
Thomas Boehm (born 21 July 1956 in Gelnhausen) is a German immunologist. He is a Director of the Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg im Breisgau. He has won a variety of prizes for his research work.

Thomas Boehm (born 21 July 1956 in Gelnhausen) is a German immunologist. He is a Director of the Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg im Breisgau. He has won a variety of prizes for his research work.
Boehm completed his medical studies at the Goethe University Frankfurt. He received his doctorate in 1982 and then worked as a research assistant in paediatrics and biochemistry at Frankfurt University Hospital. In 1988 he qualified as a professor of biochemistry. From 1987 to 1991 he was a visiting researcher and then a research associate at the Laboratory of Molecular Biology of Cambridge University. In 1991 he received a professorship at the Albert Ludwigs University of Freiburg and in 1994 a joint professorship at Heidelberg University and the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg. Since 1998 he has been a director at the Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg im Breisgau. [1]
Boehm deals with the evolution of the immune system, the development of the thymus and the relationships between lymphocytes and the interstitium. He was able to achieve groundbreaking advances in the study of the thymus. With the help of comparative studies of different animal species, essential properties of the immune systems of all vertebrates could be identified – in particular the structure of the immune system and the basis of its adaptability. Control mechanisms that cause the maturation and differentiation of immune cells were elucidated in his laboratory. Experiments with the production of artificial thymus glands have also been successful. More recent work deals with the development and function of genetic networks that are required for immune tolerance in antigen detection in vertebrates and invertebrates.
Boehm has been Chairman of the Board of Trustees of the Paul Ehrlich Foundation since 2018.
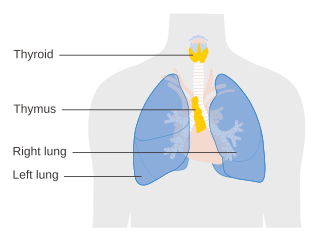
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.

Georges Jean Franz Köhler was a German biologist.
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is a component of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) which works in the immune system to protect the body from invasion in the gut.

The Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize, or Leibniz Prize, is awarded by the German Research Foundation to "exceptional scientists and academics for their outstanding achievements in the field of research". Since 1986, up to ten prizes have been awarded annually to individuals or research groups working at a research institution in Germany or at a German research institution abroad. It is considered the most important research award in Germany.

The Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg, Germany is an interdisciplinary research institute that conducts basic research in modern immunobiology, developmental biology and epigenetics. It was founded in 1961 as the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and is one of 86 institutions of the Max Planck Society. Originally named the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology, it was renamed to its current name in 2010 as it widened its research thrusts to the study of epigenetics.

Forkhead box protein N1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXN1 gene.
Hartmut Wekerle is a German medical scientist and neurobiologist. He is an emeritus director at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology and was the head of the department of Neuroimmunology until 2012.
The Paul Ehrlich and Ludwig Darmstaedter Prize is an annual award bestowed by the Paul Ehrlich Foundation since 1952 for investigations in medicine. It carries a prize money of 120,000 Euro. The prize awarding ceremony is traditionally held on 14 March, the birthday of Nobel laureate Paul Ehrlich, in the St. Paul's Church, Frankfurt am Main.
Gerd Jürgens is a plant developmental biologist and emeritus Director of the Cell Biology Department at the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology and Head of the Center for Plant Molecular Biology (ZMBP) at the Eberhard-Karls Universität Tübingen. He has published extensively in leading journals, including eight papers in the journal Nature as well as various articles in the journals Cell, Science, Journal of Cell Biology and The Plant Journal.

Peter Heinrich Krammer is a German immunologist and one of the directors of The National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT), as well as the head of the Division Immunogenetics at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Heidelberg. Peter H. Krammer is well known for his research and findings in apoptosis. He and his lab members discovered the CD95 receptor and many other molecules involved in signaling through the CD95 receptor.

Max Dale Cooper, is an American immunologist and a professor at the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine and the Emory Vaccine Center of Emory University School of Medicine. He is known for characterizing T cells and B cells.
Jawless vertebrates, which today consist entirely of lampreys and hagfish, have an adaptive immune system similar to that found in jawed vertebrates. The cells of the agnathan AIS have roles roughly equivalent to those of B-cells and T-cells, with three lymphocyte lineages identified so far:

Thomas Jenuwein is a German scientist working in the fields of epigenetics, chromatin biology, gene regulation and genome function.

Hans-Georg Rammensee is a German immunologist and cancer researcher. He has been Chair Professor and Head of the Department of Immunology at the University of Tübingen since 1996. Rammensee has contributed essentially to the research fields of MHC biology and tumor immunology and to the development of cancer immunotherapies.
Davor Solter is a Yugoslavian-born developmental biologist, particularly known for his pioneering work on mammalian genomic imprinting. He is Emeritus Member and Director, Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics; Visiting International Professor, Siriraj Center for Excellence in Stem Cell Research, Mahidol University, Thailand; and Visiting Professor, University of Zagreb Medical School.
Asifa Akhtar is a Pakistani biologist who has made significant contributions to the field of chromosome regulation. She is senior group leader and director of the Department of Chromatin Regulation at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics. Akhtar was awarded EMBO membership in 2013. She became the first international and female vice president of the Max Planck Society's Biology and Medicine Section in July 2020.
Erika L. Pearce is an American immunologist. She is the Bloomberg Distinguished Professor at the Johns Hopkins University after serving as director and a scientific member at Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg, Germany. Her work investigates the connection between metabolism and immune cell function with a particular focus on the regulation of T-cells. In 2018, she was awarded the Leibniz Prize for her "outstanding work in metabolism and inflammation research".
Hedda Wardemann is an immunologist and Professor in the Division of B cell immunology at the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, Germany.

Sucharit Bhakdi is a retired Thai-German microbiologist. In 2020 and 2021 Bhakdi became a prominent source of misinformation about the COVID-19 pandemic, claiming that the pandemic was "fake" and that COVID-19 vaccines were going to decimate the world's population.

Martina Sester is a biologist, Professor of Transplantation and Infection Immunology and Head of Department of the Institute of Infection Medicine at Saarland University Hospital as well as former Vice President for Research and Technology Transfer at Saarland University.