Related Research Articles

A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.

Thomas Guide is a series of paperback, spiral-bound atlases featuring detailed street maps of various large metropolitan areas in the United States, including Boise, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Oakland, Phoenix, Portland, Reno-Tahoe, Sacramento, San Francisco, Seattle, Tucson, and Baltimore-Washington metropolitan area. Road Atlas titles are Arizona including Las Vegas, California Including portions of Nevada, and Pacific Northwest covering Washington, Oregon, Western Idaho, Southwestern British Columbia. The map books are usually arranged by county; for example, separate Thomas Guides have been published for Los Angeles County and San Diego County. There are also guides that will have two or three counties combined, or guides that cover a metropolitan area. Each guide has a detailed index of streets and points of interest, as well as arterial maps for easy page location.

The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all degree levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields. It is one of the world's largest scientific societies by membership. The ACS is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Its headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., and it has a large concentration of staff in Columbus, Ohio.
The National Topographic System or NTS is the system used by Natural Resources Canada for providing general purpose topographic maps of the country. NTS maps are available in a variety of scales, the standard being 1:50,000 and 1:250,000 scales. The maps provide details on landforms and terrain, lakes and rivers, forested areas, administrative zones, populated areas, roads and railways, as well as other human-made features. These maps are currently used by all levels of government and industry for forest fire and flood control, depiction of crop areas, right-of-way, real estate planning, development of natural resources and highway planning. To add context, land area outside Canada is depicted on the 1:250,000 maps, but not on the 1:50,000 maps.
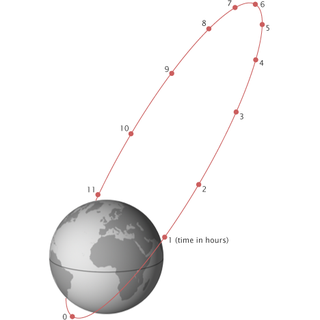
A Molniya orbit is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with an inclination of 63.4 degrees, an argument of perigee of 270 degrees, and an orbital period of approximately half a sidereal day. The name comes from the Molniya satellites, a series of Soviet/Russian civilian and military communications satellites which have used this type of orbit since the mid-1960s. A variation on the Molniya orbit is the so-called Three Apogee (TAP) orbit, whose period is a third of a sidereal day.

In geography and geodesy, a meridian is the locus connecting points of equal longitude, which is the angle east or west of a given prime meridian. In other words, it is a line of longitude. The position of a point along the meridian is given by that longitude and its latitude, measured in angular degrees north or south of the Equator. On a Mercator projection or on a Gall-Peters projection, each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitude. A meridian is half of a great circle on Earth's surface. The length of a meridian on a modern ellipsoid model of Earth has been estimated as 20,003.93 km (12,429.87 mi).

Benjamin Apthorp Gould was a pioneering American astronomer. He is noted for creating the Astronomical Journal, discovering the Gould Belt, and for founding of the Argentine National Observatory and the Argentine National Weather Service.

Argo is an international programme for researching the ocean. It uses profiling floats to observe temperature, salinity and currents. Recently it has observed bio-optical properties in the Earth's oceans. It has been operating since the early 2000s. The real-time data it provides support climate and oceanographic research. A special research interest is to quantify the ocean heat content (OHC). The Argo fleet consists of almost 4000 drifting "Argo floats" deployed worldwide. Each float weighs 20–30 kg. In most cases probes drift at a depth of 1000 metres. Experts call this the parking depth. Every 10 days, by changing their buoyancy, they dive to a depth of 2000 metres and then move to the sea-surface. As they move they measure conductivity and temperature profiles as well as pressure. Scientists calculate salinity and density from these measurements. Seawater density is important in determining large-scale motions in the ocean.

Astrology software is a type of computer programs designed to calculate horoscopes. Many of them also assemble interpretive text into narrative reports.

The tz database is a collaborative compilation of information about the world's time zones and rules for observing daylight saving time, primarily intended for use with computer programs and operating systems. Paul Eggert has been its editor and maintainer since 2005, with the organizational backing of ICANN. The tz database is also known as tzdata, the zoneinfo database or the IANA time zone database, and occasionally as the Olson database, referring to the founding contributor, Arthur David Olson.

The San Diego Natural History Museum is a museum in Balboa Park in San Diego, California. It was founded in 1874 as the San Diego Society of Natural History. It is the second oldest scientific institution west of the Mississippi and the oldest in Southern California. The present location of the museum was dedicated on January 14, 1933. A major addition to the museum was dedicated in April 2001, doubling exhibit space.
UTC−00:44 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −00:44.
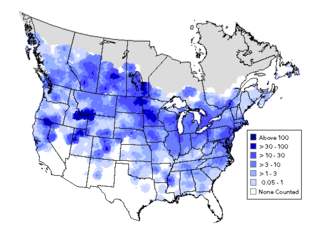
A bird atlas is an ornithological work that attempts to provide information on the distribution, abundance, long-term change as well as seasonal patterns of bird occurrence and make extensive use of maps. They often involve a large numbers of volunteers to cover a wide geographic area and the methods used are standardized so that the studies can be continued in the future and the results remain comparable. In some cases the species covered may be restricted to those that breed or are resident. Migration atlases on the other hand cover migratory birds depict maps showing summaries of ringing and recoveries.

The Rose Canyon Fault is a right-lateral strike-slip fault that runs in a north–south direction off the coast of San Diego County, California until it comes ashore near downtown San Diego. The fault is linked to the Newport–Inglewood Fault (NIFZ) in the north and either the Agua Blanca Fault or San Miguel–Vallecitos Fault Zone in the south via en echelon step overs. Conservative estimates of the fault place the length around 30–50 km (19–31 mi), while interpretations including the NIFZ place the length at 170 km (110 mi). There are not many earthquakes associated with the fault, however a magnitude 6–6.5 may have struck on the fault in 1862. The fault runs very near to populated areas when offshore, hence there is high potential for infrequent large and damaging earthquakes.
Coteau Bourgeois is an unincorporated community in Livingston Parish, Louisiana, United States. The community is located 5 miles southeast of French Settlement and 8 miles west of Sorrento. The site is on Louisiana Highway 22 and is one mile south of Head of Island on the Amite River.
Horse Bluff Landing is an unincorporated community in Livingston Parish, Louisiana, United States. The community is located less than 3 miles west of Killian and 5 miles northeast of Maurepas on the bank of Tickfaw River. The Tickfaw State Park is located 1 mile to the northwest across the Tickfaw River.
Coleman Town is an unincorporated community in St. Helena Parish, Louisiana, United States. The community is located less than 2 miles southwest of Chipola and 9 miles northwest of Greensburg.
Kedron is an unincorporated community in St. Helena Parish, Louisiana, United States. The community is located less than 4 miles northwest of Amite City and 3 miles west of Roseland.

Time in Liberia is given by a single time zone, denoted as Greenwich Mean Time. Liberia shares this time zone with several other countries, including fourteen in western Africa where it was formerly known as Western Sahara Standard Time (WSST). Liberia has never observed daylight saving time (DST).
References
- ↑ "Shanks, Thomas". Astro-Databank.
- ↑ The American Atlas: US latitudes and longitudes, time changes, and time zones, San Diego 1978, ACS publications
- ↑ The International Atlas: World latitudes, longitudes, and time changes, San Diego 1985, ACS publications