Related Research Articles

The National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children (NSPCC) is a charity campaigning and working in child protection in the United Kingdom and the Channel Islands.

Early childhood education is a branch of education theory that relates to the teaching of children from birth up to the age of eight. Traditionally, this is up to the equivalent of third grade. ECE emerged as a field of study during the Enlightenment, particularly in European countries with high literacy rates. It continued to grow through the nineteenth century as universal primary education became a norm in the Western world. In recent years, early childhood education has become a prevalent public policy issue, as municipal, state, and federal lawmakers consider funding for preschool and pre-K. The global priority placed on early childhood education is underscored with targets of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 4. It is described as an important period in a child's development. It refers to the development of a child's personality. ECE is also a professional designation earned through a post-secondary education program. For example, in Ontario, Canada, the designations ECE and RECE may only be used by registered members of the College of Early Childhood Educators, which is made up of accredited child care professionals who are held accountable to the College's standards of practice.
The Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS), also known as the Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale (BNAS), was developed in 1973 by Dr. T. Berry Brazelton and his colleagues. This test purports to provide an index of a newborn's abilities, and is usually given to an infant somewhere between the age of 3 days to 4 weeks old. This approach was innovative for recognizing that a baby is a highly developed organism, even when just newly born. The profile describes the baby's strengths, adaptive responses and possible vulnerabilities. This knowledge may help parents develop appropriate strategies for caring in intimate relationships to enhance their earliest relationship with the child.
Child neglect is a form of abuse, an egregious behavior of caregivers that results in a deprivation of child of their basic needs, including the failure to provide adequate supervision, health care, clothing, or housing, as well as other physical, emotional, social, educational, and safety needs. All societies have established that there are necessary behaviors a caregiver must provide in order for a child to develop physically, socially, and emotionally. Causes of neglect may result from several parenting problems including mental disorders, unplanned pregnancy, substance abuse, unemployment, overemployment, domestic violence, and, in special cases, poverty.
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC), developed by David Wechsler, is an individually administered intelligence test for children between the ages of 6 and 16. The Fifth Edition is the most recent version.
In education terminology, rubric means "a scoring guide used to evaluate the quality of students' constructed responses". Put simply, it is a set of criteria for grading assignments. Rubrics usually contain evaluative criteria, quality definitions for those criteria at particular levels of achievement, and a scoring strategy. They are often presented in table format and can be used by teachers when marking, and by students when planning their work.

Child protection is the safeguarding of children from violence, exploitation, abuse, and neglect. Article 19 of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child provides for the protection of children in and out of the home. One of the ways to ensure this is by giving them quality education, the fourth of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, in addition to other child protection systems.
Positive deviance (PD) is an approach to behavioral and social change based on the observation that in any community there are people whose uncommon but successful behaviors or strategies enable them to find better solutions to a problem than their peers, despite facing similar challenges and having no extra resources or knowledge than their peers. These individuals are referred to as positive deviants.
The Developmental, Individual-differences, Relationship-based (DIR) model is a developmental model for assessing and understanding any child's strengths and weaknesses. It has become particularly effective at identifying the unique developmental profiles and developing programs for children experiencing developmental delays due to autism, autism spectrum disorders, or other developmental disorders. This Model was developed by Dr. Stanley Greenspan and first outlined in 1979 in his book Intelligence and Adaptation. Evidence for the efficacy of DIR/Floortime includes results from randomized controlled trials of DIR/Floortime and the DIR/Floortime-based P.L.A.Y. Project; because of various limitations in these studies, the existing evidence is deemed to "weakly support" the efficacy of Floortime.

