Related Research Articles
The Southeastern Anatolia Project is a multi-sector integrated regional development project based on the concept of sustainable development for the 9 million people (2005) living in the Southeastern Anatolia region of Turkey. GAP's basic aim is to eliminate regional development disparities by raising incomes and living standards and to contribute to the national development targets of social stability and economic growth by enhancing the productive and employment generating capacity of the rural sector. The total cost of the project is over 100 billion Turkish lira (TL), of which 30.6 billion TL of this investment was realized at the end of 2010. The real investment was 72.6% for the end of 2010. The project area covers nine provinces which are located in the basins of the Euphrates and Tigris and in Upper Mesopotamia.

The Lesotho Highlands Water Project (LHWP) is an ongoing water supply project with a hydropower component, developed in partnership between the governments of Lesotho and South Africa. It comprises a system of several large dams and tunnels throughout Lesotho and delivers water to the Vaal River System in South Africa. In Lesotho, it involves the rivers Malibamatso, Matsoku, Senqunyane, and Senqu. It is Africa's largest water transfer scheme.
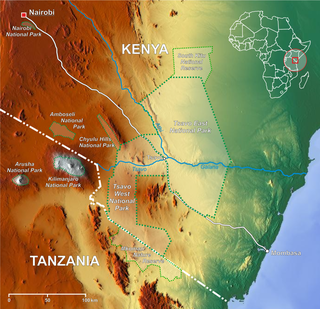
The Athi-Galana-Sabaki River is the second longest river in Kenya. It has a total length of 390 kilometres (240 mi), and drains an area of 70,000 square kilometres (27,000 sq mi). The river rises in the Gatamaiyo Forest as the Athi River and enters the Indian Ocean as the Galana River.

The Nairobi River is a river that flows across Nairobi, the capital city of Kenya. It is the main river of the Nairobi River Basin, with several parallel streams flowing eastward. All of the Nairobi basin rivers join east of Nairobi and meet the Athi River, which eventually flows into the Indian Ocean. The rivers are mostly narrow and highly polluted, though recent efforts to clean the rivers have improved water quality.

The Jin River is a river of Sichuan, China. It flows through the provincial capital of Chengdu. It consists of three parts: the Fu River, an extension of the Fu River. The Jin River has a long and complex cultural history, dating back to 256 BC when it was formed. Over the course of several dynasties, the Jin River has been has been given different names by the ruler in power at the time. Flowing the provincial capital of Chengdu city, the river historically provided a source for irrigation, boat travel, and a means to dispose of wastewater. As the cities’ population increased, pollution of the river became a major environmental concern leading to regulation projects beginning in 1993. The current ecological state of the river is degraded as it is overloaded with dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus inputs from urban sources. Alongside the riverbank of the Jin River, theme parks were built and numerous tourism programs were created.

The Tummel hydro-electric power scheme is an interconnected network of dams, power stations, aqueducts and electric power transmission in the Grampian Mountains of Scotland. Roughly bounded by Dalwhinnie in the north, Rannoch Moor in the west and Pitlochry in the east it comprises a water catchment area of around 1,800 square kilometres (690 sq mi) and primary water storage at Loch Ericht, Loch Errochty, Loch Rannoch and Loch Tummel, in Perth and Kinross. Water, depending on where it originates and the path it takes, may pass through as many as five of the schemes nine power stations as it progresses from north-west to south-east. The scheme was constructed in the 1940s and 50s incorporating some earlier sites. It is currently managed by SSE plc.

The Wudongde Dam is a large hydroelectric dam on the Jinsha River, an upper stretch of Yangtze River in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces, southwest China.

Sholayar Dam is a concrete dam built across the Chalakkudi River in Valparai in Coimbatore District,Tamil Nadu of India. The dam consists of main Sholayar Dam, Sholayar Flanking and Sholayar Saddle Dam. It also contains Sholayar Hydro Electric Power Project of TNPWD who owns the dam. Total installed capacity of the project is 54MW with 3 penstock pipes. The maximum storage capacity is 2663 feet. Sholayar is 65 km from Chalakudy town. The dam above Sholayar dam was Upper Solaiyar Dam owned by Tamil Nadu.
North Carolina Land and Water Fund (NCLWF) was created by the North Carolina General Assembly in 1996 as the 'Clean Water Management Trust Fund'. The Fund is an independent non-regulatory agency housed in the Division of Land and Water Stewardship in the North Carolina Department of Natural and Cultural Resources. The special revenue fund was created "to clean up pollution in the State's surface waters and to protect and conserve those waters that are not yet polluted. The intent of the fund is "to focus on the cleanup and prevention of pollution of the State's surface waters, the establishment of a network of riparian buffers and greenways, and the preservation of property for establishing clean water supplies, the General Assembly believes that the results of these efforts will also be beneficial to wildlife and marine fisheries habitats." NCLWF issues grants to a variety of entities including local governments, state agencies and nonprofit corporations "whose primary purpose is the conservation, preservation, and restoration of our State's environmental and natural resources".
The Hantangang Dam is a gravity dam on the Hantan River in Yeoncheon County, Gyeonggi Province, South Korea. Construction on the dam began in 2007 and completed in 2015. The primary purpose of the dam is flood control : it was proposed in 1998 after a series of floods in the late 1990s that killed 128 people, displaced over 31,000 and caused about US$900 million in property damage. Initially designed as a multi-purpose project, the design was changed solely to flood control in 2006 due to the concerns of residents upstream. It is being implemented by Korea Water Resources Corporation (K-water).
Pacheco Reservoir is a man-made reservoir in the Diablo Range in California, U.S.A. The lake is formed by a dam on the north fork of Pacheco Creek, whose waters reach Monterey Bay by way of the Pajaro River. The Pacheco Pass Water District is currently responsible for operation and maintenance of the Pacheco Reservoir. Located north of State Route 152 in eastern Santa Clara County, the lake is about an hour's drive from downtown San Jose.

