
A gluon is a type of massless elementary particle that mediates the strong interaction between quarks, acting as the exchange particle for the interaction. Gluons are massless vector bosons, thereby having a spin of 1. Through the strong interaction, gluons bind quarks into groups according to quantum chromodynamics (QCD), forming hadrons such as protons and neutrons.

The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment is one of two large general-purpose particle physics detectors built on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland and France. The goal of the CMS experiment is to investigate a wide range of physics, including the search for the Higgs boson, extra dimensions, and particles that could make up dark matter.
The BaBar experiment, or simply BaBar, is an international collaboration of more than 500 physicists and engineers studying the subatomic world at energies of approximately ten times the rest mass of a proton (~10 GeV). Its design was motivated by the investigation of charge-parity violation. BaBar is located at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, which is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy in California.

In particle physics, for models with N = 1 supersymmetry, a higgsino, symbol
H͂
, is the superpartner of the Higgs field. A higgsino is a Dirac fermionic field with spin 1/2 and it refers to a weak isodoublet with hypercharge half under the Standard Model gauge symmetries. After electroweak symmetry breaking higgsino fields linearly mix with U(1) and SU(2) gauginos leading to four neutralinos and two charginos that refer to physical particles. While the two charginos are charged Dirac fermions, the neutralinos are electrically neutral Majorana fermions. In an R-parity-conserving version of the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model, the lightest neutralino typically becomes the lightest supersymmetric particle (LSP). The LSP is a particle physics candidate for the dark matter of the universe since it cannot decay to particles with lighter mass. A neutralino LSP, depending on its composition can be bino, wino or higgsino dominated in nature and can have different zones of mass values in order to satisfy the estimated dark matter relic density. Commonly, a higgsino dominated LSP is often referred as a higgsino, in spite of the fact that a higgsino is not a physical state in the true sense.

ROOT is an object-oriented computer program and library developed by CERN. It was originally designed for particle physics data analysis and contains several features specific to the field, but it is also used in other applications such as astronomy and data mining. The latest minor release is 6.32, as of 2024-05-26.

Neutrinoless double beta decay (0νββ) is a commonly proposed and experimentally pursued theoretical radioactive decay process that would prove a Majorana nature of the neutrino particle. To this day, it has not been found.
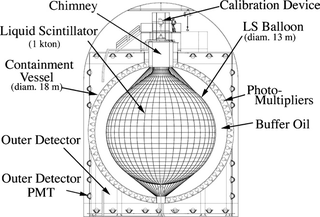
The Kamioka Liquid Scintillator Antineutrino Detector (KamLAND) is an electron antineutrino detector at the Kamioka Observatory, an underground neutrino detection facility in Hida, Gifu, Japan. The device is situated in a drift mine shaft in the old KamiokaNDE cavity in the Japanese Alps. Although located in the Kamioka Observatory, which is part of the University of Tokyo, this project is conducted by a team at Tohoku University. The site is surrounded by 53 Japanese commercial nuclear reactors. Nuclear reactors produce electron antineutrinos () during the decay of radioactive fission products in the nuclear fuel. Like the intensity of light from a light bulb or a distant star, the isotropically-emitted flux decreases at 1/R2 per increasing distance R from the reactor. The device is sensitive up to an estimated 25% of antineutrinos from nuclear reactors that exceed the threshold energy of 1.8 megaelectronvolts (MeV) and thus produces a signal in the detector.

