
Thomas Harrison (c. 1823-1894) was the first Government Surveyor of Jamaica. His maps have become an important historical resource for the island. [1]
He was apprenticed to Edward McGeachy. [2]

Thomas Harrison (c. 1823-1894) was the first Government Surveyor of Jamaica. His maps have become an important historical resource for the island. [1]
He was apprenticed to Edward McGeachy. [2]
Richmond is a market town in Saint Mary parish, in the north-east of Jamaica.

The parishes of Jamaica are the main units of local government in Jamaica. They were created following the English Invasion of Jamaica in 1655. This administrative structure for the Colony of Jamaica developed slowly. However, since 1 May 1867 Jamaica has been divided into the current fourteen parishes. These were retained after independence in 1962. They are grouped into three historic counties, which no longer have any administrative relevance. Every parish has a coast; none are landlocked.
Sabina Park is a cricket ground and the home of the Kingston Cricket Club, and is the only Test cricket ground in Kingston, Jamaica.

The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India. It was founded in 1851, is a Government of India Ministry of Mines organisation, one of the oldest of such organisations in the world and the second oldest survey in India after Survey of India, for conducting geological surveys and studies of India, and also as the prime provider of basic earth science information to government, industry and general public, as well as the official participant in steel, coal, metals, cement, power industries and international geoscientific forums.

The John Crow Mountains are a range of mountains in Jamaica. They extend parallel with the north east coast of the island, bounded to the west by the banks of the Rio Grande, and joining with the eastern end of the Blue Mountains in the southeast. The highest point in the range is a little over 3,750 feet (1,140 m).

Charles Rose Ellis, 1st Baron Seaford was a British politician.

Barking Lodge is a small village in the parish of Saint Thomas close to the south-east coast of Jamaica.
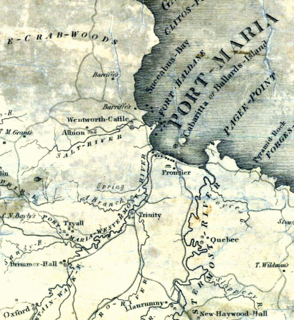
The Otram River, formerly the Port Maria River or the Port Maria Western River, is a river in Saint Mary Parish, Jamaica. It reaches the sea in the parish capital of Port Maria and contributes to flooding in that town.
The Cartography of Jamaica is the history of surveying and creation of maps of Jamaica. A list of maps of Jamaica in chronological order is shown below.

Golden Grove is a settlement in the parish of Saint Thomas, Jamaica. Historically a sugar plantation, it had a population of 3,057 in 2009.

Williamsfield is a settlement in Manchester Parish Jamaica.
George Gauld (1731–1782) was a British military engineer, artist, cartographer, geographer and surveyor.

Cross Roads is a primarily commercial neighbourhood of Kingston, Jamaica. It is centered on the intersection of five major roads: Slipe Road, Half Way Tree Road, Old Hope Road, Caledonia Avenue and Marescaux Road.
Robert Charles Dallas was a Jamaican-born British poet and conservative writer. He is known also for a contentious book on Lord Byron, and a history of the Second Maroon War.
Barry William Higman is a retired Australian historian of Caribbean studies who primarily taught at the University of the West Indies from 1971 to 1996. During his career, Higman wrote multiple books including the 1977 Bancroft Prize winning work Slave Population and Economy in Jamaica, 1807-1834 before his retirement from academics in 2014. Higman was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship in 1987 and the Musgrave Medal in 1992.

Albion was a sugar plantation in Saint David Parish, Jamaica. Created during or before the 18th century, it had at least 451 slaves when slavery was abolished in the British Empire in 1833. By the end of the 19th-century it was the most productive plantation in Jamaica due to the advanced refining technology it used. By the early 20th century, however, its cane sugar could not compete with cheaper European beet sugar, and it produced its last sugar crop in 1928. It subsequently became a banana farm for the United Fruit Company.
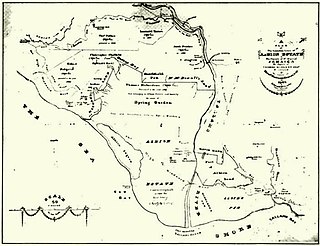
Edward McGeachy was the Crown Surveyor for the county of Surrey in Jamaica. He trained Thomas Harrison, the first Government Surveyor of Jamaica. He owned Bull Park plantation and Brighton Pen in Saint David Parish and in 1837 received compensation for the loss of eight slaves following the abolition of slavery in the British Empire in 1833.
The Act for Regulating Surveyors of 1683 was a law of the Colony of Jamaica that provided that the Crown surveyor was to be responsible for surveys in Jamaica only when the Crown was a party to the relevant matter and that otherwise, any person may make a survey. It was revised by An Act For Further Directing and Regulating the Proceedings of Surveys in the same year. The acts were significant due to the importance of surveys in the functioning of the plantation economy of the colony.

Frontier Estate was a sugar plantation located in Port Maria, Jamaica. The estate covered 1.415 acres which were worked by 325 enslaved Africans in 1832. Following emancipation in 1834, the formerly enslaved Africans were obliged to remain on the plantations as "apprentices", whereby the worked as before for three-quarters of their time, but were free to sell their labour outside these hours. Originally planned to last eight years, public pressure brought these "apprenticeships" to an end in 1838. At this time there were 268 "apprentices".

Saint Vincent and the Grenadines–Turkey relations are foreign relations between Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Turkey.
![]() Media related to Thomas Harrison (surveyor) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Thomas Harrison (surveyor) at Wikimedia Commons
| | This Jamaican biographical article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |