Landmark court decisions, in present-day common law legal systems, establish precedents that determine a significant new legal principle or concept, or otherwise substantially affect the interpretation of existing law. "Leading case" is commonly used in the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth jurisdictions instead of "landmark case" as used in the United States.

Egan v Canada, [1995] 2 SCR 513 was one of a trilogy of equality rights cases published by a very divided Supreme Court of Canada in the spring of 1995. It stands today as a landmark Supreme Court case which established that sexual orientation constitutes a prohibited basis of discrimination under section 15 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
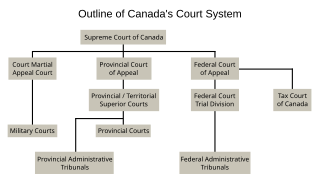
The court system of Canada forms the judicial branch of government, formally known as "the Queen on the Bench", which interprets the law and is made up of many courts differing in levels of legal superiority and separated by jurisdiction. Some of the courts are federal in nature, while others are provincial or territorial.
Section 15 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms contains guaranteed equality rights. As part of the Constitution, the section prohibits certain forms of discrimination perpetrated by the governments of Canada with the exception of ameliorative programs and rights or privileges guaranteed by or under the Constitution of Canada in respect of denominational, separate or dissentient schools.

Freedom of religion in Canada is a constitutionally protected right, allowing believers the freedom to assemble and worship without limitation or interference.

Bliss v Canada (AG) [1979] 1 S.C.R. 183 is a famous Supreme Court of Canada decision on equality rights for women under the Canadian Bill of Rights. The Court held that women were not entitled to benefits denied to them by the Unemployment Insurance Act during a certain period of pregnancy. This case has since become the prime example demonstrating the inadequacies of the Canadian Bill of Rights in protecting individuals' rights. This ruling was eventually overturned in Brooks v. Canada Safeway Ltd., [1989] 1 SCR 1219.
Section 27 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms is a section of the Charter that, as part of a range of provisions within the section 25 to section 31 bloc, helps determine how rights in other sections of the Charter should be interpreted and applied by the courts. It is believed that section 27 "officially recognized" a Canadian value, namely multiculturalism.

Little Sisters Book and Art Emporium v Canada [2000] 2 S.C.R. 1120, 2000 SCC 69 is a leading Supreme Court of Canada decision on freedom of expression and equality rights under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. It was held that the Customs Act, which gave broad powers to customs inspectors to exclude "obscene" materials, violated the right to freedom of expression under section 2 but was justifiable under section 1.

R v Drybones, [1970] S.C.R. 282, is a landmark 6-3 Supreme Court of Canada decision holding that the Canadian Bill of Rights "empowered the courts to strike down federal legislation which offended its dictates." Accordingly, the Supreme Court of Canada held that section 94(b) of the Indian Act is inoperative because it violates section 1(b) of the Canadian Bill of Rights.

Canada (AG) v Lavell, [1974] S.C.R. 1349, was a landmark 5–4 Supreme Court of Canada decision holding that Section 12(1)(b) of the Indian Act did not violate the respondents' right to "equality before the law" under Section 1 (b) of the Canadian Bill of Rights. The two respondents, Lavell and Bédard, had alleged that the impugned section was discriminatory under the Canadian Bill of Rights by virtue of the fact that it deprived Indian women of their status for marrying a non-Indian, but not Indian men.

Women's Legal Education and Action Fund, referred to by the acronym LEAF, is "the only national organization in Canada that exists to ensure the equality rights of women and girls under the law.". Established on April 19, 1985, LEAF was formed in response to the enactment of Section 15 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms to ensure that there was fair and unbiased interpretation of women's Charter rights by the courts. LEAF performs legal research and intervenes in appellate and Supreme Court of Canada cases on women's issues. LEAF has been an intervener in many significant decisions of the Supreme Court of Canada, particularly cases involving section 15 Charter challenges. In addition to its legal work, LEAF also organizes speaking engagements and projects that allow lawyers interested in women's rights to educate one another, to educate the public, and to create collective responses to legal issues related to women's equality. LEAF was created by founding mother Doris Anderson and other women.

Miron v Trudel, [1995] 2 S.C.R. 418 is a famous Supreme Court of Canada decision on equality rights under section 15 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms where the Court found "marital status" was an analogous ground for discrimination. The Court held that an insurance benefit provided only to married couples discriminated against common-law couples.
Tétreault-Gadoury v Canada , [1991] 2 S.C.R. 22 is a leading Supreme Court of Canada decision on the jurisdiction of tribunals to hear Charter challenges. The Court held that the board of referees under unemployment insurance legislation was not able to hear an equality rights challenge for benefits that were denied to the claimant who was over the age of sixty-five.

The Foundation for Equal Families is a Canadian gay and lesbian rights group founded in 1994 following the failure of Bill 167 in the Legislative Assembly of Ontario. The group's mandate is "Dedicated to achieving recognition and equality for same sex relationships and associated family rights through education and legal action". Meeting this mandate was accomplished by intervening in various precedent-setting legal cases, through representation at various pride parades and most notably in suing the Canadian federal government over failure to amend 58 pieces of federal legislation that were charter-infringing due to the definition of spouse.
United States v. Davis, 370 U.S. 65 (1962), is a federal income tax case argued before the United States Supreme Court in 1962, holding that a taxpayer recognizes a gain on the transfer of appreciated property in satisfaction of a legal obligation.
Lucas v. Earl, 281 U.S. 111 (1930), is a United States Supreme Court case concerning U.S. Federal income taxation, about a man who reported only half of his earnings for years 1920 and 1921. Earl C. Guy and his wife had entered into a contract that would potentially save a lot of tax. The contract specified that earnings were owned by the couple as joint tenants. It is unlikely that it was tax-motivated, since there was no income tax in 1901 when they executed the contract. Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. delivered the Court’s opinion which generally stands for the proposition that income from services is taxed to the party who performed the services. The case is used to support the proposition that the substance of the transaction, rather than the form, is controlling for tax purposes.
Tax protester Sixteenth Amendment arguments are assertions that the imposition of the U.S. federal income tax is illegal because the Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which reads "The Congress shall have power to lay and collect taxes on incomes, from whatever source derived, without apportionment among the several States, and without regard to any census or enumeration", was never properly ratified, or that the amendment provides no power to tax income. Proper ratification of the Sixteenth Amendment is disputed by tax protesters who argue that the quoted text of the Amendment differed from the text proposed by Congress, or that Ohio was not a State during ratification. Sixteenth Amendment ratification arguments have been rejected in every court case where they have been raised and have been identified as legally frivolous.
Tax protesters in the United States advance a number of constitutional arguments asserting that the imposition, assessment and collection of the federal income tax violates the United States Constitution. These kinds of arguments, though related to, are distinguished from statutory and administrative arguments, which presuppose the constitutionality of the income tax, as well as from general conspiracy arguments, which are based upon the proposition that the three branches of the federal government are involved together in a deliberate, on-going campaign of deception for the purpose of defrauding individuals or entities of their wealth or profits. Although constitutional challenges to U.S. tax laws are frequently directed towards the validity and effect of the Sixteenth Amendment, assertions that the income tax violates various other provisions of the Constitution have been made as well.




