Related Research Articles

An octopus is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda. The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates.

A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.

Perch is a common name for freshwater fish from the genus Perca, which belongs to the family Percidae of the large order Perciformes. The name comes from Greek: πέρκη, romanized: perke, meaning the type species of this genus, the European perch.

Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.

A seashell or sea shell, also known simply as a shell, is a hard, protective outer layer usually created by an animal or organism that lives in the sea. The shell is part of the body of the animal. Empty seashells are often found washed up on beaches by beachcombers. The shells are empty because the animal has died and the soft parts have decomposed or been eaten by another animal.

The nautilus is an ancient pelagic marine mollusc of the cephalopod family Nautilidae. The nautilus is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and of its smaller but near equal suborder, Nautilina.

The gastropods, commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda.
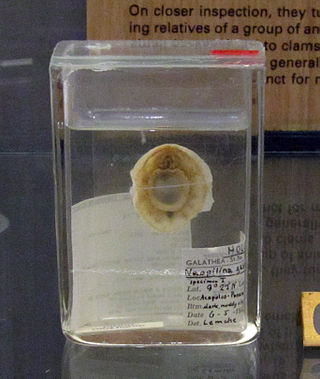
Monoplacophora, meaning "bearing one plate", is a polyphyletic superclass of molluscs with a cap-like shell inhabiting deep sea environments. Extant representatives were not recognized as such until 1952; previously they were known only from the fossil record, and were thought to have become extinct 375 million years ago.

Goniatids, informally goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago. Goniatites (goniatitids) survived the Late Devonian extinction to flourish during the Carboniferous and Permian only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 139 million years later.

Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living Nautilus and Allonautilus. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms (orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day.

A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda.

The tusk shells or tooth shells, technically the Scaphopoda, are members of a class of shelled marine mollusc with worldwide distribution, and are the only class of exclusively infaunal marine molluscs. Shells of species within this class range from about 0.5 to 18 cm in length. Members of the order Dentaliida tend to be larger than those of the order Gadilida.

An orthocone is an unusually long straight shell of a nautiloid cephalopod. During the 18th and 19th centuries, all shells of this type were named Orthoceras, creating a wastebasket taxon, but it is now known that many groups of nautiloids developed or retained this type of shell.

Limpets are a group of aquatic snails that exhibit a conical shell shape (patelliform) and a strong, muscular foot. Limpets are members of the class Gastropoda, but are polyphyletic, meaning the various groups called "limpets" descended independently from different ancestral gastropods. This general category of conical shell is known as "patelliform" (dish-shaped). All members of the large and ancient marine clade Patellogastropoda are limpets. Within that clade, the members of the Patellidae family in particular are often referred to as "true limpets".
The analytic–synthetic distinction is a semantic distinction used primarily in philosophy to distinguish between propositions that are of two types: analytic propositions and synthetic propositions. Analytic propositions are true or not true solely by virtue of their meaning, whereas synthetic propositions' truth, if any, derives from how their meaning relates to the world.

The common octopus is a mollusc belonging to the class Cephalopoda. Octopus vulgaris is one of the most studied of all octopus species, and also one of the most intelligent. It ranges from the eastern Atlantic, extends from the Mediterranean Sea and the southern coast of England, to the southern coast of South Africa. It also occurs off the Azores, Canary Islands, and Cape Verde Islands. The species is also common in the Western Atlantic.

Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals, after the Arthropoda; members are known as molluscs or mollusks. Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied.
The cephalopods have a long geological history, with the first nautiloids found in late Cambrian strata, and purported stem-group representatives present in the earliest Cambrian lagerstätten.
Plectronoceratoidea is a superorder or subclass containing primitive nautiloids from the Late Cambrian and Early Ordovician. This group is best considered a paraphyletic grade of early cephalopods, as it contains the ancestors of subsequent post-Cambrian cephalopod orders.
References
- ↑ Edwin Ray Lankester (1906). A Treatise on Zoology - Part 5. p. 331.
- ↑ "The erroneous distinction between tetrabranchiate and dibranchiate cephalopods". 2000.