
The politics of New Zealand function within a framework of a unitary parliamentary representative democracy. The structure of government is based on the Westminster system, and the legal system is modelled on the common law of England. New Zealand is a constitutional monarchy, in which Queen Elizabeth II is the sovereign and head of state.
The New Zealand dollar is the official currency and legal tender of New Zealand, the Cook Islands, Niue, the Ross Dependency, Tokelau, and a British territory, the Pitcairn Islands. Within New Zealand, it is almost always abbreviated with the dollar sign ($), with "NZ$" sometimes used to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies.
A state highway, state road, or state route is usually a road that is either numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered by a state or province falls below numbered national highways in the hierarchy. Roads maintained by a state or province include both nationally numbered highways and un-numbered state highways. Depending on the state, "state highway" may be used for one meaning and "state road" or "state route" for the other.

The New Zealand royal honours system, a system of orders, decorations and medals, recognises achievements of, or service by, New Zealanders or others in connection with New Zealand. Until 1975, New Zealand used the British honours system. Since then the country has introduced a number of uniquely New Zealand honours, and as of 2021, only the dynastic British honours continue in active use in New Zealand, with the exception of the Order of the Companions of Honour.

The New Zealand Parliament is the unicameral legislature of New Zealand, consisting of the Queen of New Zealand (Queen-in-Parliament) and the New Zealand House of Representatives. The Queen is usually represented by her governor-general. Before 1951, there was an upper chamber, the New Zealand Legislative Council. The New Zealand Parliament was established in 1854 and is one of the oldest continuously functioning legislatures in the world. It has met in Wellington, the capital of New Zealand, since 1865.

The New Zealand Order of Merit is an order of merit in the New Zealand royal honours system. It was established by royal warrant on 30 May 1996 by Elizabeth II, Queen of New Zealand, "for those persons who in any field of endeavour, have rendered meritorious service to the Crown and nation or who have become distinguished by their eminence, talents, contributions or other merits", to recognise outstanding service to the Crown and people of New Zealand in a civil or military capacity.

Skelton Glacier is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica.

The conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status exist and are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels as well as for consumer use.

The Realm of New Zealand consists of the entire area in which the monarch of New Zealand functions as head of state. The Realm of New Zealand is not a federation; it is a constitutional concept encompassing the three autonomous legal systems of New Zealand, the Cook Islands, and Niue. It is a collection of states and territories united under its monarch. New Zealand is an independent and sovereign state. It has one Antarctic territorial claim, one dependent territory (Tokelau), and two associated states.

New Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island and the South Island —and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country, covering a total area of 268,021 square kilometres (103,500 sq mi). New Zealand is about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland.
Prior to 1999 the New Zealand armed forces received honours of the United Kingdom, including military decorations and campaign medals. Since the end of World War II there have been constant moves towards an independent New Zealand honours system. This has resulted in a new system of New Zealand honours, military gallantry and civil bravery awards, and campaign medals.
The New Zealand bravery awards are civil (non-military) decorations for bravery.
The law of New Zealand uses the English common law system, inherited from being a part of the British Empire.

The New Zealand Threat Classification System is used by the Department of Conservation to assess conservation priorities of species in New Zealand.

The Māori are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand. Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed their own distinctive culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori.
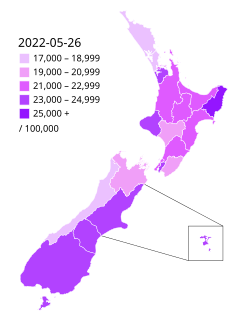
The COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand is part of the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first case of the disease in New Zealand was reported on 28 February 2020. As of 24 April 2022, the country has had a total of 884,289 cases. 636 people have died with the virus, with cases recorded in all twenty district health board (DHB) areas. The pandemic first peaked in early April 2020, with 89 new cases recorded per day and 929 active cases. Cases peaked again in October 2021 with 134 new cases reported on 22 October. A total of 5,884,095 COVID tests have been carried out as of 23 January 2022.

Managed isolation and quarantine (MIQ) is a quarantine system implemented by the New Zealand Government during the country's COVID-19 pandemic. Under the system, people entering New Zealand, COVID-19 positive cases and some of their close contacts are required to isolate at an MIQ facility for 14 days. Compulsory managed isolation and quarantine was announced by Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern at the 1pm press conference on 9 April 2020, with the system coming into effect for people boarding flights to New Zealand from midnight that day. The government has contracted dozens of hotels in five cities that are exclusively used as managed isolation facilities. The task is organised by the Managed Isolation and Quarantine (MIQ) unit, part of the COVID-19 All-of-Government Response Group.
A four-tier alert level restrictions system was in place in during the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand between March 2020 and December 2021, with levels 3 and 4 being forms of lockdown. In level 1 there were no restrictions; in level 2 there were limits on gatherings; in level 3 only purposeful travel was allowed and there were strict limits on gatherings; and in level 4 only essential travel was allowed and gatherings were banned.
The COVID-19 Protection Framework is a system used by the New Zealand Government during the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand. The three-tier traffic light system uses vaccination and community transmission rates to determine the level of restrictions needed. It came into effect at 11:59 pm on 2 December 2021, replacing the four-tier alert level system, which used lockdowns.











