
Al-Qaeda is a pan-Islamist militant organization led by Sunni Jihadists who self-identify as a vanguard spearheading a global Islamist revolution to unite the Muslim world under a supra-national Islamic caliphate. Its membership is mostly composed of Arabs, but also includes people from other ethnic groups. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian, economic and military targets of the US and its allies; such as the 1998 US embassy bombings, the USS Cole bombing and the September 11 attacks. The organization is designated as a terrorist group by NATO, the UN Security Council, the European Union, and various countries around the world.

Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden was a Saudi Arabian-born Islamist dissident and militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda from 1988 until his death in 2011. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, he participated in the Afghan jihad against the Soviet Union and supported the activities of the Bosnian mujahideen during the Yugoslav Wars. Bin Laden is most widely known as the mastermind behind the September 11 attacks in the United States.
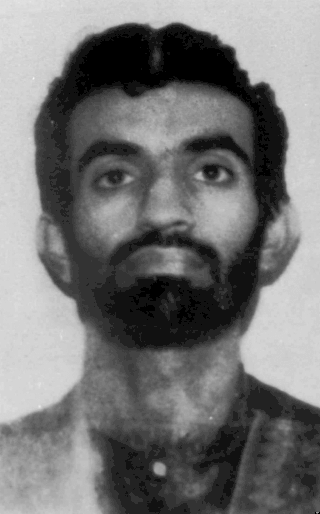
Ramzi Ahmed Yousef is a convicted terrorist who was one of the main perpetrators of the 1993 World Trade Center bombing and the bombing of Philippine Airlines Flight 434; he was also a co-conspirator in the Bojinka plot. In 1995, he was arrested by the Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) and U.S. Diplomatic Security Service at a guest house in Islamabad, Pakistan, while trying to set a bomb in a doll, then extradited to the United States.

Mohammed Jamal Khalifa (1 February 1957 – 31 January 2007) was a Saudi businessman from Jeddah who married one of Osama bin Laden's sisters. He has been accused of funding terror plots and groups in the Philippines in the 1990s while head of the International Islamic Relief Organization branch there. He was murdered in Madagascar in 2007.
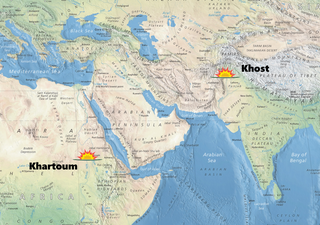
Operation Infinite Reach was the codename for American cruise missile strikes on al-Qaeda bases that were launched concurrently across two continents on 20 August 1998. Launched by the U.S. Navy, the strikes hit the al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory in Khartoum, Sudan, and a camp in Khost Province, Afghanistan, in retaliation for al-Qaeda's August 7 bombings of American embassies in Kenya and Tanzania, which killed 224 people and injured over 4,000 others. Operation Infinite Reach was the first time the United States acknowledged a preemptive strike against a violent non-state actor.

Richard Alan Clarke is an American national security expert, novelist, and former government official. He served as the Counterterrorism Czar for the National Coordinator for Security, Infrastructure Protection, and Counter-Terrorism for the United States between 1998 and 2003.

Simon Alan Reeve is an English author, journalist, adventurer, documentary filmmaker and television presenter.

The Hamburg cell was, according to U.S. and German intelligence agencies, a group of radical Islamists based in Hamburg, Germany, that included students from different Arab countries who eventually came to be key operatives in the 9/11 attacks. Important members included Mohamed Atta, who led the four hijacking teams in 2001 and piloted American Airlines Flight 11; Ramzi bin al-Shibh, who conspired with the other three members but was unable to enter the United States; Marwan al-Shehhi, who piloted United Airlines Flight 175; and Ziad Jarrah, who piloted United Airlines Flight 93 and failed to hit a target in Washington, D.C.. Other members included Said Bahaji, Zakariya Essabar, Mounir el-Motassadeq, and Abdelghani Mzoudi.
On September 11, 2001, 19 al-Qaeda terrorists took control of four commercial aircraft and used them as suicide weapons in a series of four coordinated acts of terrorism to strike the World Trade Center in New York City, The Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, and an additional target in Washington, D.C. Two aircraft hit the World Trade Center while the third hit the Pentagon. A fourth plane did not arrive at its target, but crashed into a field in Pennsylvania after a passenger revolt. The intended target is believed to have been the United States Capitol. As a result, 2,977 victims were killed, making it the deadliest foreign attack on U.S. soil, exceeding Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941, which killed 2,335 members of the United States Armed Forces and 68 civilians. The effort was carefully planned by al-Qaeda, which sent 19 terrorists to take over Boeing 757 and Boeing 767 aircraft, operated by American Airlines and United Airlines.

