Related Research Articles

Cyprus, officially called the Republic of Cyprus, is an island nation in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. It is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, and is located south of Turkey; west of Syria; northwest of Lebanon, Israel and Palestine; north of Egypt; and southeast of Greece. Nicosia is the country's capital and largest city.
The Republic of Cyprus is a unitary presidential representative republic, whereby the President of Cyprus is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the parliament. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

The Cyprus dispute, also known as the Cyprus conflict, Cyprus issue, or Cyprus problem, is an ongoing dispute between Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots. Initially, with the occupation of the island by the British Empire from the Ottoman Empire in 1878 and subsequent annexation in 1914, the "Cyprus dispute" was a conflict between the Turkish and Greek islanders.

Northern Cyprus, officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, is a de facto state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recognised only by Turkey, Northern Cyprus is considered by all other states to be part of the Republic of Cyprus.
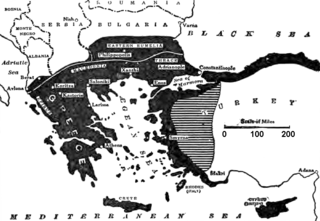
The Megali Idea was an irredentist concept that expressed the goal of reviving the Byzantine Empire, by establishing a Greek state, which would include the large Greek populations that were still under Ottoman rule after the end of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1828) and all the regions that traditionally belonged to Greeks since ancient times.

Enosis is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist concept of a Greek state that dominated Greek politics following the creation of modern Greece in 1830. The Megali Idea called for the annexation of all ethnic Greek lands, parts of which had participated in the Greek War of Independence in the 1820s but were unsuccessful and so remained under foreign rule.

The national flag of Cyprus came into use on 16 August 1960, under the Zurich and London Agreements, whereby a constitution was drafted and Cyprus was proclaimed an independent state. The flag was designed by art teacher İsmet Güney. The design of the flag deliberately employs peaceful and neutral symbols in an attempt to indicate harmony between the Greek and Turkish Cypriot communities, an ideal that has not yet been realised. In 1963, Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot communities separated because of Cypriot intercommunal violence.

A referendum on the Annan Plan was held in the Republic of Cyprus and the non recognized Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus on 24 April 2004. The two communities were asked whether they approved of the fifth revision of the United Nations proposal for reuniting the island, which had been divided since 1974. While it was approved by 65% of Turkish Cypriots, it was rejected by 76% of Greek Cypriots. Turnout for the referendum was high at 89% among Greek Cypriots and 87% among Turkish Cypriots, which was taken as indicative of great interest in the issue on the part of the electorates.
The Annan Plan, also known as the Cyprus reunification plan, was a United Nations proposal to resolve the Cyprus dispute. The different parts of the proposal were based on the argumentation put forward by each party in meetings held under the auspices of the UN. The proposal was to restructure the Republic of Cyprus to become the "United Republic of Cyprus", a federation of two states. It was revised a number of times before it was put to the people of Cyprus in a 2004 referendum, and was supported by 65% of Turkish Cypriots, but only 24% of Greek Cypriots.

Europe, the westernmost portion of Eurasia—is often divided into regions based on geographical, cultural or historical criteria. Many European structures currently exist. Some are cultural, economic, or political; examples include the Council of Europe, the European Broadcasting Union with the Eurovision Song Contest, and the European Olympic Committees with the European Games. Russia dominates the continent by both area and population; spanning roughly 40% of its total landmass, with over 15% of its total population.

This article is about the history of Cyprus from 1878 to the present.

The Turkish invasion of Cyprus, code-named by Turkey as Operation Atilla, was launched on 20 July 1974, following the Cypriot coup d'état on 15 July 1974.

Politics of Northern Cyprus takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the president is head of state and the prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Assembly of the Republic. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

Nicosia International Airport is a largely disused airport located 8.2 km (5.1 mi) west of the Cypriot capital city of Nicosia in the Lakatamia suburb. It was originally the main airport for the island, but commercial activity ceased following the Turkish invasion of Cyprus in 1974. The airport site is now mainly used as the headquarters of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus.

The London and Zürich Agreements for the constitution of Cyprus started with an agreement on the 19 February 1959 in Lancaster House, London, between Turkey, Greece, the United Kingdom and Cypriot community leaders. On that basis, a constitution was drafted and agreed together with two further Treaties of Alliance and Guarantee in Zürich on 11 February 1959.
Cypriot refugees are the Cypriot nationals or Cyprus residents who had their main residence in an area forcibly evacuated during the Cyprus conflict. The government of Cyprus also recognizes as refugees the descendants of the original refugees in the male line regardless of place of birth.
Vodafone Mobile Operations Ltd., doing business as KKTC Telsim, was the first GSM operator in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus. It was granted a licence in August 1995, and started service accepting subscribers on 23 October 1995.

Turkish Cypriots and the European Union have somewhat strained relations because the European Union (EU) does not recognise the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.
Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus, also referred to as Turkish immigrants are a group of mainland Turkish people who have settled in Northern Cyprus since the Turkish invasion in 1974. It is estimated that these settlers and their descendants now make up about half the population of Northern Cyprus. The vast majority of the Turkish settlers were given houses and land that legally belong to Greek Cypriots by the government of Northern Cyprus, who is solely recognised by Turkey. The group is heterogeneous in nature and is composed of various sub-groups, with varying degrees of integration. Mainland Turks are generally considered to be more conservative than the highly secularized Turkish Cypriots, and tend to be more in favor of a two-state Cyprus. However, not all settlers support nationalist policies.
References
- ↑ "Agreements - The Third Vienna Agreement (2 August 1975) - PIO". www.pio.gov.cy. Retrieved 2021-05-22.