
The Book of Leviticus is the third book of the Torah and of the Old Testament; scholars generally agree that it developed over a long period of time, reaching its present form during the Persian Period between 538–332 BC.

Scabies is a contagious skin infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin. In a first-ever infection, the infected person will usually develop symptoms within two to six weeks. During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours. These symptoms can be present across most of the body or just certain areas such as the wrists, between fingers, or along the waistline. The head may be affected, but this is typically only in young children. The itch is often worse at night. Scratching may cause skin breakdown and an additional bacterial infection in the skin.

Sarcoptes scabiei or the itch mite is a parasitic mite that burrows into skin and causes scabies. The mite is found in all parts of the world. Humans are not the only mammals that can become infected. Other mammals, such as wild and domesticated dogs and cats as well as ungulates, wild boars, bovids, wombats, koalas, and great apes are affected.

Tinea cruris, also known as Jock itch, is a common type of contagious, superficial fungal infection of the groin region, which occurs predominantly but not exclusively in men and in hot-humid climates.
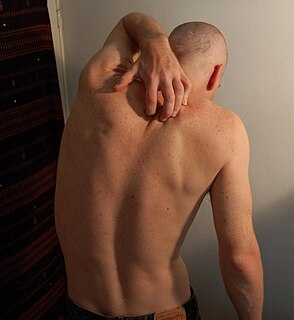
Itch is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itch leads to a scratch reflex.

Ichthyosis vulgaris is a skin disorder causing dry, scaly skin. It is the most common form of ichthyosis, affecting around 1 in 250 people. For this reason it is known as common ichthyosis. It is usually an autosomal dominant inherited disease, although a rare non-heritable version called acquired ichthyosis exists.

Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis, is a common skin infection of the feet caused by fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as tinea.

Pityriasis rosea is a type of skin rash. Classically, it begins with a single red and slightly scaly area known as a "herald patch". This is then followed, days to weeks later, by a rash of many similar but smaller round or oval lesions, mainly on the trunk and upper limbs. About 20% of cases show atypical deviations from this pattern. It usually lasts less than three months and goes away without treatment. Sometimes malaise or a fever may occur before the start of the rash or itchiness, but often there are few other symptoms.
Formication is the sensation that resembles that of small insects crawling on the skin when there is nothing there. It is one specific form of a set of sensations known as paresthesias, which also include the more common prickling, tingling sensation known as "pins and needles". Formication is a well documented symptom, which has numerous possible causes. The word is derived from formica, the Latin word for ant.

Cutaneous larva migrans is a skin disease in humans, caused by the larvae of various nematode parasites of the hookworm family (Ancylostomatidae). These parasites live in the intestines of dogs, cats, and wild animals and should not be confused with other members of the hookworm family for which humans are definitive hosts, namely Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.
Aquagenic pruritus is a skin condition characterized by the development of severe, intense, prickling-like epidermal itching without observable skin lesions and evoked by contact with water.
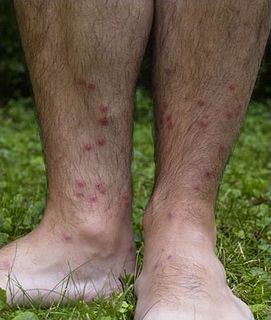
Swimmer's itch, cercarial dermatitis or schistosome dermatitis is a short-term allergic immune reaction occurring in the skin of humans that have been infected by water-borne schistosomes, a type of flatworms. It is common in freshwater, brackish and marine habitats worldwide. Incidence may be on the rise, although this may also be attributed to better monitoring. Nevertheless, the condition has been regarded as emerging infectious disease.

Prurigo nodularis (PN), also known as nodular prurigo, is a skin disease characterised by pruritic (itchy) nodules which usually appear on the arms or legs. Patients often present with multiple excoriated lesions caused by scratching. PN is also known as Hyde prurigo nodularis, Picker's nodules, atypical nodular form of neurodermatitis circumscripta, lichen corneus obtusus.
Pruritus ani is the irritation of the skin at the exit of the rectum, known as the anus, causing the desire to scratch. The intensity of anal itching increases from moisture, pressure, and rubbing caused by clothing and sitting. At worst, anal itching causes intolerable discomfort that often is accompanied by burning and soreness. It is estimated that up to 5% of the population of the United States experiences this type of discomfort daily.

Grover's disease (GD) is a polymorphic, pruritic, papulovesicular dermatosis characterized histologically by acantholysis with or without dyskeratosis. Once confirmed, most cases of Grover's disease last six to twelve months, which is why it was originally called "transient". However it may last much longer. Nevertheless, it is not to be confused with relapsing linear acantholytic dermatosis.

Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, pityriasis versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock itch. It can be taken by mouth or applied as a cream to the skin or in the vagina.

Schamberg's disease, is a chronic discoloration of the skin found in people of all ages, usually only affecting the feet, legs or thighs or a combination. It may occur as a single event or subsequent bouts may cause further spread. It is most common in males. It is named after Jay Frank Schamberg, who described it in 1901. There is no known cure for this disease but it is not a life-threatening condition and is mainly of cosmetic concern, although, because it can appear so suddenly, so extensively and because it usually leaves permanent discoloration of the skin, it can cause understandable psychological concern. The skin lesions sometimes cause itching, which can be treated by applying cortisone cream. The cortisone cream will only help with the itching and does not improve the discoloration of the skin. Schamberg's disease causes no other symptoms beside skin discoloration and itching. The condition is caused by inflammation of capillaries near the surface of skin and subsequent leaking of red blood cells into surrounding tissues. As the red blood cells break down and get mostly resorbed, some of the iron released by the red blood cells remains in the skin and causes the characteristic rust-colored appearance. The cause of the capillary inflammation is usually unknown.

Trombiculidae are a family of mites. Chiggers are often confused with jiggers - a type of flea. Several species of Trombiculidae in their larva stage bite their animal or human host and by embedding their mouthparts into the skin causing "intense irritation" or "a wheal, usually with severe itching and dermatitis",
Grain itch is a cutaneous condition caused by several types of mites, and characterized by intense pruritus.
Cholestatic pruritus is the sensation of itch due to nearly any liver disease, but the most commonly associated entities are primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, obstructive choledocholithiasis, carcinoma of the bile duct, cholestasis, and chronic hepatitis C viral infection and other forms of viral hepatitis.