally, it made geometrical drawing instruments for schools. From 1888 it made cameras and photographic lenses. During the First World War, Goerz's main production was for the German and Austrian military. Goerz is known primarily for Anschütz strut-folding cameras, Dagor and Tengor lenses, Tenax cameras and Minicord subminiature cameras. C. P. Goerz also made a series of telescopic sights for sporting rifles that saw some use during the shortage of military sniping rifles experienced during the early stages of the trench warfare that was to characterise much of the First World War.

The Rollei 35 is a 35mm miniature viewfinder camera built by Rollei. The original Rollei 35, when introduced at photokina in 1966, was the smallest existing 135 film camera. The Rollei 35 series remains one of the smallest 35 mm cameras after the Minolta TC-1 and Minox 35. In 30 years, about 2 million Rollei 35 series cameras were manufactured. The Rollei 35 was manufactured by DHW Fototechnik up to 2015, the successor of Franke & Heidecke as small-batch production. The last version is the Rollei 35 Classic, an updated Rollei 35 SE.

The Robot II was a mechanical 135 film camera by Robot introduced in 1938. It was a slightly larger camera than the Robot I, with some significant improvements but still using the basic mechanism. Among the standard objectives were 3 cm Zeiss Tessar and a 33⁄4 cm Zeiss Tessar in 1:2,8 and 1:3,5 variations, a 1:2,0/40 mm Zeiss Biotar and 1:4/7,5 cm Zeiss Sonnar.

The Contaflex series is a family of 35mm leaf-shuttered SLR cameras, produced by Zeiss Ikon in the 1950s and 1960s. The name was first used in 1935 on a 35mm Twin-lens reflex camera, the Contaflex TLR also by Zeiss Ikon, the -flex part in the name referring to integral mirror for the viewfinder. The first models, the Contaflex I and II have fixed lenses, while the later models have interchangeable lenses, and eventually the Contaflexes became a camera system with a wide variety of accessories.

The Kolibri 523/18 was a camera by Zeiss Ikon, made between 1930 and 1935.

The Kodak Retina Reflex is a discontinued series of four single-lens reflex cameras made by Kodak, continuing the brand Kodak Retina.
The design of photographic lenses for use in still or cine cameras is intended to produce a lens that yields the most acceptable rendition of the subject being photographed within a range of constraints that include cost, weight and materials. For many other optical devices such as telescopes, microscopes and theodolites where the visual image is observed but often not recorded the design can often be significantly simpler than is the case in a camera where every image is captured on film or image sensor and can be subject to detailed scrutiny at a later stage. Photographic lenses also include those used in enlargers and projectors.

During the 1930s, Zeiss Ikon (ZI) made a wide range of miniature cameras for the 35mm film format. Most cameras used the standard 24×36 mm frame size, like the Contax, Nettax and Super Nettel. However, the ability to take images in fast sequence was a popular marketing element at the time, and several fast-operating models were made. Among these were the Otto Berning's motor-driven Robot cameras as well as the ZI lever-operated Tenax I and Tenax II. These have the smaller square format of 24×24 mm, enhancing faster frame advance.

The Contarex is a 35mm SLR camera made by Zeiss Ikon. It was first presented at Photokina in 1958 and initially scheduled for delivery in the spring of 1959, but it was not made generally available until March 1960. It is popularly known as the Contarex I, the Bullseye or the Cyclops. The camera was aimed at the high-end and professional markets; in 1961, the retail price was $499.

The Kine Exakta was the first 35mm single-lens reflex (SLR) still camera in regular production. It was presented by Ihagee Kamerawerk Steenbergen GmbH, Dresden at the Leipziger Frühjahrsmesse in March 1936. The Exakta name had already been used by Ihagee on a roll film rangefinder RF camera line since 1933, among these the Vest Pocket Exakta Model B from which the Kine Exakta inherited its general layout and appearance. The word Kine never appeared on the camera itself, only in the instruction manuals and advertising to distinguish it from the roll film variants. Several of its features constituted the foundation for the majority of 35mm SLR cameras produced ever since, although at this stage in a relatively primitive state.

















