A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.

Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half fish.

Crux is a constellation of the southern sky that is centred on four bright stars in a cross-shaped asterism commonly known as the Southern Cross. It lies on the southern end of the Milky Way's visible band. The name Crux is Latin for cross. Even though it is the smallest of all 88 modern constellations, Crux is among the most easily distinguished as its four main stars each have an apparent visual magnitude brighter than +2.8. It has attained a high level of cultural significance in many Southern Hemisphere states and nations.

Camelopardalis is a large but faint constellation of the northern sky representing a giraffe. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by Petrus Plancius. Some older astronomy books give Camelopardalus or Camelopardus as alternative forms of the name, but the version recognized by the International Astronomical Union matches the genitive form, seen suffixed to most of its key stars.

A Flamsteed designation is a combination of a number and constellation name that uniquely identifies most naked eye stars in the modern constellations visible from southern England. They are named for John Flamsteed who first used them while compiling his Historia Coelestis Britannica.
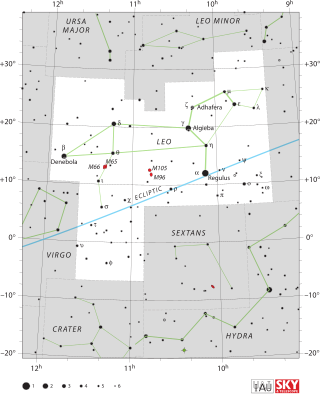
Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac, between Cancer the crab to the west and Virgo the maiden to the east. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for lion, and to the ancient Greeks represented the Nemean Lion killed by the mythical Greek hero Heracles as one of his twelve labors. Its old astronomical symbol is (♌︎). One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Leo remains one of the 88 modern constellations today, and one of the most easily recognizable due to its many bright stars and a distinctive shape that is reminiscent of the crouching lion it depicts.

Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for maiden, and its old astronomical symbol is . Between Leo to the west and Libra to the east, it is the second-largest constellation in the sky and the largest constellation in the zodiac. The ecliptic intersects the celestial equator within this constellation and Pisces. Underlying these technical two definitions, the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, within this constellation, at the September equinox. Virgo can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica.

The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Also within this zodiac belt appear the Moon and the brightest planets, along their orbital planes. The zodiac is divided along the ecliptic into 12 equal parts ("signs"), each occupying 30° of celestial longitude. These signs roughly correspond to the astronomical constellations with the following modern names: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces.

H. A. Rey was a German-born American illustrator and author, known best for the series of children's picture books that he and his wife Margret Rey created about Curious George.

Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials".

Coma Berenices is an ancient asterism in the northern sky, which has been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is in the direction of the fourth galactic quadrant, between Leo and Boötes, and it is visible in both hemispheres. Its name means "Berenice's Hair" in Latin and refers to Queen Berenice II of Egypt, who sacrificed her long hair as a votive offering. It was introduced to Western astronomy during the third century BC by Conon of Samos and was further corroborated as a constellation by Gerardus Mercator and Tycho Brahe. It is the only modern constellation named for a historic person.

In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the vernal equinox. The astrological signs are Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by the Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Over the centuries, Western astrology's zodiacal divisions have shifted out of alignment with the constellations they were named after by axial precession of the Earth while Hindu astrology measurements correct for this shifting. Astrology was developed in Chinese and Tibetan cultures as well but these astrologies are not based upon the zodiac but deal with the whole sky.

An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the 88 formally defined constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux.
The Catasterismi or Catasterisms is a lost work by Eratosthenes of Cyrene. It was a comprehensive compendium of astral mythology including origin myths of the stars and constellations. Only a summary of the original work survives, called the Epitome Catasterismorum, by an unknown author sometimes referred to as pseudo-Eratosthenes.
Sagittarius (♐︎) is the ninth astrological sign, which is associated with the constellation Sagittarius and spans 240–270th degrees of the zodiac. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this sign between approximately November 22 and December 21. Greek mythology associates Sagittarius with the centaur Chiron, who mentored Achilles, a Greek hero of the Trojan War, in archery.

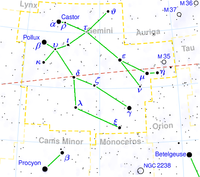
Gemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for twins, and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology. Its old astronomical symbol is (♊︎).

Babylonian astronomy collated earlier observations and divinations into sets of Babylonian star catalogues, during and after the Kassite rule over Babylonia. These star catalogues, written in cuneiform script, contained lists of constellations, individual stars, and planets. The constellations were probably collected from various other sources. The earliest catalogue, Three Stars Each, mentions stars of Akkad, of Amurru, of Elam and others. Various sources have theorized a Sumerian origin for these Babylonian constellations, but an Elamite origin has also been proposed. A connection to the star symbology of Kassite kudurru border stones has also been claimed, but whether such kudurrus really represented constellations and astronomical information aside from the use of the symbols remains unclear.

Constellation families are collections of constellations sharing some defining characteristic, such as proximity on the celestial sphere, common historical origin, or common mythological theme. In the Western tradition, most of the northern constellations stem from Ptolemy's list in the Almagest, and most of the far southern constellations were introduced by sailors and astronomers who traveled to the south in the 16th to 18th centuries. Separate traditions arose in India and China.

Urania's Mirror; or, a view of the Heavens is a set of 32 astronomical star chart cards, first published in November 1824. They are illustrations based on Alexander Jamieson's A Celestial Atlas, but the addition of holes punched in them allow them to be held up to a light to see a depiction of the constellation's stars. They were engraved by Sidney Hall, and were said to be designed by "a lady", but have since been identified as the work of the Reverend Richard Rouse Bloxam, an assistant master at Rugby School.