Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is against all forms of authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state with stateless societies and voluntary free associations. As a historically left-wing movement, this reading of anarchism is placed on the farthest left of the political spectrum, usually described as the libertarian wing of the socialist movement.

Queer is an umbrella term for people who are not heterosexual or are not cisgender. Originally meaning 'strange' or 'peculiar', queer came to be used pejoratively against LGBT people in the late 19th century. Beginning in the late 1980s, queer activists, such as the members of Queer Nation, began to reclaim the word as a deliberately provocative and politically radical alternative to the more assimilationist branches of the LGBT community.
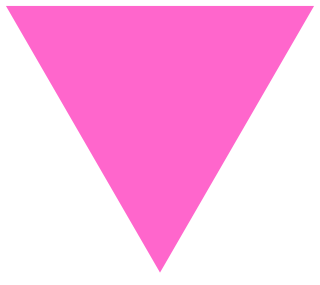
A pink triangle has been a symbol for the LGBT community, initially intended as a badge of shame, but later reclaimed as a positive symbol of self-identity. In Nazi Germany in the 1930s and 1940s, it began as one of the Nazi concentration camp badges, distinguishing those imprisoned because they had been identified by authorities as gay men. In the 1970s, it was revived as a symbol of protest against homophobia, and has since been adopted by the larger LGBT community as a popular symbol of LGBT pride and the LGBT movements and queer liberation movements.
Queer theory is a field of post-structuralist critical theory that emerged in the early 1990s out of queer studies and women's studies.
"New queer cinema" is a term first coined by the academic B. Ruby Rich in Sight & Sound magazine in 1992 to define and describe a movement in queer-themed independent filmmaking in the early 1990s.

Terms used to describe homosexuality have gone through many changes since the emergence of the first terms in the mid-19th century. In English, some terms in widespread use have been sodomite, Achillean, Sapphic, Uranian, homophile, lesbian, gay, effeminate, queer, homoaffective, and same-gender attracted. Some of these words are specific to women, some to men, and some can be used of either. Gay people may also be identified under the umbrella term LGBT.
Martin Bauml Duberman is an American historian, biographer, playwright, and gay rights activist. Duberman is Professor of History Emeritus at Lehman College in the Bronx, New York City.

Bisexual erasure, also called bisexual invisibility, is the tendency to ignore, remove, falsify, or re-explain evidence of bisexuality in history, academia, the news media, and other primary sources.

Queer anarchism, or anarcha-queer, is an anarchist school of thought that advocates anarchism and social revolution as a means of queer liberation and abolition of hierarchies such as homophobia, lesbophobia, transmisogyny, biphobia, transphobia, aphobia, heteronormativity, patriarchy, and the gender binary.

Daniel Guérin was a French libertarian-communist author, best known for his work Anarchism: From Theory to Practice, as well as his collection No Gods No Masters: An Anthology of Anarchism in which he collected writings on the idea and movement it inspired, from the first writings of Max Stirner in the mid-19th century through the first half of the 20th century. He is also known for his opposition to Nazism, fascism, capitalism, imperialism and colonialism, in addition to his support for the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) during the Spanish Civil War. His revolutionary defense of free love and homosexuality influenced the development of queer anarchism.

Growing Up Absurd is a 1960 book by Paul Goodman on the relationship between American juvenile delinquency and societal opportunities to fulfill natural needs. Contrary to the then-popular view that juvenile delinquents should be led to respect societal norms, Goodman argued that young American men were justified in their disaffection because their society lacked the preconditions for growing up, such as meaningful work, honorable community, sexual freedom, and spiritual sustenance.

The Empire City is a 1959 epic novel by Paul Goodman.

Communitas: Means of Livelihood and Ways of Life is a 1947 book on community and city planning by Percival and Paul Goodman. Presented as an illustrated primer on how city planning affects socioeconomic order and citizens' empowerment to better their communities, the book reviews historical and modern approaches to urban planning before proposing three of the Goodmans' own provocative community paradigms.

The May Pamphlet is a collection of six anarchist essays written and published by Paul Goodman in 1945. Goodman discusses the problems of living in a society that represses individual instinct through coercion. He suggests that individuals resist such conditions by reclaiming their natural instincts and initiative, and by "drawing the line", an ideological delineation beyond which an individual should refuse to conform or cooperate with social convention. While themes from The May Pamphlet—decentralization, peace, social psychology, youth liberation—would recur throughout his works, Goodman's later social criticism focused on practical applications rather than theoretical concerns.

This is a list of works by Paul Goodman (1911–1972), including his nonfiction, novels, short stories, poetry, and plays.

People or Personnel is a critique of centralized power written by Paul Goodman and published by Random House in 1965.
LGBT erasure refers to the tendency to intentionally or unintentionally remove LGBT groups or people from record, or downplay their significance, which includes lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender people and those who identify as queer. This erasure can be found in a number of written and oral texts, including popular and scholarly texts.
Anarchism and libertarianism, as broad political ideologies with manifold historical and contemporary meanings, have contested definitions. Their adherents have a pluralistic and overlapping tradition that makes precise definition of the political ideology difficult or impossible, compounded by a lack of common features, differing priorities of subgroups, lack of academic acceptance, and contentious historical usage.

The history of bisexuality concerns the history of the bisexual sexual orientation. Ancient and medieval history of bisexuality, when the term did not exist as such, consists of anecdotes of sexual behaviour and relationships between people of the same and different sexes. A modern definition of bisexuality began to take shape in the mid-19th century within three interconnected domains of knowledge: biology, psychology and sexuality. In modern Western culture, the term bisexual was first defined in a binary approach as a person with romantic or sexual attraction to both men and women. The term bisexual is defined later in the 20th century as a person who is sexually and/or romantically attracted to both males and females, or as a person who is sexually and/or romantically attracted to people regardless of sex or gender identity, which is sometimes termed pansexuality.

Paul Goodman was an American writer and public intellectual best known for his 1960s works of social criticism. Paul Goodman was prolific across numerous literary genres and non-fiction topics including the arts, civil rights, decentralization, democracy, education, media, politics, psychology, technology, urban planning, and war. As a humanist and self-styled man of letters, his works often addressed a common theme of the individual citizen's duties in the larger society, and the responsibility to exercise autonomy, act creatively, and realize one's own human nature.












