Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicine, food, and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as toxicity or infection.

Basidiomycota is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya within the kingdom Fungi.
Penicillium species are usually regarded as unimportant in terms of causing human disease. Penicillium marneffei, now called Talaromyces marneffei, discovered in 1956, is an exception. It is now regarded as one of the world's ten most feared fungi. This is the only known thermally dimorphic species of Penicillium, and it can cause a lethal systemic infection (penicilliosis) with fever and anaemia similar to disseminated cryptococcosis.

In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are born. The fruitbody is part of the sexual phase of a fungal life cycle, while the rest of the life cycle is characterized by vegetative mycelial growth and asexual spore production.
Filobasidiella is a genus of fungi in the family Tremellaceae. Species are parasitic on other fungi and do not produce distinct basidiocarps. The genus is the teleomorphic (sexual) state of the yeast genus Cryptococcus, some species of which are human pathogens.
Arxula adeninivorans is a dimorphic yeast with unusual characteristics. The first description of A. adeninivorans was provided in the mid-eighties. The species was initially designated as Trichosporon adeninovorans. After the first identification in the Netherlands, strains of this species were later on also found in Siberia and in South Africa in soil and in wood hydrolysates. Recently, A. adeninivorans was renamed as Blastobotrys adeninivorans after a detailed phylogenetic comparison with other related yeast species. However, many scientists desire to maintain the popular name A. adeninivorans.

Lasiodiplodia theobromae is a plant pathogen with a very wide host range. It causes rotting and dieback in most species it infects. It is a common post harvest fungus disease of citrus known as stem-end rot. It is a cause of bot canker of grapevine. It also infects Biancaea sappan, a species of flowering tree also known as Sappanwood.

Paracoccidioides brasiliensis is a dimorphic fungus and the causative agent of the disease paracoccidioidomycosis. The fungus has been affiliated with the family Ajellomycetaceae although a sexual state or teleomorph has not yet been found.
Exophiala jeanselmei is a saprotrophic fungus in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. Four varieties have been discovered: Exophiala jeanselmei var. heteromorpha, E. jeanselmei var. lecanii-corni, E. jeanselmei var. jeanselmei, and E. jeanselmei var. castellanii. Other species in the genus Exophiala such as E. dermatitidis and E. spinifera have been reported to have similar annellidic conidiogenesis and may therefore be difficult to differentiate.
The International Mycological Institute was a non-profit organisation, based in England, that undertook research and disseminated information on fungi, particularly plant pathogenic species causing crop diseases. It was established as the Imperial Bureau of Mycology at Kew in 1920 and amalgamated with CAB International in 1998.

Blastomyces dermatitidis is the causal agent of blastomycosis, an invasive and often serious fungal infection found occasionally in humans and other animals in regions where the fungus is endemic. The causal organism is a fungus living in soil and wet, decaying wood, often in an area close to a waterway such as a lake, river or stream. Indoor growth may also occur, for example, in accumulated debris in damp sheds or shacks. The fungus is endemic to parts of eastern North America, particularly boreal northern Ontario, southeastern Manitoba, Quebec south of the St. Lawrence River, parts of the U.S. Appalachian mountains and interconnected eastern mountain chains, the west bank of Lake Michigan, the state of Wisconsin, and the entire Mississippi Valley including the valleys of some major tributaries such as the Ohio River. In addition, it occurs rarely in Africa both north and south of the Sahara Desert, as well as in the Arabian Peninsula and the Indian subcontinent. Though it has never been directly observed growing in nature, it is thought to grow there as a cottony white mold, similar to the growth seen in artificial culture at 25 °C (77 °F). In an infected human or animal, however, it converts in growth form and becomes a large-celled budding yeast. Blastomycosis is generally readily treatable with systemic antifungal drugs once it is correctly diagnosed; however, delayed diagnosis is very common except in highly endemic areas.