The climate in Texas is changing partially due to global warming and rising trends in greenhouse gas emissions. As of 2016, most area of Texas had already warmed by 1.5 °F (0.83 °C) since the previous century because of greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and other countries. Texas is expected to experience a wide range of environmental impacts from climate change in the United States, including rising sea levels, more frequent extreme weather events, and increasing pressure on water resources.

Aruvikkara Dam is located in Aruvikkara in Thiruvananthapuram District, Kerala. This Gravity and Masonry dam was built across the Karamana River and was completed in 1972 is used for irrigation and supplying drinking water to the city of Thiruvananthapuram. The Aruvikkara dam project came up in the 1930s and has been supported by the Peppara dam built in 1983. The height of the dam is 14.01 meters and the length is 83.21 meters. The Aruvikkara Dam meets the irrigation needs of Thiruvananthapuram. The reservoir is also one of the water tourism sites in Kerala.

Pampa Dam is a dam built on the river Pampa in the Ranni forest area of Seethathodu Grama Panchayat in Pathanamthitta district of Kerala. It was built in 1967 as part of the Sabarigiri Hydroelectric Project. Sabarigiri Hydro Electric Project (IHEP) is the second largest hydro electric project in Kerala. Pampa dam's reservoir is connected to the nearby Kaki Dam's reservoir by a 3.21 km long underground tunnel. The dam is 281 m long and 57.2 m high and is located at an elevation of 981.45 m above sea level. The dam is located in a forest area adjacent to the Periyar National Park. The water stored in the Pampa and Kaki dams is conveyed to the Sabarigiri powerhouse through penstock pipes. The dam was commissioned in 1967.

Veluthodu dam is a part of Kakkad Hydro Electric Project and is located in Seethathode panchayath of Ranni Taluk in Pathanamthitta District of Kerala, India. Its a Concrete-Gravity dam built across the Veluthodu river, a tributary of Kakkad River which is again a tributary of Pamba River The dam is built primarily for electricity. This diversion dam diverts water to the water conductor system from Moozhiyar reservoir to Kakkad Power Station. This power station utilises the tail race water from Sabarigiri power station and flow received from moozhiyar and velluthode rivers. After power generation, water from Kakkad power station is released to the Kakkad River. Taluks through which release flow are Ranni, Konni, Kozhencherry, Thiruvalla, Chengannur, Kuttanadu, Mavelikara and Karthikappally It is operated by Kerala State Electricity Board.
Ondiri Wetland or Ondiri Swamp is a protected wetland and peatbog that is the source of the Nairobi River near Kikuyu, Kenya in Kiambu County. The wetland is under pressure because of water extraction, deforestation and accelerated erosion. Listed in 2021, the project's conservation is part of a larger initiative by the Kenyan government to reduce pollution to major waterways that provide water supply to Nairobi as part of the Thwake Dam project. The waterway is also important for local greenhouse agriculture. Ondiri Wetland covers 3,713,549 square feet and is a source to 40 springs, which provide water to the local community.

R. A. Headworks or Ramaswamy Aiyar Headworks is a masonry type weir situated in Munnar panchayath of Munnar village in Idukki district of Kerala, India impounding mudirapuzha river. It is also called as Munnar Headworks. It is a part of Pallivasal Hydro Electric Project, the first hydro power project of Kerala State. There are two dams and one diversion weir as part of this project. These are Kundala Dam, Maduppetty Dam and R. A. Head works.

Perunthenaruvi Weir is a divertion dam built across Pamba river at villages of Naranammoozhi and Vechoochira in Pathanamthitta District of Kerala, India. Perumthenaruvi SHEP 6 MW (2×3) is a run- of- the- river scheme in river Pamba, and the weir is a part of this scheme. This envisages the utilization of water from 442 Km catchment of Pamba and Azhutha river for electricity generation under a net head of 18.00 m. The power house is located on the left bank of Pamba river. The weir is a concrete gravity type with a height of 10.93 metres (35.9 ft) and a length of 227.50 metres (746.4 ft).

Upper moozhiyar dam is an Earthen Dam constructed across Moozhiyar River in Seethathodu village of Pathanamthitta district in Kerala, India. This dam was constructed as a part of Sabarigiri Augmentation Scheme. The stream is located in southern side of Kakki reservoir. It is an embankment structure. Sabarigiri Hydro Electric Project is the second largest hydro electric project of Kerala and is located in Pathanamthitta district. This dam is constructed for diverting the upper reaches of Moozhiyar river, a tributory of Pamba river to the Kakki -Anathode reservoir through a tunnel. The surplus over the storage flows over the rock cut spillway to Moozhiyar river. Taluks through which release flow are Ranni, Konni, Kozhencherry, Thiruvalla, Chengannur, Kuttanadu, Mavelikara, and Karthikappally. Nearest city is Vandiperiyar.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Otieno, Jullias. "Uhuru: Thwake Dam construction will be complete by June next year". The Star. Retrieved 2021-07-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 "Thwake Multi-purpose Dam project timeline and all you need to know". Construction Review Online. 2021-07-13. Retrieved 2021-07-27.
- 1 2 3 Koech, Gilbert (25 October 2020). "Nema shifts focus to Athi after Nairobi River cleaned up". The Star. Retrieved 2021-07-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Kenya - Thwake Multi-purpose Water Development Program – Phase I". projectsportal.afdb.org. Retrieved 2021-07-27.
- ↑ "Sh81b Thwake Dam project water 'unfit for human use'". People Daily. 2021-06-30. Retrieved 2021-07-27.