
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns.

Spandex, Lycra, or elastane is a synthetic fiber known for its exceptional elasticity. It is a polyether-polyurea copolymer that was invented in 1958 by chemist Joseph Shivers at DuPont.
Eastman Chemical Company is an American company primarily involved in the chemical industry. Once a subsidiary of Kodak, today it is an independent global specialty materials company that produces a broad range of advanced materials, chemicals and fibers for everyday purposes. Founded in 1920 and based in Kingsport, Tennessee, the company operates 36 manufacturing sites worldwide and employs approximately 14,000 people.

The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in plants and insects, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing.

The Industrial Technology Research Institute is a technology research and development institution in Taiwan. It was founded in 1973 and is headquartered in Hsinchu City, Taiwan, with branch offices in the U.S., Europe, and Japan.

Fast fashion is the business model of replicating recent catwalk trends and high-fashion designs, mass-producing them at a low cost, and bringing them to retail quickly while demand is at its highest. The term fast fashion is also used generically to describe the products of this business model, particularly clothing and footwear. Retailers who employ the fast fashion strategy include Primark, H&M, Shein, and Zara, all of which have become large multinationals by driving high turnover of inexpensive seasonal and trendy clothing that appeals to fashion-conscious consumers.
Heinz Joseph Gerber was an American inventor and businessman. An Austrian-born Jewish Holocaust survivor who immigrated in 1940, he pioneered computer-automated manufacturing systems for an array of industries. Described as the "Thomas Edison of manufacturing", he was one of the first to recognize and develop the productivity-enhancing potential for computer automation in skill-intensive industrial sectors.

Textile recycling is the process of recovering fiber, yarn, or fabric and reprocessing the material into new, useful products. Textile waste is split into pre-consumer and post-consumer waste and is sorted into five different categories derived from a pyramid model. Textiles can be either reused or mechanically/chemically recycled.

Upcycling, also known as creative reuse, is the process of transforming by-products, waste materials, useless, or unwanted products into new materials or products perceived to be of greater quality, such as artistic value or environmental value.

Sustainable fashion is a term describing efforts within the fashion industry to reduce its environmental impacts, protect workers producing garments and uphold animal welfare. Sustainability in fashion encompasses a wide range of factors, including cutting CO2 emissions, addressing overproduction, reducing pollution and waste, supporting biodiversity and ensuring that garment workers are paid a fair wage and have safe working conditions.

Electronic textiles or e-textiles are fabrics that enable electronic components such as batteries, lights, sensors, and microcontrollers to be embedded in them. Many smart clothing, wearable technology, and wearable computing projects involve the use of e-textiles.

Jersey is a knit fabric used predominantly for clothing manufacture. It was originally made of wool, but is now made of wool, cotton and synthetic fibers.
Zero-waste fashion refers to a fashion design strategy, that generates little or no textile waste during the production process, particularly focusing on the pattern making and cutting stages. It is a reaction to the high amount of discarded clothing items going into landfills around the world.
Kornit Digital Ltd. is an Israeli-American international manufacturing company. It produces high-speed industrial inkjet printers, pigmented ink and chemical products for the garment and apparel, home goods, textile accessories and decorating industry.
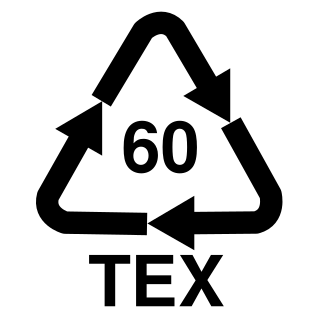
Cotton recycling is the process of converting cotton fabric into fibers that can be reused into other textile products.

Clothing industry or garment industry summarizes the types of trade and industry along the production and value chain of clothing and garments, starting with the textile industry, embellishment using embroidery, via the fashion industry to apparel retailers up to trade with second-hand clothes and textile recycling. The producing sectors build upon a wealth of clothing technology some of which, like the loom, the cotton gin, and the sewing machine heralded industrialization not only of the previous textile manufacturing practices. Clothing industries are also known as allied industries, fashion industries, garment industries, or soft goods industries.
The Federation of Hong Kong Industries is the only statutory industrial organization in Hong Kong, established under the Federation of Hong Kong Industries Ordinance, Cap. 321 of the laws of Hong Kong, in 1960.
The Taiwan Textile Research Institute is a government funded research institute in Taiwan (ROC) which supports the textile industry.
Recover Textile Systems, mainly known as Recover, is a materials science company and producer of mechanically recycled cotton fiber and recycled cotton fiber blends, created in 2020 with its headquarters in Banyeres de Mariola, Spain.














