
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages. Yiddish has traditionally been written using the Hebrew alphabet.

Ashkenazi Jews constitute a Jewish diaspora population that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language that originated in the 9th century, and largely migrated towards northern and eastern Europe during the late Middle Ages due to persecution. Hebrew was primarily used as a literary and sacred language until its 20th-century revival as a common language in Israel.

The history of the Jews in the United States goes back to the 1600s and 1700s. There have been Jewish communities in the United States since colonial times, with individuals living in various cities before the American Revolution. Early Jewish communities were primarily composed of Sephardi immigrants from Brazil, Amsterdam, or England, many of them fleeing the Inquisition.

American Jews or Jewish Americans are American citizens who are Jewish, whether by culture, ethnicity, or religion. According to a 2020 poll conducted by Pew Research, approximately two thirds of American Jews identify as Ashkenazi, 3% identify as Sephardic, and 1% identify as Mizrahi. An additional 6% identify as some combination of the three categories, and 25% do not identify as any particular category.

Jewish culture is the culture of the Jewish people, from its formation in ancient times until the current age. Judaism itself is not simply a faith-based religion, but an orthoprax and ethnoreligion, pertaining to deed, practice, and identity. Jewish culture covers many aspects, including religion and worldviews, literature, media, and cinema, art and architecture, cuisine and traditional dress, attitudes to gender, marriage, family, social customs and lifestyles, music and dance. Some elements of Jewish culture come from within Judaism, others from the interaction of Jews with host populations, and others still from the inner social and cultural dynamics of the community. Before the 18th century, religion dominated virtually all aspects of Jewish life, and infused culture. Since the advent of secularization, wholly secular Jewish culture emerged likewise.

Jewish Autonomism, not connected to the contemporary political movement autonomism, was a non-Zionist political movement and ideology that emerged in the Russian and Austro-Hungarian empires, before spreading throughout Eastern Europe in the late 19th and early 20th century. In the late 19th century, Jewish Autonomism was seen "together with Zionism [as] the most important political expression of the Jewish people in the modern era." One of its first and major proponents was the historian and activist Simon Dubnow. Jewish Autonomism is often referred to as "Dubnovism" or "folkism".
Italian Jews or Roman Jews can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living in or with roots in Italy, or, in a narrower sense, to mean the Italkim, an ancient community living in Italy since the Ancient Roman era, who use the Italian liturgy as distinct from those Jewish communities in Italy dating from medieval or modern times who use the Sephardic liturgy or the Nusach Ashkenaz.

The community of Sephardic Jews in the Netherlands, particularly in Amsterdam, was of major importance in the seventeenth century. The Portuguese Jews in the Netherlands did not refer to themselves as "Sephardim", but rather as "Hebrews of the Portuguese Nation." The Portuguese-speaking community grew from conversos, Jews forced to convert to Catholicism in Spain and Portugal, who rejudaized under rabbinical authority, to create an openly self-identified Portuguese Jewish community. As a result of the expulsions from Spain in 1492 and Portugal in 1496, as well as the religious persecution by the Inquisition that followed, many Spanish and Portuguese Jews left the Iberian Peninsula at the end of the 15th century and throughout the 16th century, in search of religious freedom. Some migrated to the newly independent Dutch provinces which allowed Jews to become residents. Many Jews who left for the Dutch provinces were crypto-Jews. Others had been sincere New Christians, who, despite their conversion, were targeted by Old Christians as suspect. Some of these sought to return to the religion of their ancestors. Ashkenazi Jews began migrating to the Netherlands in the mid-seventeenth century, but Portuguese Jews viewed them with ambivalence.

