
Jack J. Dongarra ForMemRS; is an American University Distinguished Professor of Computer Science in the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department at the University of Tennessee. He holds the position of a Distinguished Research Staff member in the Computer Science and Mathematics Division at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Turing Fellowship in the School of Mathematics at the University of Manchester, and is an adjunct professor in the Computer Science Department at Rice University. He served as a faculty fellow at Texas A&M University's institute for advanced study (2014–2018). Dongarra is the founding director of Innovative Computing Laboratory.
Michael Thomas Heath is a retired computer scientist who specializes in scientific computing. He is the director of the Center for the Simulation of Advanced Rockets, a Department of Energy-sponsored computing center at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, and the former Fulton Watson Copp Professor of Computer Science at UIUC. Heath was inducted as member of the European Academy of Sciences in 2002, a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery in 2000, and a Fellow of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics in 2010. He also received the 2009 Taylor L. Booth Education Award from IEEE. He became an emeritus professor in 2012.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing or scientific computation (SC), is a rapidly growing field that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex problems. It is an area of science which spans many disciplines, but at its core, it involves the development of models and simulations to understand natural systems.

The Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences is the mathematics research school of New York University (NYU), and is among the most prestigious mathematics schools and mathematical sciences research centers in the world. Founded in 1935, it is named after Richard Courant, one of the founders of the Courant Institute and also a mathematics professor at New York University from 1936 to 1972, and serves as a center for research and advanced training in computer science and mathematics. It is located on Gould Plaza next to the Stern School of Business and the economics department of the College of Arts and Science.
Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) is an academic association dedicated to the use of mathematics in industry. SIAM is the world's largest professional association devoted to applied mathematics, and roughly two-thirds of its membership resides within the United States. Founded in 1951, the organization began holding annual national meetings in 1954, and now hosts conferences, publishes books and scholarly journals, and engages in lobbying in issues of interest to its membership. The focus for the society is applied, computational, and industrial mathematics, and the society often promotes its acronym as "Science and Industry Advance with Mathematics". Members include engineers, scientists, and mathematicians, both those employed in academia and those working in industry. The society supports educational institutions promoting applied mathematics.
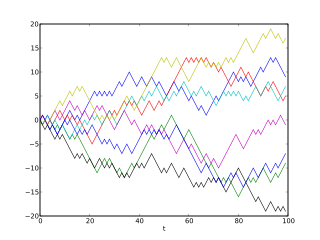
Computational finance is a branch of applied computer science that deals with problems of practical interest in finance. Some slightly different definitions are the study of data and algorithms currently used in finance and the mathematics of computer programs that realize financial models or systems.

Eduardo Daniel Sontag is an American mathematician, and Distinguished University Professor at Northeastern University, who works in the fields control theory, dynamical systems, systems molecular biology, cancer and immunology, theoretical computer science, neural networks, and computational biology.
A masters degree in quantitative finance concerns the application of mathematical methods to the solution of problems in financial economics. There are several like-titled degrees which may further focus on financial engineering, financial risk management, computational finance and/or mathematical finance.

Computational science and engineering (CSE) is a relatively new discipline that deals with the development and application of computational models and simulations, often coupled with high-performance computing, to solve complex physical problems arising in engineering analysis and design as well as natural phenomena. CSE has been described as the "third mode of discovery".

Kurt Mehlhorn is a German theoretical computer scientist. He has been a vice president of the Max Planck Society and is director of the Max Planck Institute for Computer Science.

Scott Joel Aaronson is an American theoretical computer scientist and David J. Bruton Jr. Centennial Professor of Computer Science at the University of Texas at Austin. His primary areas of research are quantum computing and computational complexity theory.
Mohammed Yousuff Hussaini is an Indian born American applied mathematician. He is the Sir James Lighthill Professor of Mathematics and Computational Science & Engineering at the Florida State University, United States. Hussaini is also the holder of the TMC Eminent Scholar Chair in High Performance Computing at FSU. He is widely known for his research in scientific computation, particularly in the field of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and Control and optimization. Hussaini co-authored the popular book Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics with Claudio Canuto, Alfio Quarteroni, and Thomas Zang. He is the editor-in-chief of the journal Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics.

Applied mathematics is the application of mathematical methods by different fields such as physics, engineering, medicine, biology, finance, business, computer science, and industry. Thus, applied mathematics is a combination of mathematical science and specialized knowledge. The term "applied mathematics" also describes the professional specialty in which mathematicians work on practical problems by formulating and studying mathematical models.
Quantitative analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods in finance and investment management. Those working in the field are quantitative analysts (quants). Quants tend to specialize in specific areas which may include derivative structuring or pricing, risk management, algorithmic trading and investment management. The occupation is similar to those in industrial mathematics in other industries. The process usually consists of searching vast databases for patterns, such as correlations among liquid assets or price-movement patterns. The resulting strategies may involve high-frequency trading.
Michele Mosca is co-founder and deputy director of the Institute for Quantum Computing at the University of Waterloo, researcher and founding member of the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, and professor of mathematics in the department of Combinatorics & Optimization at the University of Waterloo. He has held a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Quantum Computation since January 2002, and has been a scholar for the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research since September 2003. Mosca's principal research interests concern the design of quantum algorithms, but he is also known for his early work on NMR quantum computation together with Jonathan A. Jones.
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling of financial markets. See Quantitative analyst.
Robert B. Schnabel is an American computer scientist, and is executive director and CEO of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), a position he has held since November 1, 2015.

Haesun Park is a professor and chair of Computational Science and Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology. She is an IEEE Fellow, ACM Fellow, and Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics Fellow. Park's main areas of research are Numerical Algorithms, Data Analysis, Visual Analytics and Parallel Computing. She has co-authored over 100 articles in peer-reviewed journals and conferences.
Donald Goldfarb is an American mathematician, best known for his works in mathematical optimization and numerical analysis.

Yuying Li is a Chinese-Canadian professor of computer science in the David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science at the University of Waterloo in Canada. Her research interests include mathematical optimization, scientific computing, data mining, and tail risk in computational finance.










