
John Claggett Danforth is an American politician, attorney, diplomat, and Episcopal priest who served as the Attorney General of Missouri from 1969 to 1976 and as a United States Senator from 1976 to 1995. A member of the Republican Party, he later served as Special Counsel for the U.S. Department of Justice from 1999 to 2000 and as the United States Ambassador to the United Nations from 2004 to 2005.

The Tariff Act of 1930, commonly known as the Smoot–Hawley Tariff or Hawley–Smoot Tariff, was a law that implemented protectionist trade policies in the United States. Sponsored by Senator Reed Smoot and Representative Willis C. Hawley, it was signed by President Herbert Hoover on June 17, 1930. The act raised US tariffs on over 20,000 imported goods.
Paleoconservatism is a political philosophy and a paternalistic strain of conservatism in the United States stressing American nationalism, Christian ethics, regionalism, traditionalist conservatism, and non-interventionism. Paleoconservatism's concerns overlap with those of the Old Right that opposed the New Deal in the 1930s and 1940s as well as with paleolibertarianism. By the start of the 21st century, the movement had begun to focus more on issues of race.

The 15th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in the Old Brick Capitol in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1817, to March 4, 1819, during the first two years of James Monroe's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1810 United States census. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority.

Willis Chatman Hawley was an American politician and educator in the state of Oregon. A native of the state, he would serve as president of Willamette University in Salem, Oregon, where he earned his undergraduate and law degrees before entering politics. A Republican, he served 13 terms as a member of the United States House of Representatives from Oregon from 1907 to 1933. He is best known as a lead sponsor of the Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act in 1930.

Desmond Sandford "Sandy" Hawley, is a Canadian Hall of Fame jockey.

Broadway Stores, Inc., was an American retailer based in Southern California. Known through its history as Carter Hawley Hale Stores and Broadway Hale Stores over time, it acquired other retail store chains in regions outside its California home base and became in certain retail sectors a regional and national retailer in the 1970s and 1980s. The company was able to survive takeover attempts in 1984 and 1986, and also a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in 1991 by selling off most of its assets until August 1995 when its banks refused to advance enough additional credit in order for the company to be able to pay off suppliers. At that point, the company sold itself to Federated Department Stores for $1.6 billion with the acquisition being completed on October 12, 1995.

The 71st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislature of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1929, to March 4, 1931, during the first two years of Herbert Hoover's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1910 United States census.

Joseph Roswell Hawley was the 42nd Governor of Connecticut, a U.S. politician in the Republican and Free Soil parties, a Civil War general, and a journalist and newspaper editor. He served two terms in the United States House of Representatives and was a four-term U.S. Senator.

The 53rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1893, to March 4, 1895, during the first two years of Grover Cleveland's second presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1890 United States census.

The 42nd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1871, to March 4, 1873, during the third and fourth years of Ulysses S. Grant's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1860 United States census. Both chambers had a Republican majority.

The 49th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1885, to March 4, 1887, during the first two years of Grover Cleveland's first presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1880 United States census. The Senate had a Republican majority, and the House had a Democratic majority.

Thomas Hawley was a long-serving officer of arms at the College of Arms in London. He began his career of royal service as a groom porter to Queen Margaret of Scotland from her marriage in 1503 until 1508. Although he may have been made Rose Blanche Pursuivant in the reign of King Henry VII, his first permanent heraldic appointment came in 1509.

The 1876 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Cincinnati, Ohio on June 14–16, 1876. President Ulysses S. Grant had considered seeking a third term, but with various scandals, a poor economy and heavy Democratic gains in the House of Representatives that led many Republicans to repudiate him, he declined to run. The convention resulted in the nomination of Governor Rutherford B. Hayes of Ohio for president and Representative William A. Wheeler of New York for vice president.

The 1884 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Chicago, on June 3–6, 1884. It resulted in the nomination of former House Speaker James G. Blaine from Maine for president and Senator John A. Logan of Illinois for vice president. The ticket lost in the election of 1884 to Democrats Grover Cleveland and Thomas A. Hendricks.
Hawley House may refer to:

The 2016 Missouri Attorney General election was held on November 8, 2016, to elect the Attorney General of Missouri, concurrently with the 2016 U.S. presidential election, as well as elections to the United States Senate and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Republican Josh Hawley defeated the Democratic nominee Teresa Hensley.

Joshua David Hawley is an American politician and lawyer serving as the senior United States senator from Missouri, a seat he has held since 2019. A member of the Republican Party, Hawley served as the 42nd attorney general of Missouri from 2017 to 2019, before defeating two-term incumbent Democratic senator Claire McCaskill in the 2018 election and winning reelection in 2024.
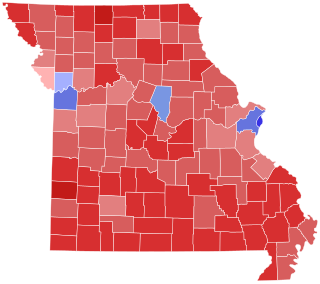
The 2018 United States Senate election in Missouri took place on November 6, 2018, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Missouri, concurrently with other elections to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives, and various state and local elections, including Missouri's quadrennial State Auditor election.














