
Northern Ireland is a part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland that is variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares an open border to the south and west with the Republic of Ireland. At the 2021 census, its population was 1,903,175, making up around 3% of the UK's population and 27% of the population on the island of Ireland. The Northern Ireland Assembly, established by the Northern Ireland Act 1998, holds responsibility for a range of devolved policy matters, while other areas are reserved for the UK Government. The government of Northern Ireland cooperates with the government of Ireland in several areas under the terms of the Belfast Agreement. The Republic of Ireland also has a consultative role on non-devolved governmental matters through the British–Irish Governmental Conference (BIIG).
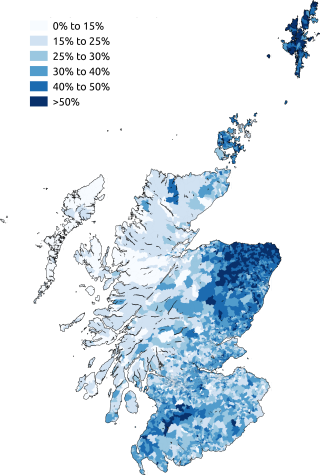
Scots is a language variety descended from Early Middle English in the West Germanic language family. Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, the Northern Isles of Scotland, and northern Ulster in Ireland, it is sometimes called: Lowland Scots, to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides, and Galloway after the sixteenth century; or Broad Scots, to distinguish it from Scottish Standard English. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged from the same medieval form of English.

Rathlin Island is an island and civil parish off the coast of County Antrim in Northern Ireland. It is Northern Ireland's northernmost point. As of the 2021 Census there are 141 people living on the island.

Ulster Scots or Ulster-Scots, also known as Ulster Scotch and Ullans, is the dialect spoken in parts of Ulster, being almost exclusively spoken in parts of Northern Ireland and County Donegal. It is normally considered a dialect or group of dialects of Scots, although groups such as the Ulster-Scots Language Society and Ulster-Scots Academy consider it a language in its own right, and the Ulster-Scots Agency and former Department of Culture, Arts and Leisure have used the term Ulster-Scots language.

English is the most widely spoken and de facto official language of the United Kingdom. A number of regional and migrant languages are also spoken. Regional English variant languages include Scots and Ulster Scots, and indigenous Celtic languages include Irish, Scottish Gaelic, and Welsh. There are many non-native languages spoken by immigrants, including Polish, Hindi, and Urdu. British Sign Language is sometimes used as well as liturgical and hobby languages such as Latin and a revived form of Cornish.
The Ulster Scots people or Scots-Irish are an ethnic group descended largely from Scottish and Northern English Borders settlers who moved to the northern province of Ulster in Ireland mainly during the 17th century. There is an Ulster Scots dialect of the Scots language.

Kircubbin is a village and townland in County Down, Northern Ireland. The village had a population of 1,153 people in the 2011 Census.
Craic or crack is a term for news, gossip, fun, entertainment, and enjoyable conversation, particularly prominent in Ireland. It is often used with the definite article – the craic – as in the expression "What's the craic?", meaning "How are you?" or "What's happening?". The Scots and English crack was borrowed into Irish as craic in the mid-20th century and the Irish spelling was then reborrowed into English. Under both spellings, the term has become popular and significant in Ireland.
Scotch-Irish Americans are American descendants of primarily Ulster Scots people who emigrated from Ulster to the United States during the 18th and 19th centuries. Their ancestors had originally migrated to Ulster, mainly from the Scottish Lowlands and Northern England in the 17th century. In the 2017 American Community Survey, 5.39 million reported Scottish ancestry, an additional 3 million identified more specifically with Scotch-Irish ancestry, and many people who claim "American ancestry" may actually be of Scotch-Irish ancestry.
The Ulster-Scots Agency is a cross-border body for Ireland which seeks to "promote the study, conservation and development of Ulster-Scots as a living language, to encourage and develop the full range of its attendant culture, and to promote an understanding of the history of the Ulster-Scots [people]."
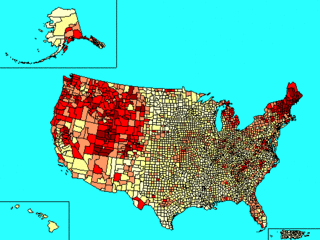
Scottish Americans or Scots Americans are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Scotland. Scottish Americans are closely related to Scotch-Irish Americans, descendants of Ulster Scots, and communities emphasize and celebrate a common heritage. The majority of Scotch-Irish Americans originally came from Lowland Scotland and Northern England before migrating to the province of Ulster in Ireland and thence, beginning about five generations later, to North America in large numbers during the eighteenth century. The number of Scottish Americans is believed to be around 25 million, and celebrations of Scottish identity can be seen through Tartan Day parades, Burns Night celebrations, and Tartan Kirking ceremonies.
Ian Adamson OBE was an Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) politician and paediatrician, who was the Lord Mayor of Belfast from 1996 to 1997, having been Deputy Lord Mayor from 1994 to 1995.

