Related Research Articles

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBTQ people in society. Although there is not a primary or an overarching central organization that represents all LGBTQ people and their interests, numerous LGBT rights organizations are active worldwide. The first organization to promote LGBT rights was the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, founded in 1897 in Berlin.

Before 1933, male homosexual acts were illegal in Germany under Paragraph 175 of the German Criminal Code. The law was not consistently enforced, however, and a thriving gay culture existed in major German cities. After the Nazi takeover in 1933, the first homosexual movement's infrastructure of clubs, organizations, and publications was shut down. After the Röhm purge in 1934, persecuting homosexuals became a priority of the Nazi police state. A 1935 revision of Paragraph 175 made it easier to bring criminal charges for homosexual acts, leading to a large increase in arrests and convictions. Persecution peaked in the years prior to World War II and was extended to areas annexed by Germany, including Austria, the Czech lands, and Alsace–Lorraine.

Wilfred Edward Salter Owen MC was an English poet and soldier. He was one of the leading poets of the First World War. His war poetry on the horrors of trenches and gas warfare was much influenced by his mentor Siegfried Sassoon and stood in contrast to the public perception of war at the time and to the confidently patriotic verse written by earlier war poets such as Rupert Brooke. Among his best-known works – most of which were published posthumously – are "Dulce et Decorum est", "Insensibility", "Anthem for Doomed Youth", "Futility", "Spring Offensive" and "Strange Meeting". Owen was killed in action on 4 November 1918, a week before the war's end, at the age of 25.

Queer is an umbrella term for people who are not heterosexual or are not cisgender. Originally meaning 'strange' or 'peculiar', queer came to be used pejoratively against LGBT people in the late 19th century. From the late 1980s, queer activists began to reclaim the word as a neutral or positive self-description.

Regeneration is a historical and anti-war novel by Pat Barker, first published in 1991. The novel was a Booker Prize nominee and was described by the New York Times Book Review as one of the four best novels of the year in its year of publication. It is the first of three novels in the Regeneration Trilogy of novels on the First World War, the other two being The Eye in the Door and The Ghost Road, which won the Booker Prize in 1995. The novel was adapted into a film by the same name in 1997 by Scottish film director Gillies MacKinnon and starring Jonathan Pryce as Rivers, James Wilby as Sassoon and Jonny Lee Miller as Prior. The film was successful in the UK and Canada, receiving nominations for a number of awards.

The Ghost Road is a war novel by Pat Barker, first published in 1995 and winner of the Booker Prize. It is the third volume of a trilogy that follows the fortunes of shell-shocked British army officers towards the end of the First World War. The other books in the trilogy are Regeneration and The Eye in the Door.
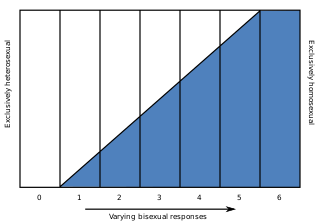
The Kinsey scale, also called the Heterosexual–Homosexual Rating Scale, is used in research to describe a person's sexual orientation based on one's experience or response at a given time. The scale typically ranges from 0, meaning exclusively heterosexual, to a 6, meaning exclusively homosexual. In both the male and female volumes of the Kinsey Reports, an additional grade, listed as "X", indicated "no socio-sexual contacts or reactions" (asexuality). The reports were first published in Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) by Alfred Kinsey, Wardell Pomeroy, and others, and were also prominent in the complementary work Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953).
Societal attitudes towards same-sex relationships have varied over time and place. Attitudes to male homosexuality have varied from requiring males to engage in same-sex relationships to casual integration, through acceptance, to seeing the practice as a minor sin, repressing it through law enforcement and judicial mechanisms, and to proscribing it under penalty of death. In addition, it has varied as to whether any negative attitudes towards men who have sex with men have extended to all participants, as has been common in Abrahamic religions, or only to passive (penetrated) participants, as was common in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Female homosexuality has historically been given less acknowledgment, explicit acceptance, and opposition.

Henry Havelock Ellis was an English-French physician, eugenicist, writer, progressive intellectual and social reformer who studied human sexuality. He co-wrote the first medical textbook in English on homosexuality in 1897, and also published works on a variety of sexual practices and inclinations, as well as on transgender psychology. He developed the notions of narcissism and autoeroticism, later adopted by psychoanalysis.

Edward Carpenter was an English utopian socialist, poet, philosopher, anthologist, an early activist for gay rights and prison reform whilst advocating vegetarianism and taking a stance against vivisection. As a philosopher, he was particularly known for his publication of Civilisation: Its Cause and Cure. Here, he described civilisation as a form of disease through which human societies pass.