Holy War, Inc.: Inside the Secret World of Bin Laden is a book by CNN investigative journalist and documentarian Peter Bergen. It was published in November 2001, two months after the September 11 attacks, and was a New York Times Best Seller in 2001.

Muhammad Sa'id Ali Hasan al-Umda, also known as Gharib al-Taezi, was self-implicated on videotape as a possible terrorist in 2002, and was wanted by the United States Department of Justice's FBI, which was seeking information about his identity and whereabouts. He was once a bodyguard for Osama bin Laden and was a field commander for al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. In January 2002, he was discovered as one of five men who had been videotaped pledging martyrdom, and who were then consequently placed on the original version, upon inception, of the FBI's third major wanted list, which is now known as the FBI Seeking Information - War on Terrorism list. He was later removed by the FBI from the list after being detained by the Saudi government and then transferred to Yemen. He was convicted in 2005 of involvement in the 2002 attack on the MV Limburg oil tanker. In February 2006, he escaped from a Sana'a prison along with 22 other militants.

Mohammed Saddiq Odeh is a Saudi-born al-Qaeda member, sentenced in October 2001 to life imprisonment for his parts in the US embassy bombings in Kenya and Tanzania on August 7, 1998. Odeh was convicted along with three co-conspirators: Mohamed Rashed Daoud Al-Owhali, Khalfan Khamis Mohamed and Wadih el Hage. Another defendant, Ali Mohamed, pleaded guilty the previous year. Another, Mahdouh Salim, was awaiting trial, and three additional defendants were fighting extradition in England.

Several sources have alleged that the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) had ties with Osama bin Laden's faction of "Afghan Arab" fighters when it armed Mujahideen groups to fight the Soviet Union during the Soviet–Afghan War.
Osama bin Laden, a militant Islamist and co-founder of al-Qaeda, in conjunction with several other Islamic militant leaders, issued two fatawa – in 1996 and then again in 1998—that military personnel from the United States and allied countries until they withdraw support for Israel and withdraw military forces from Islamic countries. He was indicted in United States federal court for his alleged involvement in the 1998 U.S. embassy bombings in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania and Nairobi, Kenya, and was on the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation's Ten Most Wanted Fugitives list until his death.
Carried out by the Egyptian Islamic Jihad, the 19 November 1995 attack on the Egyptian embassy in Islamabad, Pakistan was retaliation against the diplomatic staffers who were accused of gathering intelligence on Jihad factions inside Pakistan. It was the deadliest attack against the Egyptian government, since it had been declared apostate three years earlier by Islamic militants.

The September 11 attacks were carried out by 19 hijackers of the Islamist militant organization al-Qaeda. In the 1990s, al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden declared a holy war against the United States of America, and issued two fatāwā in 1996 and 1998. In the 1996 fatwā, he quoted the Sword Verse. In both of these fatāwā, bin Laden sharply criticized the financial contributions of the American government to the Saudi royal family as well as American military intervention in the Arab world.
At around 9:30 pm on September 11, 2001, George Tenet, director of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), told President George W. Bush and U.S. senior officials that the CIA's Counterterrorism Center had determined that Osama bin Laden and al-Qaeda were responsible for the September 11 attacks. Two weeks after the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001, the Federal Bureau of Investigation connected the hijackers to al-Qaeda, a militant Salafist Islamist multi-national organization. In a number of video, audio, interview and printed statements, senior members of al-Qaeda have also asserted responsibility for organizing the September 11 attacks.
In the aftermath of the September 11 attacks on New York City and Washington, D.C., by the al-Qaeda terrorist group, a number of investigations were conducted to determine what intelligence may have existed before the attacks and whether this information was ignored by authorities.

Mohammed Atef was an Egyptian militant and prominent military chief of al-Qaeda, and a deputy of Osama bin Laden, although Atef's role in the organization was not well known by intelligence agencies for years. He was killed in a US airstrike in November 2001.
Al-Riyad, or Riyadh, is one of the neighbourhoods of Khartoum, Sudan, located in the southern side of Khartoum. The affluent neighbourhood hosted Osama bin Laden's house in Khartoum.