John Dunn Laird, Baron Laird,, of Artigarvan was a Northern Irish politician, life peer and former chairman of the cross-border Ulster-Scots Agency. In 2013 Laird allegedly offered to lobby for a firm against parliamentary rules. Consequently, he resigned from the Ulster Unionist Party.
James Fenton was a linguist and poet who wrote in Ulster Scots.
A Kist o Wurds is a BBC Northern Ireland Ulster-Scots radio programme that has been running since 2002. The show is produced by Chris Spurr, for Blackthorn Productions. Each week it contains a selection of music, poetry and news from across the country and is a source of information on the Ulster-Scots language, culture, literary traditions and history. Broadcast on BBC Radio Ulster on Sundays at 4pm and repeated on Wednesdays at 7.30pm on Radio Ulster and Radio Foyle.

The Scottish people or Scots are an ethnic group and nation native to Scotland. Historically, they emerged in the early Middle Ages from an amalgamation of two Celtic peoples, the Picts and Gaels, who founded the Kingdom of Scotland in the 9th century. In the following two centuries, Celtic-speaking Cumbrians of Strathclyde and Germanic-speaking Angles of Northumbria became part of Scotland. In the High Middle Ages, during the 12th-century Davidian Revolution, small numbers of Norman nobles migrated to the Lowlands. In the 13th century, the Norse-Gaels of the Western Isles became part of Scotland, followed by the Norse of the Northern Isles in the 15th century.

English is by far the most spoken, and the "de facto" national language of Northern Ireland,; it occurs in various forms, including Ulster English and Hiberno-English. Irish is an official language of Northern Ireland since 2022, and the local variety of Scots, known as Ulster Scots, has official minority status, with services in the language provided by public authorities. Northern Ireland Sign Language and Irish Sign Language have also been recognised with minority status since 29 March 2004.
Ulster Protestants are an ethnoreligious group in the Irish province of Ulster, where they make up about 43.5% of the population. Most Ulster Protestants are descendants of settlers who arrived from Britain in the early 17th century Ulster Plantation. This was the settlement of the Gaelic, Catholic province of Ulster by Scots and English speaking Protestants, mostly from the Scottish Lowlands and Northern England. Many more Scottish Protestant migrants arrived in Ulster in the late 17th century. Those who came from Scotland were mostly Presbyterians, while those from England were mostly Anglicans. There is also a small Methodist community and the Methodist Church in Ireland dates to John Wesley's visit to Ulster in 1752. Although most Ulster Protestants descend from Lowland Scottish people, many descend from English, and to a lesser extent, from Irish, Welsh and Huguenots.
fUSe FM Ballymoney is the first Ulster Scots community radio station in the UK and is currently run under the Ullans Speakers Association. Broadcasting on FM 107.5, online and via the TuneIn app from their studio based in Ballymoney, Co. Antrim, Northern Ireland, within the Fuse Centre.









