Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve goals and meet success criteria at a specified time. The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, quality and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.

A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller components. A work breakdown structure is a key project deliverable that organizes the team's work into manageable sections. The Project Management Body of Knowledge defines the work-breakdown structure as a "hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables."
Contemporary business and science treat a project as any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular aim.
A project plan, according to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), is: "...a formal, approved document used to guide both project execution and project control. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning assumptions and decisions, facilitate communication among project stakeholders, and document approved scope, cost, and schedule baselines. A project plan may be summarized or detailed."

The Project Management Body of Knowledge is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The body of knowledge evolves over time and is presented in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a book whose sixth edition was released in 2017. The Guide is a document resulting from work overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers the CAPM and PMP certifications.
In a project network, a dependency is a link amongst a project's terminal elements.
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), the term project stakeholder refers to, "an individual, group, or organization, who may affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by a decision, activity, or outcome of a project." ISO 21500 uses a similar definition.
A risk management plan is a document that a project manager prepares to foresee risks, estimate impacts, and define responses to risks. It also contains a risk assessment matrix.
Project Management Professional (PMP) is an internationally recognized professional designation offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). As of 31 July 2020, there are 1,036,367 active PMP certified individuals and 314 chartered chapters across 214 countries and territories worldwide. The exam is based on the PMI Project Management Body of Knowledge.
Scope statements can take many forms depending on the type of project being implemented and the nature of the organization. The scope statement details the project deliverables and describes the major objectives. The objectives should include measurable success criteria for the project.

The Project Initiation Documentation (PID) is one of the most significant artifacts in project management, which provides the foundation for the business project.

Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value to and improve an organization's operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control and governance processes. Internal auditing achieves this by providing insight and recommendations based on analyses and assessments of data and business processes. With commitment to integrity and accountability, internal auditing provides value to governing bodies and senior management as an objective source of independent advice. Professionals called internal auditors are employed by organizations to perform the internal auditing activity.
Project governance is the management framework within which project decisions are made. Project governance is a critical element of any project, since the accountabilities and responsibilities associated with an organization’s business as usual activities are laid down in their organizational governance arrangements; seldom does an equivalent framework exist to govern the development of its capital investments (projects). For instance, the organization chart provides a good indication of who in the organization is responsible for any particular operational activity the organization conducts. But unless an organization has specifically developed a project governance policy, no such chart is likely to exist for project development activity.
In project management, a project charter, project definition, or project statement is a statement of the scope, objectives, and participants in a project. It provides a preliminary delineation of roles and responsibilities, outlines the project's key goals, identifies the main stakeholders, and defines the authority of the project manager.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
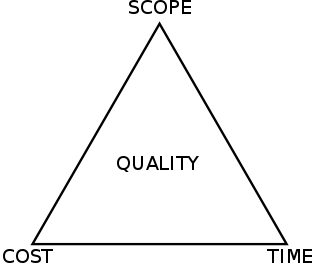
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
In project management, scope is the defined features and functions of a product, or the scope of work needed to finish a project. Scope involves getting information required to start a project, and the features the product would have that would meet its stakeholders requirements.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
The Goals breakdown structure (GBS) is a hierarchical structure linking high-level objectives or goals to more detailed goals. The GBS was originally developed for project management, but applies to product development and the organization as a whole. The concept is based on the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) popular in the project management discipline. Like the WBS, project goals exhibit a hierarchical structure. The highest-level defines the overall goal or mission for the project. The next level down sets the goals the organization intends to achieve from the project. These might include such items as profit, market share, etc. The next layer down defines the features the products must exhibit to achieve the organization's goals. The next layer down defines the specifications each product or component of the product must have to meet the products features.
The Project Management Plan Document also known as Project Plan Document or Detailed Project Report (DPR) or simply Project Plan is a document that contains the strategy for managing the project and the processes related to all areas of the project which are known as Knowledge Areas according to PMI. Many project management processes are mentioned in PMBOK® Guide, but determining which processes need to be used based on the needs of the project which is called Tailoring is part of developing the project management plan.




