Related Research Articles

A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word laser is an anacronym that originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.

Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz. The visible band sits adjacent to the infrared and the ultraviolet, called collectively optical radiation.

Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

In optics, the refractive index of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the medium to the speed in air or vacuum. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2, where θ1 and θ2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices n1 and n2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity and Brewster's angle.

In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface. The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an objective, and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it.
The term biophotonics denotes a combination of biology and photonics, with photonics being the science and technology of generation, manipulation, and detection of photons, quantum units of light. Photonics is related to electronics and photons. Photons play a central role in information technologies, such as fiber optics, the way electrons do in electronics.
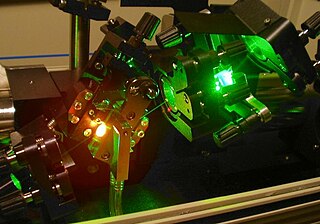
Titanium-sapphire lasers (also known as Ti:sapphire lasers, Ti:Al2O3 lasers or Ti:sapphs) are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses thanks to its broad light emission spectrum. Lasers based on Ti:sapphire were first constructed and invented in June 1982 by Peter Moulton at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory.

Laser propulsion is a form of beam-powered propulsion where the energy source is a remote laser system and separate from the reaction mass. This form of propulsion differs from a conventional chemical rocket where both energy and reaction mass come from the solid or liquid propellants carried on board the vehicle.

Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. While typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser most commonly through optics. The laser optics and CNC are used to direct the laser beam to the material. A commercial laser for cutting materials uses a motion control system to follow a CNC or G-code of the pattern to be cut onto the material. The focused laser beam is directed at the material, which then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish.

Plastic welding is welding for semi-finished plastic materials, and is described in ISO 472 as a process of uniting softened surfaces of materials, generally with the aid of heat. Welding of thermoplastics is accomplished in three sequential stages, namely surface preparation, application of heat and pressure, and cooling. Numerous welding methods have been developed for the joining of semi-finished plastic materials. Based on the mechanism of heat generation at the welding interface, welding methods for thermoplastics can be classified as external and internal heating methods, as shown in Fig 1.

Laser beam welding (LBW) is a welding technique used to join pieces of metal or thermoplastics through the use of a laser. The beam provides a concentrated heat source, allowing for narrow, deep welds and high welding rates. The process is frequently used in high volume and precision requiring applications using automation, as in the automotive and aeronautics industries. It is based on keyhole or penetration mode welding.

Laser pumping is the act of energy transfer from an external source into the gain medium of a laser. The energy is absorbed in the medium, producing excited states in its atoms. When for a period of time the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in the ground state or a less-excited state, population inversion is achieved. In this condition, the mechanism of stimulated emission can take place and the medium can act as a laser or an optical amplifier. The pump power must be higher than the lasing threshold of the laser.

An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are immune to electromagnetic interference. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, such as fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.
In laser science, the beam parameter product (BPP) is the product of a laser beam's divergence angle (half-angle) and the radius of the beam at its narrowest point. The BPP quantifies the quality of a laser beam, and how well it can be focused to a small spot.

A laser weapon is a type of directed-energy weapon that uses lasers to inflict damage. Whether they will be deployed as practical, high-performance military weapons remains to be seen. One of the major issues with laser weapons is atmospheric thermal blooming, which is still largely unsolved. This issue is exacerbated when there is fog, smoke, dust, rain, snow, smog, foam, or purposely dispersed obscurant chemicals present. In essence, a laser generates a beam of light that requires clear air or a vacuum to operate.
Photodarkening is an optical effect observed in the interaction of laser radiation with amorphous media (glasses) in optical fibers. Until now, such creation of color centers was reported only in glass fibers. Photodarkening limits the density of excitations in fiber lasers and amplifiers. The experimental results suggest that operating at a saturated regime helps to reduce photodarkening.
Ophir Optronics Solutions is a multinational company that sells optronics solutions. The company develops, manufactures and markets infrared (IR) optics and laser measurement equipment. Founded in 1976, the company was traded on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange from 1991 until it was acquired, and was a constituent of its Tel-tech index. Headquartered in the Har Hotzvim industrial park in Jerusalem, Israel Ophir owns a 100,000-square-foot (9,300 m2) complex that includes the group's main production plant. Ophir has additional production plants in North Andover, Massachusetts and Logan, Utah in the US and sales offices in the US, Japan and Europe. In 2006, Ophir acquired Spiricon Group, a US-based company in the beam-profiling market. Ophir's sales increased sharply from $45 million in 2005 to $74 million in 2007. During 2007, Ophir established a Swiss-based subsidiary to market lenses and components for surveillance and imaging systems in Europe. In May 2010, Ophir acquired Photon Inc., another US-based beam-profiling company. Newport Corporation, a global supplier in photonics solutions, completed its acquisition of the Ophir company in October 2011. In 2016, metrology firm MKS Instruments bought Newport Corporation, including the Ophir brand, for $980 million.
Photothermal spectroscopy is a group of high sensitivity spectroscopy techniques used to measure optical absorption and thermal characteristics of a sample. The basis of photothermal spectroscopy is the change in thermal state of the sample resulting from the absorption of radiation. Light absorbed and not lost by emission results in heating. The heat raises temperature thereby influencing the thermodynamic properties of the sample or of a suitable material adjacent to it. Measurement of the temperature, pressure, or density changes that occur due to optical absorption are ultimately the basis for the photothermal spectroscopic measurements.
The thermo-optic coefficient of a material is the change in refractive index with the response to temperature. This value itself also depends on the present temperature of the material and so has second-order behaviours. At low temperatures (0-400 °C), the relationship is linear but at higher ones it exhibits a second-order polynomial behaviour.
Laser welding of polymers is a set of methods used to join polymeric components through the use of a laser. It can be performed using CO2 lasers, Nd:YAG lasers, Diode lasers and Fiber lasers.
References
- ↑ Lukin, V.P.; Fortes, B.V. (2002). Adaptive Beaming and Imaging in the Turbulent Atmosphere. SPIE Press monograph. SPIE Press. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-8194-4337-3 . Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- ↑ Paschotta, Dr Rüdiger. "Thermal Lensing". www.rp-photonics.com. Retrieved 2022-11-12.
- ↑ Babu, Mahalingam; Bongu, Sudhakara Reddy; Shetty, Pritam P.; Varrla, Eswaraiah; Reddy, G Ramachandra; Bingi, Jayachandra (December 23, 2023). "Demonstration of spatial self phase modulation based photonic diode functionality in MoS2/h-BN medium". Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing. 168: 107831. arXiv: 2309.09209 . doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2023.107831.
- Tyson, R. (2012). Principles Of Adaptive Optics. Elsevier Science. pp. 40–42. ISBN 978-0-323-15659-2 . Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- Zohuri, B. (2016). Directed Energy Weapons: Physics of High Energy Lasers (HEL). Springer International Publishing. p. 381. ISBN 978-3-319-31289-7 . Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- Dawes, C. (1992). Laser Welding: A Practical Guide. Series in Welding and Other Jo. Abington. p. 210. ISBN 978-1-85573-034-2 . Retrieved September 5, 2017.