Related Research Articles

Running is a method of terrestrial locomotion by which humans and other animals move rapidly on foot. Running is a gait with an aerial phase in which all feet are above the ground. This is in contrast to walking, where one foot is always in contact with the ground, the legs are kept mostly straight, and the center of gravity vaults over the stance leg or legs in an inverted pendulum fashion. A feature of a running body from the viewpoint of spring-mass mechanics is that changes in kinetic and potential energy within a stride co-occur, with energy storage accomplished by springy tendons and passive muscle elasticity. The term "running" can refer to a variety of speeds ranging from jogging to sprinting.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula.

Calisthenics or callisthenics is a form of strength training that utilizes an individual's body weight as resistance to perform multi-joint, compound movements with little or no equipment.

In human anatomy, a hamstring is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles between the hip and the knee.

In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
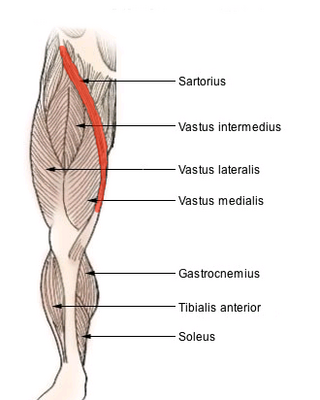
The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment.

The push-up is a common calisthenics exercise beginning from the prone position. By raising and lowering the body using the arms, push-ups exercise the pectoral muscles, triceps, and anterior deltoids, with ancillary benefits to the rest of the deltoids, serratus anterior, coracobrachialis and the midsection as a whole. Push-ups are a basic exercise used in civilian athletic training or physical education and commonly in military physical training. They are also a common form of punishment used in the military, school sport, and some martial arts disciplines. Variations of push-ups, such as wide-arm push-ups, diamond push-ups target specific muscle groups and provide further challenges.

Cock and ball torture (CBT) is a sexual activity involving the application of pain or constriction to the male genitals. This may involve directly painful activities, such as genital piercing, wax play, genital spanking, squeezing, ball-busting, genital flogging, urethral play, tickle torture, erotic electrostimulation, kneeing or kicking. The recipient of such activities may receive direct physical pleasure via masochism, or emotional pleasure through erotic humiliation, or knowledge that the play is pleasing to a sadistic dominant. Many of these practices carry significant health risks.

An isometric exercise is an exercise involving the static contraction of a muscle without any visible movement in the angle of the joint. The term "isometric" combines the Greek words isos (equal) and -metria (measuring), meaning that in these exercises the length of the muscle and the angle of the joint do not change, though contraction strength may be varied. This is in contrast to isotonic contractions, in which the contraction strength does not change, though the muscle length and joint angle do.

In human anatomy, the groin, also known as the inguinal region or iliac region, is the junctional area between the torso and the thigh. The groin is at the front of the body on either side of the pubic tubercle, where the lower part of the abdominal wall meets the thigh. A fold or crease is formed at this junction known as the inguinal groove, or crease. This is also the area of the medial compartment of the thigh that contains attachments of the adductor muscles of the hip or the groin muscles. The groin is the common site for a hernia.
BowFlex, Inc., formerly Nautilus, Inc., located in Vancouver, Washington, United States, is the American worldwide marketer, developer, and manufacturer of fitness equipment brands Bowflex, Schwinn, and JRNY, its adaptive fitness platform. The company changed its corporate name from Nautilus, Inc. to BowFlex, Inc. in 2023. BowFlex Inc. is a publicly traded company listed on the OTC Markets Group as BFXXQ, and formerly on the New York Stock Exchange. The company's products are sold globally to customers through e-commerce, call centers, and retail stores.
The iliotibial tract or iliotibial band is a longitudinal fibrous reinforcement of the fascia lata. The action of the muscles associated with the ITB flex, extend, abduct, and laterally and medially rotate the hip. The ITB contributes to lateral knee stabilization. During knee extension the ITB moves anterior to the lateral condyle of the femur, while ~30 degrees knee flexion, the ITB moves posterior to the lateral condyle. However, it has been suggested that this is only an illusion due to the changing tension in the anterior and posterior fibers during movement. It originates at the anterolateral iliac tubercle portion of the external lip of the iliac crest and inserts at the lateral condyle of the tibia at Gerdy's tubercle. The figure shows only the proximal part of the iliotibial tract.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.
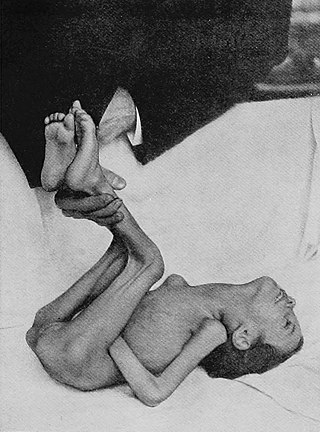
Kernig's sign is a test used in physical examination to look for evidence of irritation of the meninges. The test involves flexing the thighs at the hip, and the knees, at 90 degree angles, and assessing whether subsequent extension of the knee is painful, in which case it is deemed positive. This may indicate subarachnoid haemorrhage or meningitis. Patients may also show opisthotonus—spasm of the whole body that leads to legs and head being bent back and body bowed forward.