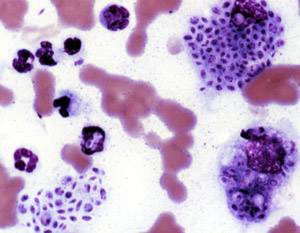
Dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold and yeast. An example is Penicillium marneffei, a human pathogen that grows as a mold at room temperature, and as a yeast at human body temperature.
M. indicus is among the most important members of zygomycetes fungi. This dimorphic fungus is capable of production of several valuable products.
“Black yeasts”, sometimes also black fungi, dematiaceous fungi, microcolonial fungi or meristematic fungi is a diverse group of slow-growing microfungi which reproduce mostly asexually. Only few genera reproduce by budding cells, while in others hyphal or meristematic (isodiametric) reproduction is preponderant. Black yeasts share some distinctive characteristics, in particular melanisation of their cell wall. Morphological plasticity, incrustation of the cell wall with melanins and presence of other protective substances like carotenoids and mycosporines represent passive physiological adaptations which enable black fungi to be highly resistant against environmental stresses. The term "polyextremotolerance" has been introduced to describe this phenotype, a good example of which is the species Aureobasidium pullulans. Presence of 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene melanin in the cell wall confers to the microfungi their characteristic olivaceous to dark brown/black colour.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fungi:
Histoplasma duboisii is a saprotrophic fungus responsible for the invasive infection known as African histoplasmosis. This species is a close relative of Histoplasma capsulatum, the agent of classical histoplasmosis, and the two occur in similar habitats. Histoplasma duboisii is restricted to continental Africa and Madagascar, although scattered reports have arisen from other places usually in individuals with an African travel history. Like, H. capsulatum, H. duboisii is dimorphic – growing as a filamentous fungus at ambient temperature and a yeast at body temperature. It differs morphologically from H. capsulatum by the typical production of a large-celled yeast form. Both agents cause similar forms of disease, although H. duboisii predominantly causes cutaneous and subcutaneous disease in humans and non-human primates. The agent responds to many antifungal drug therapies used to treat serious fungal diseases.

Exophiala phaeomuriformis is thermophilic fungus belonging to the genus Exophiala and the family Herpotrichiellaceae. it is a member of the group of fungi known as black yeasts, and is typically found in hot and humid locations, such as saunas, bathrooms, and dishwashers. This species can cause skin infections and is typically classified as a Biosafety Risk Group 2 agent.

Neoscytalidium dimidiatum was first described in 1933 as Hendersonula toruloidea from diseased orchard trees in Egypt. Decades later, it was determined to be a causative agent of human dermatomycosis-like infections and foot infections predominantly in the tropical areas; however the fungus is considered to be widespread. A newer name, Scytalidium dimidiatum, was applied to synanamorph of Nattrassia mangiferae, otherwise known as Neofusicoccum mangiferae. Substantial confusion has arisen in the literature on this fungus resulting from the use of multiple different names including: Torula dimidiata, Scytalidium dimidiatum, Fusicoccum dimidiatum, and Hendersonula toruloidea.

Cladophialophora carrionii is a melanized fungus in the genus Cladophialophora that is associated with decaying plant material like cacti and wood. It is one of the most frequent species of Cladophialophora implicated in human disease. Cladophialophora carrionii is a causative agent of chromoblastomycosis, a subcutaneous infection that occurs in sub-tropical areas such as Madagascar, Australia and northwestern Venezuela. Transmission occurs through traumatic implantation of plant material colonized by C. carrionii, mainly infecting rural workers. When C. carrionii infects its host, it transforms from a mycelial state to a muriform state to better tolerate the extreme conditions in the host's body.

Rhizopus stolonifer is commonly known as black bread mold. It is a member of Zygomycota and considered the most important species in the genus Rhizopus. It is one of the most common fungi in the world and has a global distribution although it is most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions. It is a common agent of decomposition of stored foods. Like other members of the genus Rhizopus, R. stolonifer grows rapidly, mostly in indoor environments.