The X Window System is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.

GNUstep is a free software implementation of the Cocoa Objective-C frameworks, widget toolkit, and application development tools for Unix-like operating systems and Microsoft Windows. It is part of the GNU Project.
ANSI escape sequences are a standard for in-band signaling to control the cursor location, color, and other options on video text terminals and terminal emulators. Certain sequences of bytes, most starting with Esc and '[', are embedded into the text, which the terminal looks for and interprets as commands, not as character codes.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system, which share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

Enlightenment, also known simply as E, is a compositing window manager for the X Window System. Since version 20, Enlightenment is also a Wayland compositor. Enlightenment developers have referred to it as "the original eye-candy window manager."

A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that is used for entering data into, and displaying or printing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early day hardcopy terminal, and predated the use of a computer screen by decades.
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97. The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.
freedesktop.org (fd.o) is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free software desktop environments for the X Window System (X11) and Wayland on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington from Red Hat in March 2000. The project's servers are hosted by Portland State University, which in turn are sponsored by HP, Intel and Google.
RealVNC is a company that provides remote access software. The software consists of a server and client application for the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) protocol to control another computer's screen remotely.
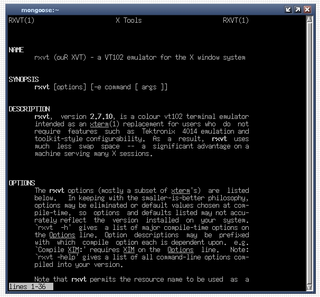
rxvt is a terminal emulator for the X Window System.

DOSBox is an emulator program which emulates an IBM PC compatible computer running a DOS operating system. Many IBM PC compatible graphics and sound cards are also emulated. This means that original DOS programs are provided with an environment in which they can run correctly, even though the modern computers have dropped support for that old environment.
The Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL) are a set of graphics libraries that grew out of the development of Enlightenment, a window manager and Wayland compositor. The project's focus is to make the EFL a flexible yet powerful and easy to use set of tools to extend the capabilities of both the Enlightenment window manager and other software projects based on the EFL. The libraries are meant to be portable and optimized to be functional even on mobile devices such as smart phones and tablets.

GNOME Terminal is a terminal emulator for the GNOME desktop environment written by Havoc Pennington and others. Terminal emulators allow users to access a UNIX shell while remaining on their graphical desktop.
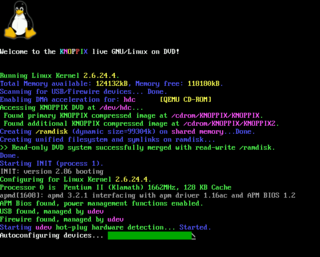
A virtual console (VC) – also known as a virtual terminal (VT) – is a conceptual combination of the keyboard and display for a computer user interface. It is a feature of some Unix-like operating systems such as BSD, Linux, illumos and UnixWare in which the system console of the computer can be used to switch between multiple virtual consoles to access unrelated user interfaces. Virtual consoles date back at least to Xenix and Concurrent CP/M in the 1980s.
Terminology is the study of terms and their use.

Wayland is a communication protocol that specifies the communication between a display server and its clients, as well as a C library implementation of that protocol. A display server using the Wayland protocol is called a Wayland compositor, because it additionally performs the task of a compositing window manager.

GNOME is a free and open-source desktop environment for Unix-like operating systems. GNOME was originally an acronym for GNU Network Object Model Environment, but the acronym was dropped because it no longer reflected the vision of the GNOME project.

Bodhi Linux is a lightweight Linux distribution based on Ubuntu that uses the Moksha window manager. The philosophy for the distribution is to provide a minimal base system so that users can populate it with the software they want. Thus, by default it only includes software that is essential to most Linux users, including a file browser (PCManFM), a web browser (Midori) and a terminal emulator (Terminology). It does not include software or features that its developers deem unnecessary. To make populating systems with software easy, Bodhi Linux developers maintain an online database of lightweight software that can be installed in one click via apturl.
Kmscon is a virtual console that runs in userspace and intends to replace the Linux console, a terminal built into the Linux kernel. Kmscon uses the KMS driver for its output, it is multiseat-capable, and supports internationalized keyboard input and UTF-8 terminal output. The input support is implemented using X keyboard extension (XKB). Development of Kmscon stopped in March 2015. There is a new project called systemd-consoled, but this project was also later dropped in July 2015.