Patricia Mary W. Barker,, Hon FBA is a British writer and novelist. She has won many awards for her fiction, which centres on themes of memory, trauma, survival and recovery. Her work is described as direct, blunt and plainspoken. In 2012, The Observer named the Regeneration Trilogy as one of "The 10 best historical novels".
The Uranians were a late-19th-century and early-20th-century clandestine group of up to several dozen male homosexual poets and prose writers who principally wrote on the subject of the love of adolescent boys. In a strict definition they were an English literary and cultural movement; in a broader definition there were also American Uranians. The movement reached its peak between the late 1880s and mid 1890s, but has been regarded as stretching between 1858, when William Johnson Cory's poetry collection Ionica appeared, and 1930, the year of publication of Samuel Elsworth Cottam's Cameos of Boyhood and Other Poems and of E. E. Bradford's last collection, Boyhood.
Uranian is a historical term for homosexual men. The word was also used as an adjective in association with male homosexuality or inter-male attraction regardless of sexual orientation.

Terms used to describe homosexuality have gone through many changes since the emergence of the first terms in the mid-19th century. In English, some terms in widespread use have been sodomite, Achillean, Sapphic, Uranian, homophile, lesbian, gay, effeminate, queer, homoaffective, and same-gender attracted. Some of these words are specific to women, some to men, and some can be used of either. Gay people may also be identified under the umbrella term LGBT.
The connection between left-leaning ideologies and LGBT rights struggles has a long and mixed history. The status of LGBT people in socialist states have varied throughout history.

The Eye in the Door is a novel by Pat Barker, first published in 1993, and forming the second part of the Regeneration trilogy.

Regeneration is a 1997 British film, an adaptation of the 1991 novel of the same name by Pat Barker. The film is directed by Gillies MacKinnon. It was released as Behind the Lines in the US in 1998. The film follows the stories of a number of officers of the British Army during World War I who are brought together in Craiglockhart War Hospital where they are treated for various traumas. It features the story of Siegfried Sassoon, his open letter reprinted in The Times criticising the conduct of the war and his return to the front.
Sea queens is a term referring to gay men who worked aboard mainly merchant vessels before the 1960s. They were predominantly effeminate gay men who worked either in entertainment or as waiters on cruise ships, often becoming off-shore 'wives' for heterosexual sailors for the duration of voyages. They could also be found within the Navy as the nonfiction historical monograph Hello Sailor! The Hidden History of Gay Life at Sea by Paul Baker and Jo Stanley describes through the stories and experiences of sea queens from the Navy. In addition to this, the use of the Polari language can be drawn back to sea queens along with the attempted expulsion of gay, male sailors in Newport, Rhode Island after WWI.

In September 1960, two U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) cryptologists, William Hamilton Martin and Bernon F. Mitchell, defected to the Soviet Union. A secret 1963 NSA study said that: "Beyond any doubt, no other event has had, or is likely to have in the future, a greater impact on the Agency's security program."
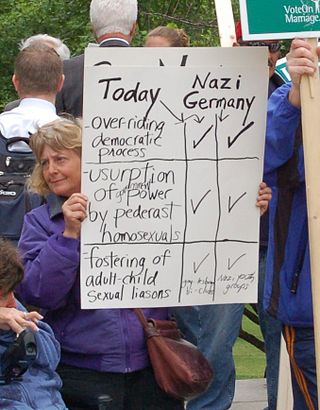
There is a widespread and long-lasting myth alleging that homosexuals were numerous and prominent as a group in the Nazi Party or the identification of Nazism with homosexuality more generally. It has been promoted by various individuals and groups from before World War II through the present, especially by left-wing Germans during the Nazi era and the Christian right in the United States more recently. Although some gay men joined the Nazi Party, there is no evidence that they were overrepresented. The Nazis harshly criticized homosexuality and severely persecuted gay men, going as far as murdering them en masse. Therefore, historians regard the myth as having no merit.
References
- ↑ Flood, M. (2007) International Encyclopedia of Men and Masculinities, Abingdon: Routledge, p. 315
- ↑ Bremer, John (2012). C.S. Lewis, Poetry, and the Great War: 1914-1918. Plymouth, UK: Lexington Books. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-7391-7152-3.
- ↑ Barker, Pat (1992). Regeneration . New York, United States: Dutton. pp. 53–4. ISBN 0525934278.