Related Research Articles
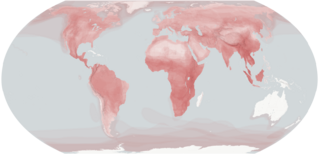
Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the sixth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, ranging from the cold polar regions of Earth to the hyper-arid region of the Sahara Desert and the open seas. Carnivorans exhibit a wide array of body plans, varying greatly in size and shape.

The orca, or killer whale, is a toothed whale and the largest member of the oceanic dolphin family. It is the only extant species in the genus Orcinus and is recognizable by its black-and-white patterned body. A cosmopolitan species, it is found in diverse marine environments, from Arctic to Antarctic regions to tropical seas.

A mammal is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia. Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy.

Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of the defining features of marsupials is their unique reproductive strategy, where the young are born in a relatively undeveloped state and then nurtured within a pouch on their mother's abdomen.

The platypus, sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or monotypic taxon of its family Ornithorhynchidae and genus Ornithorhynchus, though a number of related species appear in the fossil record.

Sex is the biological trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. During sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote, which develops into an offspring that inherits traits from each parent. By convention, organisms that produce smaller, more mobile gametes are called male, while organisms that produce larger, non-mobile gametes are called female. An organism that produces both types of gamete is hermaphrodite.

The narwhal is a species of toothed whale native to the Arctic. It is the only member of the genus Monodon and one of two living representatives of the family Monodontidae. The narwhal is a stocky cetacean with a relatively blunt snout, a large melon, and a shallow ridge in place of a dorsal fin. Males of this species have a large long tusk, which is a protruding left canine thought to function as a weapon, a tool for feeding, in attracting mates or sensing water salinity. Specially adapted slow-twitch muscles, along with the jointed neck vertebrae and shallow dorsal ridge allow for easy movement through the Arctic environment, where the narwhal spends extended periods at great depths. The narwhal's geographic range overlaps with that of the similarly built and closely related beluga whale, and the animals are known to interbreed.

Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine (saltwater) ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine environments for feeding and survival.

Colugos, flying lemurs, or cobegos, are arboreal gliding euarchontogliran mammals that are native to Southeast Asia. Their closest evolutionary relatives are primates. There are just two living species of colugos: the Sunda flying lemur and the Philippine flying lemur. These two species make up the entire family Cynocephalidae and order Dermoptera.

Dall's porpoise is a species of porpoise endemic to the North Pacific. It is the largest of porpoises and the only member of the genus Phocoenoides. The species is named after American naturalist W. H. Dall.

A cloaca, pl.: cloacae, or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, and a few mammals have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have separate orifices for evacuation and reproduction. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes called cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is called cloacal copulation and cloacal kissing.
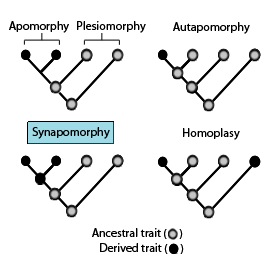
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form. A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology.

Repenomamus is a genus of opossum- to badger-sized gobiconodontid mammal containing two species, Repenomamus robustus and Repenomamus giganticus. Both species are known from fossils found in China that date to the early Cretaceous period, about 125-123.2 million years ago. R. robustus is one of several Mesozoic mammals for which there is good evidence that it fed on vertebrates, including dinosaurs. Though it is not entirely clear whether or not these animals primarily hunted live dinosaurs or scavenged dead ones, evidence for the former is present in fossilized remains showcasing the results of what was most likely a predation attempt by R. robustus directed at a specimen of the dinosaur Psittacosaurus lujiatunensis. R. giganticus is among the largest mammals known from the Mesozoic era, only surpassed by Patagomaia.

Phacochoerus is a genus in the family Suidae, commonly known as warthogs. They are pigs who live in open and semi-open habitats, even in quite arid regions, in sub-Saharan Africa. The two species were formerly considered conspecific under the scientific name Phacochoerus aethiopicus, but today this is limited to the desert warthog, while the best-known and most widespread species, the common warthog, is Phacochoerus africanus.

A penis is a male sex organ that is used to inseminate female or hermaphrodite animals during copulation. Such organs occur in both vertebrates and invertebrates, including humans, but not in all male animals.
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.
An organism's sex is female if it produces the ovum, the type of gamete that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.

Monotremes are mammals of the order Monotremata. They are the only group of living mammals that lay eggs, rather than bearing live young. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and the four species of echidnas. Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brains, jaws, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and other body parts, compared to the more common mammalian types. Although they are different from almost all mammals in that they lay eggs, like all mammals, the female monotremes nurse their young with milk.

Artiofabula is a clade made up of the Suina and the Cetruminantia. The clade was found in molecular phylogenetic analyses and contradicted traditional relationships based on morphological analyses.
References
- ↑ Benton, Michael J. (2008-11-27). The History of Life: A Very Short Introduction. OUP Oxford. pp. 150–. ISBN 9780199226320.
- ↑ Lombardi, Julian (2012-12-06). Comparative Vertebrate Reproduction. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4615-4937-6.
- ↑ Bernd Würsig; J.G.M. Thewissen; Kit M. Kovacs (27 November 2017). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-0-12-804381-3.