Related Research Articles
Artificial intelligence (AI), in its broadest sense, is intelligence exhibited by machines, particularly computer systems. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to perceive their environment and use learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. Such machines may be called AIs.
Topcoder is a crowdsourcing company with an open global community of designers, developers, data scientists, and competitive programmers. Topcoder pays community members for their work on the projects and sells community services to corporate, mid-size, and small-business clients. Topcoder also organizes the annual Topcoder Open tournament and a series of smaller regional events.
Collaborative intelligence characterizes multi-agent, distributed systems where each agent, human or machine, is autonomously contributing to a problem solving network. Collaborative autonomy of organisms in their ecosystems makes evolution possible. Natural ecosystems, where each organism's unique signature is derived from its genetics, circumstances, behavior and position in its ecosystem, offer principles for design of next generation social networks to support collaborative intelligence, crowdsourcing individual expertise, preferences, and unique contributions in a problem solving process.
Tim van Gelder is an Australian researcher who is the co-founder of Austhink Software, an Australian software development company, and the Managing Director of Austhink Consulting.

The Disruptive Technology Office (DTO) was a funding agency within the United States Intelligence Community. It was previously known as the Advanced Research and Development Activity (ARDA). In December 2007, DTO was folded into the newly created IARPA.
Human-based computation (HBC), human-assisted computation, ubiquitous human computing or distributed thinking is a computer science technique in which a machine performs its function by outsourcing certain steps to humans, usually as microwork. This approach uses differences in abilities and alternative costs between humans and computer agents to achieve symbiotic human–computer interaction. For computationally difficult tasks such as image recognition, human-based computation plays a central role in training Deep Learning-based Artificial Intelligence systems. In this case, human-based computation has been referred to as human-aided artificial intelligence.

Crowdsourcing involves a large group of dispersed participants contributing or producing goods or services—including ideas, votes, micro-tasks, and finances—for payment or as volunteers. Contemporary crowdsourcing often involves digital platforms to attract and divide work between participants to achieve a cumulative result. Crowdsourcing is not limited to online activity, however, and there are various historical examples of crowdsourcing. The word crowdsourcing is a portmanteau of "crowd" and "outsourcing". In contrast to outsourcing, crowdsourcing usually involves less specific and more public groups of participants.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to artificial intelligence:

The Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) is an organization, within the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), that is responsible for leading research to overcome difficult challenges facing the United States Intelligence Community. IARPA characterizes its mission as follows: "To envision and lead high-risk, high-payoff research that delivers innovative technology for future overwhelming intelligence advantage."
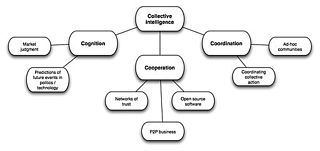
Collective intelligence (CI) is shared or group intelligence (GI) that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision making. The term appears in sociobiology, political science and in context of mass peer review and crowdsourcing applications. It may involve consensus, social capital and formalisms such as voting systems, social media and other means of quantifying mass activity. Collective IQ is a measure of collective intelligence, although it is often used interchangeably with the term collective intelligence. Collective intelligence has also been attributed to bacteria and animals.

Figure Eight was a human-in-the-loop machine learning and artificial intelligence company based in San Francisco.
Government crowdsourcing is a form of crowdsourcing employed by governments to better leverage their constituents' collective knowledge and experience. It has tended to take the form of public feedback, project development, or petitions in the past, but has grown to include public drafting of bills and constitutions, among other things. This form of public involvement in the governing process differs from older systems of popular action, from town halls to referendums, in that it is primarily conducted online or through a similar IT medium.
Aggregative Contingent Estimation (ACE) was a program of the Office of Incisive Analysis (OIA) at the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA). The program ran from June 2010 until June 2015.
SciCast is a collaborative platform for science and technology forecasting created by George Mason University with the help of a grant from the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) as part of its ForeST program. SciCast is currently on hiatus, after losing its main IARPA funding. It was expected to re-open in the fall of 2015 with the support of a major Science & Technology sponsor, but this had not occurred by January 2016.
The National Strategic Computing Initiative (NSCI) is a United States initiative calling for the accelerated development of technologies for exascale supercomputers, and funding research into post-semiconductor computing. The initiative was created by an executive order issued by President Barack Obama in July 2015. Ten United States government departments and independent agencies are involved in the initiative. The initiative initially brought together existing programs, with some dedicated funding increases proposed in the Obama administration's 2017 budget request. The initiative's strategic plan was released in July 2016.
Crowdmapping is a subtype of crowdsourcing by which aggregation of crowd-generated inputs such as captured communications and social media feeds are combined with geographic data to create a digital map that is as up-to-date as possible on events such as wars, humanitarian crises, crime, elections, or natural disasters. Such maps are typically created collaboratively by people coming together over the Internet.
Applied Research Associates Inc. (ARA), is an engineering, management, and public sector consulting firm and a research and development company headquartered in Albuquerque, New Mexico, founded in 1979. As of 2018, its revenue was estimated at between $100 and $750 million by The Washington Post. As of 2011, it had approximately 1,600 employees.
Toloka, based in Amsterdam, is a crowdsourcing and generative AI services provider.

Louis Barry Rosenberg is an American engineer, researcher, inventor, and entrepreneur. He researches augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. He was the Cotchett Endowed Professor of Educational Technology at the California Polytechnic. He founded the Immersion Corporation and Unanimous A.I., and he wrote the screenplay for the 2009 romantic comedy film, Lab Rats.
References
- ↑ "The SWARM Project: Participate in Pioneering Research on Reasoning". The SWARM Project: Participate in Pioneering Research on Reasoning. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- ↑ "Making big sense of big data: The quest to improve human reasoning". Pursuit. 6 February 2017. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- ↑ "Melbourne awarded up to US$19M for Intelligence research". The Melbourne Newsroom. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- 1 2 "Leveraging the wisdom (and ignorance) of crowds -- GCN". GCN. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- ↑ "Australian unis score research funding from US spooks". Computerworld. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- ↑ "IARPA Program Seeks to Build Up Analytic Reasoning Through Crowdsourcing-Based Platforms - Executive Gov". Executive Gov. Retrieved 13 March 2017.
- ↑ "CREATE". www.iarpa.gov. Retrieved 13 March 2017.