A tear of a meniscus is a rupturing of one or more of the fibrocartilage strips in the knee called menisci. When doctors and patients refer to "torn cartilage" in the knee, they actually may be referring to an injury to a meniscus at the top of one of the tibiae. Menisci can be torn during innocuous activities such as walking or squatting. They can also be torn by traumatic force encountered in sports or other forms of physical exertion. The traumatic action is most often a twisting movement at the knee while the leg is bent. In older adults, the meniscus can be damaged following prolonged 'wear and tear'. Especially acute injuries can lead to displaced tears which can cause mechanical symptoms such as clicking, catching, or locking during motion of the joint. The joint will be in pain when in use, but when there is no load, the pain goes away.

The Abdominizer was an abdominal exerciser invented in 1984 by Canadian chiropractor Dennis Colonello and marketed through infomercials by the Fitness Quest corporation of Canton, Ohio, selling around six million. It was designed to protect the lower back during sit-ups.

Suzanne Marie Somers was an American actress, author, and businesswoman. She played the television roles of Chrissy Snow on Three's Company (1977–1981) and Carol Foster Lambert on Step by Step (1991–1998).

Barre is a form of physical exercise, usually conducted in group classes in gyms or specialty studios. It is distinguished from other group fitness activities by its use of the ballet barre and its incorporation of movements derived from ballet. These classical dance movements and positions are combined with those drawn from yoga and pilates, and other equipment is sometimes used in addition to the barre, such as resistance bands, yoga straps, exercise balls and hand weights. Barre classes typically focus on small, pulsing movements with emphasis on form, alignment and core engagement. Participants hold their bodies still while contracting specific, targeted sets of muscles in isometric exercises. Repetitions tend to be high, range-of-motion small, and weights, when used, light. Barre classes focus on the lower body and core, developing strength and flexibility from the ankles up though the calves, knees, thighs, glutes and abdominals. Holding muscles in contraction for extended periods frequently leads to them shaking as they fatigue. This is particularly true of thighs, as the quadriceps tire.

Jacki Sorensen is the American originator of aerobic dancing, popularly known as aerobics. Inspired by Dr. Kenneth H. Cooper's 1968 book on aerobic exercise, she created for women an aerobic dance routine to music in 1969 in Puerto Rico, teaching U.S. Air Force wives. She expanded this concept into a teaching method and studio franchise, Aerobic Dancing Inc., that rose to 1,500 locations and 4,000 instructors teaching 170,000 students in 1981 at its peak.
References
- ↑ Berkman, Meredith (1992-05-22). "Suzanne Somers and the ThighMaster". EW.com. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ↑ O'Neill, Molly (1995-03-29). "Time for a Fitness Pyramid?; After Thigh Master, a Stream of Fitness Gadgets". The New York Times. Retrieved 2010-12-22.
- ↑ "A Meeting Of Behinds With A Thigh Master". Sun Sentinel. March 8, 1995. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ↑ "Advice on fitness gadgets: try to exercise restraint". Orlando Sentinel . 1996-01-26. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ↑ "Suzanne Somers' Thigh Master - As Seen On TV Fitness Products: Do They Work?". Shape Magazine. 2012-10-28. Retrieved 2018-10-27.
- 1 2 Friedlander, Whitney (2009-01-05). "Working out old school: Is it time to pull out the ThighMaster?". The Los Angeles Times . Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ↑ "The Newest ThighMaster Vibrates, Is Finally Useful". Jezebel.com. 24 April 2015. Retrieved 2015-10-22.
- ↑ "Suzanne Somers Says Her Vibrating ThighMaster 'Makes Sex More Enjoyable'". HuffPost. 2015-04-17. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ↑ "Obituary: Dr. Anne Marie Bennstrom Prescott 1928-2018". Idyllwild Town Crier. 28 February 2018. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ↑ "Physical exerciser USD343882S". Google Patents. USPTO. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ↑ T.M. Shine (1993-03-17). "Inventor Of The Thighmaster Stays On The Ball". Orlando Sentinel. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ↑ "O.C. inventor squeezed ThighMaster into American culture". Ocregister.com. 5 December 2013. Retrieved 2015-10-22.
- ↑ "Thigh Master - In Photos: 10 Corny But Effective Cable TV Ads". Forbes. Archived from the original on October 6, 2011. Retrieved 2015-10-22.
- ↑ Voorhees, Don (3 May 2011). The Indispensable Book of Useless Information: Just When You Thought It ... - Don Voorhees. Penguin. ISBN 9781101514795 . Retrieved 2015-10-22.
- ↑ "Debunking 4 Popular Exercise Fads – Advanced Physical Medicine". Advancedphysicalmedicine.org. 2013-02-18. Retrieved 2015-10-22.
- ↑ https://www.entrepreneur.com/growing-a-business/suzanne-somers-explains-how-thighmaster-squeezed-its-way/352389 [ bare URL ]