Safeguarding is a term used in the United Kingdom and Ireland to denote measures to protect the health, well-being and human rights of individuals, which allow people — especially children, young people and vulnerable adults — to live free from abuse, harm and neglect.
Early detection of children with developmental-behavioral delays and disabilities is essential to making sure that those with difficulties receive the benefits of early intervention.
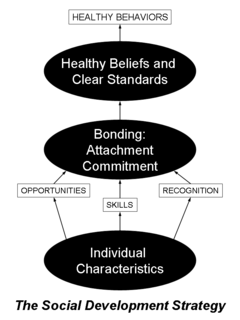
Communities That Care (CTC) is a program of the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) in the office of the United States Government's Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). CTC is a coalition-based prevention operating system that uses a public health approach to prevent youth problem behaviors such as violence, delinquency, school drop out and substance abuse. Using strategic consultation, training, and research-based tools, CTC is designed to help community stakeholders and decision makers understand and apply information about risk and protective factors, and programs that are proven to make a difference in promoting healthy youth development, in order to most effectively address the specific issues facing their community's youth.
The Lexile Framework for Reading is an educational tool that uses a measure called a Lexile to match readers with books, articles and other leveled reading resources. Readers and books are assigned a score on the Lexile scale, in which lower scores reflect easier readability for books and lower reading ability for readers. The Lexile framework uses quantitative methods, based on individual words and sentence lengths, rather than qualitative analysis of content to produce scores. Accordingly, the scores for texts do not reflect factors such as multiple levels of meaning or maturity of themes. Hence, the United States Common Core State Standards recommend the use of alternative, qualitative methods for selecting books for students at grade 6 and over. In the US, Lexile measures are reported from reading programs and assessments annually. Thus, about half of U.S. students in grades 3rd through 12th receive a Lexile measure each year. In addition to being used in schools in all 50 states, Lexile measures are also used outside of the United States.
Video interaction guidance (VIG) is a video feedback intervention through which a “guider” helps a client to enhance communication within relationships. The client is guided to analyse and reflect on video clips of their own interactions. Applications include a caregiver and infant, and other education and care home interactions. VIG is used in more than 15 countries and by at least 4000 practitioners. Video Interaction Guidance has been used where concerns have been expressed over possible parental neglect in cases where the focus child is aged 2–12, and where the child is not the subject of a child protection plan.
Video feedback interventions are used in health and social care situations. Typically a “guider” helps a client to enhance communication within relationships. The client is guided to analyse and reflect on video clips of their own interactions. Applications include a caregiver and infant, and other education and care home interactions. Video feedback interventions have also been used where concerns have been expressed over possible parental neglect in cases where the focus child is aged 2–12, and where the child is not the subject of a child protection plan.
The Autism Treatment Evaluation Scale (ATEC) is a 77-item diagnostic assessment tool that was developed by Bernard Rimland and Stephen Edelson at the Autism Research Institute. The ATEC was originally designed to evaluate the effectiveness of autism treatments, but it may also be beneficial as a screening tool for children. The questionnaire, which is completed by a parent, takes about 10–15 minutes to complete and is designed for use with children ages 5–12. The ATEC is currently available in 17 different languages.
The North Carolina Family Assessment Scale (NCFAS) measures family functioning from the perspective of the worker most involved with the family. It guides professionals to make a decision on whether action should be taken. It does this by having professionals rate a family from -3 to +2 across a range of areas of family functioning, where a negative score means that there is a legal or ethical reason for intervening.
The SafeCare programme is a preventive programme in the United Kingdom working with parents of children under 6 years old who are at risk of experiencing significant harm through neglect. The programme is delivered in the home by trained practitioners, over 18 to 20 sessions and focuses on 3 key areas: parent-infant/child interaction; home safety and child health.
Pediatric Early Warning Signs (PEWS) are clinical manifestations that indicate rapid deterioration in pediatric patients, infancy to adolescence. PEWS Score or PEWS System are objective assessment tools that incorporate the clinical manifestations that have the greatest impact on patient outcome.
PSYCHLOPS is a type of psychological testing, a tool used in primary care to measure mental health outcomes and as a quality of life measure.
References
- ↑ NSPCC & Dr.O.P.Srivastava (2015). "The Graded Care Profile Scale". NSPCC. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ↑ "Grade Care Profile Manual and Tool" (PDF).
- ↑ Luton Safeguarding Children's Board (2015). "What is the Graded Care Profile Tool?". Luton Safeguarding Children's Board. Archived from the original on 21 November 2015. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 Johnson, R. & Cotmore, R. (2015). "National Evaluation of the Graded Care Profile" (PDF). NSPCC. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
5. Srivastava, OP & Polnay, L. (1997).Field trial of the Graded care Profile (GCP) Scale: A New measure of Care. Archives of Diseases of Childhood. 76: 337 - 340.