Related Research Articles
Shareware is a type of proprietary software that is initially shared by the owner for trial use at little or no cost. Often the software has limited functionality or incomplete documentation until the user sends payment to the software developer. Shareware is often offered as a download from a website. Shareware differs from freeware, which is fully-featured software distributed at no cost to the user but without source code being made available; and free and open-source software, in which the source code is freely available for anyone to inspect and alter.

Roguelike is a style of role-playing game traditionally characterized by a dungeon crawl through procedurally generated levels, turn-based gameplay, grid-based movement, and permanent death of the player character. Most roguelikes are based on a high fantasy narrative, reflecting their influence from tabletop role-playing games such as Dungeons & Dragons.
Ancient Domains of Mystery is a roguelike video game designed and developed by Thomas Biskup and released in 1994. The player's goal is to stop the forces of Chaos that invade the world of Ancardia. The game has been identified as one of the "major roguelikes" by John Harris.

Rogue is a dungeon crawling video game by Michael Toy and Glenn Wichman with later contributions by Ken Arnold. Rogue was originally developed around 1980 for Unix-based minicomputer systems as a freely distributed executable. It was later included in the Berkeley Software Distribution 4.2 operating system (4.2BSD). Commercial ports of the game for a range of personal computers were made by Toy, Wichman, and Jon Lane under the company A.I. Design and financially supported by the Epyx software publishers. Additional ports to modern systems have been made since by other parties using the game's now-open source code.
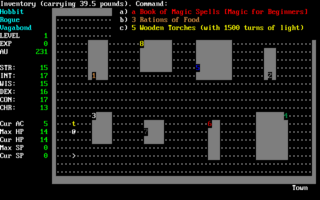
Angband is a dungeon-crawling roguelike video game derived from Umoria. It is based on the writings of J. R. R. Tolkien, in which Angband is the fortress of Morgoth. The current version of Angband is available for all major operating systems, including Unix, Windows, Mac OS X, and Android. It is identified as one of the "major roguelikes" by John Harris. Angband is free and open source game under the GNU GPLv2 or the angband license

curses is a terminal control library for Unix-like systems, enabling the construction of text user interface (TUI) applications.
A software license is a legal instrument governing the use or redistribution of software. Under United States copyright law, all software is copyright protected, in both source code and object code forms, unless that software was developed by the United States Government, in which case it cannot be copyrighted. Authors of copyrighted software can donate their software to the public domain, in which case it is also not covered by copyright and, as a result, cannot be licensed.
Larn is a roguelike computer game written by Noah Morgan in 1986 for the UNIX operating system. Morgan's original version of Larn remains part of the NetBSD games collection.
Mystery Dungeon, known in Japan as Fushigi no Dungeon, is a series of roguelike role-playing video games. Most were developed by Chunsoft, now Spike Chunsoft since the merging in 2012, and select games were developed by other companies with Chunsoft's permission. The series began when co–creator of Dragon Quest, Koichi Nakamura, was inspired by Seiichiro Nagahata's experience with Rogue, who is also a fellow developer from the company, and a desire to create an original series. It began on the Super Famicom, progressing to almost all of Nintendo's and Sony's home and handheld consoles, WonderSwan, Dreamcast, Windows, and mobile devices.

Torneko's Great Adventure: Mystery Dungeon is a 1993 role-playing video game by Chunsoft. The first entry in the Mystery Dungeon series, the game features Torneko, a merchant from Dragon Quest IV, and his adventures around the Mystery Dungeon in search of items.

The Mystery of the Druids is a single-player adventure video game developed by the German company House of Tales and published by cdv Software Entertainment. The game was first released in March 2001 for Microsoft Windows.
Elona is a single-player, roguelike game developed by Japanese developer Noa; it was released in August, 2007.

The Binding of Isaac is a roguelike video game designed by independent developers Edmund McMillen and Florian Himsl. It was released in 2011 for Microsoft Windows, then ported to OS X, and Linux. The game's title and plot are inspired by the Biblical story of the Binding of Isaac. In the game, Isaac's mother receives a message from God demanding the life of her son as proof of her faith, and Isaac, fearing for his life, flees into the monster-filled basement of their home where he must fight to survive. Players control Isaac or one of the 33 other unlockable characters through a procedurally generated dungeon in a roguelike manner, fashioned after those of The Legend of Zelda, defeating monsters in real-time combat while collecting items and power-ups to defeat bosses and eventually Isaac's mother.

Dragon Fin Soup is a role-playing video game created by the independent development studio Grimm Bros. It is the studio's first title and was released on Microsoft Windows, PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3, and PlayStation Vita. It is influenced by roguelike games and uses procedural generation for parts of the game. The game has two modes: Story mode follows a story and is more like a typical role-playing game, while Survival mode skips the story and focuses on the surviving within the game and constrains players with permadeath—once the player character dies, the game must be restarted from the beginning.

Mystery Chronicle: One Way Heroics is a role-playing video game developed by Spike Chunsoft for the PlayStation 4 and PlayStation Vita, released in Japan on July 30, 2015. It is a spin-off of the Mystery Dungeon series, and is based on the indie game One Way Heroics.
A roguelike deck-building game is a hybrid genre of video games that combines the nature of deck-building card games with procedural-generated randomness from roguelike games.
A Soulslike is a subgenre of action role-playing games known for high levels of difficulty and emphasis on environmental storytelling, typically in a dark fantasy setting. It had its origin in Demon's Souls and the Dark Souls series by FromSoftware, the themes and mechanics of which directly inspired several other games. Soulslike games developed by FromSoftware themselves have been specifically referred to as Soulsborne games, a portmanteau of Souls and Bloodborne. The "Soulslike" name has been adopted by a number of critics and developers. However, there have also been questions whether it is a true genre or a collection of shared mechanics.
References
- 1 2 Author Profile: Thomas Biskup reloaded.org
- ↑ Pearson, Dan (2013-01-30). "Where I'm @: A Brief Look At The Resurgence of Roguelikes". GameIndustry.biz . Retrieved 2014-08-30.
- ↑ Smith, Adam (6 June 2014). "Actual Roguelike Alert: Ancient Domains Of Mystery". Rock, Paper, Shotgun . Retrieved 4 May 2015.