Maria Spiropulu is a Greek particle physicist. She is the Shang-Yi Ch'en Professor of Physics at the California Institute of Technology.
In particle physics, a B-factory, or sometimes a beauty factory, is a particle collider experiment designed to produce and detect a large number of B mesons so that their properties and behavior can be measured with small statistical uncertainty. Tau leptons and D mesons are also copiously produced at B-factories.
In particle physics, tracking is the process of reconstructing the trajectory of electrically charged particles in a particle detector known as a tracker. The particles entering such a tracker leave a precise record of their passage through the device, by interaction with suitably constructed components and materials. The presence of a calibrated magnetic field, in all or part of the tracker, allows the local momentum of the charged particle to be directly determined from the reconstructed local curvature of the trajectory for known electric charge of the particle.
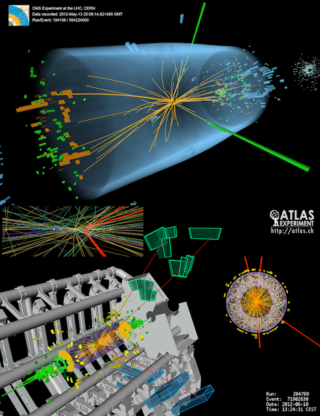
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the quantum excitation of the Higgs field, one of the fields in particle physics theory. In the Standard Model, the Higgs particle is a massive scalar boson with zero spin, even (positive) parity, no electric charge, and no colour charge that couples to mass. It is also very unstable, decaying into other particles almost immediately upon generation.

Sir Tejinder Singh Virdee,, is a Kenyan-born British experimental particle physicist and Professor of Physics at Imperial College London. He is best known for originating the concept of the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) with a few other colleagues and has been referred to as one of the 'founding fathers' of the project. CMS is a world-wide collaboration which started in 1991 and now has over 3500 participants from 50 countries.

In nuclear and particle physics, a geoneutrino is a neutrino or antineutrino emitted during the decay of naturally-occurring radionuclides in the Earth. Neutrinos, the lightest of the known subatomic particles, lack measurable electromagnetic properties and interact only via the weak nuclear force when ignoring gravity. Matter is virtually transparent to neutrinos and consequently they travel, unimpeded, at near light speed through the Earth from their point of emission. Collectively, geoneutrinos carry integrated information about the abundances of their radioactive sources inside the Earth. A major objective of the emerging field of neutrino geophysics involves extracting geologically useful information from geoneutrino measurements. Analysts from the Borexino collaboration have been able to get to 53 events of neutrinos originating from the interior of the Earth.

Kam-Biu Luk is a professor of physics, with a focus on particle physics, at UC Berkeley and a senior faculty scientist in the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's physics division. Luk has conducted research on neutrino oscillation and CP violation. Luk and his collaborator Yifang Wang were awarded the 2014 Panofsky Prize "for their leadership of the Daya Bay experiment, which produced the first definitive measurement of θ13 angle of the neutrino mixing matrix." His work on neutrino oscillation also received 2016 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics shared with other teams. He also received a Doctor of Science honoris causa from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in 2016. Luk is a fellow of the American Physical Society, and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Wang Yifang is a Chinese particle and accelerator physicist. He is director of the Institute of High Energy Physics (IHEP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing and known for contributions to neutrino physics, in particular his leading role at Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment to determine the last unknown neutrino mixing angle θ 13.
John "Jack" Francis Gunion is an American physicist, specializing in theoretical high energy physics.
Michel Della Negra is a French experimental particle physicist known for his role in the 2012 discovery of the Higgs Boson.

Atsuto Suzuki is an experimental particle physicist known for his observations of neutrinos and anti-neutrinos.
Tulika Bose is a professor of physics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, whose research focuses on developing triggers for experimental searches of new phenomena in high energy physics. Bose is a leader within the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment, a CERN collaboration famous for its experimental observation of the Higgs boson in 2012.
Oliver Buchmueller is a scientist and professor of physics at the Faculty of Natural Science, Imperial College London. Buchmueller is presently serving as one of the lead scientists on the Compact Muon Solenoid experiment at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider, the principal investigator of the Atom Interferometer Observatory and Network and also one of the lead authors at Atomic Experiment for Dark Matter and Gravity Exploration in Space (AEDGE). Previously he has been associated with the ALEPH experiment at CERN’s LEP collider and the BaBar experiment at SLAC. Buchmueller was among the group of scientists responsible for the discovery of Higgs Boson particle at the LHC, CERN and later in the scientific exploration to find the traces of dark matter through the LHC.