The history of the Jews in Croatia dates back to at least the 3rd century, although little is known of the community until the 10th and 15th centuries. According to the 1931 census, the community numbered 21,505 members, and it is estimated that on the eve of the Second World War the population was around 25,000 people. Most of the population was murdered during the Holocaust that took place on the territory of the Nazi puppet state called the Independent State of Croatia. After the war, half of the survivors chose to settle in Israel, while an estimated 2,500 members continued to live in Croatia. According to the 2011 census, there were 509 Jews living in Croatia, but that number is believed to exclude those born of mixed marriages or those married to non-Jews. More than 80 percent of the Zagreb Jewish Community were thought to fall in those two categories.

The history of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina spans from the arrival of the first Bosnian Jews as a result of the Spanish Inquisition to the survival of the Bosnian Jews through the Holocaust and the Yugoslav Wars. Jews are one of the minority peoples of Bosnia and Herzegovina, according to the country's constitution. The Bosnian Jewish community is composed of both Sephardic and Ashkenazi Jews.
The history of the Jews in Jamaica predominantly dates back to migrants from Spain and Portugal. Starting in 1509, many Jews began fleeing from Spain because of the persecution of the Holy Inquisition. When the English captured Jamaica from Spain in 1655, the Jews who were living as conversos began to practice Judaism openly. By 1611, the Island of Jamaica had reached an estimated population of 1,500 people. An estimated 75 of those people were described as "foreigners," which may have included some Portuguese Jews. Many Jamaican Jews were involved in the Atlantic slave trade, both owning and trading in enslaved Black people.
Isaac in America: A Journey With Isaac Bashevis Singer is a 1986 documentary made by director Amram Nowak and producer Kirk Simon. It was broadcast on the PBS series American Masters.
The Old Yishuv were the Jewish communities of the region of Palestine during the Ottoman period, up to the onset of Zionist aliyah waves, and the consolidation of the new Yishuv by the end of World War I. Unlike the new Yishuv, characterized by secular and Zionist ideologies promoting labor and self-sufficiency, the Old Yishuv primarily consisted of religious Jews who relied on external donations (halukka) for support.
Lebanese Jewish Migration to Israel included thousands of Jews, who moved to Israel, similar to how 1948 witnessed the emigration of hundreds of thousands of Jews from Arab countries. Yet, "unlike Jewish communities in many other Arab states, the Jewish communities in Lebanon grew after 1948 and it was not until the end of the civil war of 1975 that the community started to emigrate." This "Lebanese difference" derives from two components: more positive Lebanese relationships with European authorities during the French Mandate than experienced by other Arab states, leading to a more pluralistic outlook in Lebanon than its neighbors; some elements in the Maronite Christian community who were tolerant of Zionism.
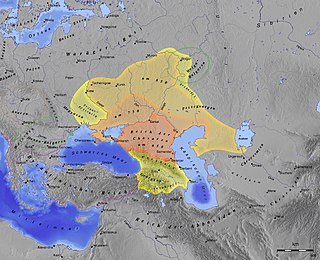
The Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestry, often called the Khazar myth by its critics, is a largely abandoned historical hypothesis that postulated that Ashkenazi Jews were primarily, or to a large extent, descended from Khazars, a multi-ethnic conglomerate of mostly Turkic peoples who formed a semi-nomadic khanate in and around the northern and central Caucasus and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. The hypothesis also postulated that after collapse of the Khazar empire, the Khazars fled to Eastern Europe and made up a large part of the Jews there. The hypothesis draws on medieval sources such as the Khazar Correspondence, according to which at some point in the 8th–9th centuries, a small number of Khazars were said by Judah Halevi and Abraham ibn Daud to have converted to Rabbinic Judaism. The scope of the conversion within the Khazar Khanate remains uncertain, but the evidence used to tie the subsequent Ashkenazi communities to the Khazars is meager and subject to conflicting interpretations.
The history of the Jews in Colombia begins in the Spanish colonial period with the arrival of the first Jews during the Spanish colonization of the Americas.

Turkish Jews in Israel are immigrants and descendants of the immigrants of the Turkish Jewish communities, who now reside within the State of Israel. They number around 100,000-150,000.











