
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamily Apoidea. They are currently considered a clade, called Anthophila. There are over 20,000 known species of bees in seven recognized biological families. Some species – including honey bees, bumblebees, and stingless bees – live socially in colonies while most species (>90%) – including mason bees, carpenter bees, leafcutter bees, and sweat bees – are solitary.

A honey bee is a eusocial flying insect within the genus Apis of the bee clade, all native to mainland Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America, North America, and Australia.
Beekeeping is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in artificial beehives. Honey bees in the genus Apis are the most commonly kept species but other honey producing bees such as Melipona stingless bees are also kept. Beekeepers keep bees to collect honey and other products of the hive: beeswax, propolis, bee pollen, and royal jelly. Other sources of beekeeping income include pollination of crops, raising queens, and production of package bees for sale. Bee hives are kept in an apiary or "bee yard".

A drone is a male bee. Unlike the female worker bee, a drone has no stinger. He does not gather nectar or pollen and cannot feed without assistance from worker bees. His only role is to mate with a maiden queen in nuptial flight.
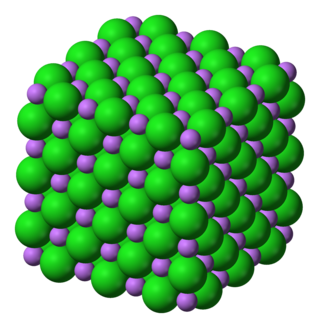
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula LiCl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorides, such as extraordinary solubility in polar solvents (83.05 g/100 mL of water at 20 °C) and its hygroscopic properties.

In beekeeping, a Langstroth hive is any vertically modular beehive that has the key features of vertically hung frames, a bottom board with entrance for the bees, boxes containing frames for brood and honey and an inner cover and top cap to provide weather protection. In a Langstroth hive, the bees build honeycomb into frames, which can be moved with ease. The frames are designed to prevent bees from attaching honeycombs where they would either connect adjacent frames, or connect frames to the walls of the hive. The movable frames allow the beekeeper to manage the bees in a way which was formerly impossible.

A hive frame or honey frame is a structural element in a beehive that holds the honeycomb or brood comb within the hive enclosure or box. The hive frame is a key part of the modern movable-comb hive. It can be removed in order to inspect the bees for disease or to extract the excess honey.

Varroa destructor, the Varroa mite, is an external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on honey bees and is one of the most damaging honey bee pests in the world. A significant mite infestation leads to the death of a honey bee colony, usually in the late autumn through early spring. Without management for Varroa mite, honey bee colonies typically collapse within 2 to 3 years in temperate climates. These mites can infest Apis mellifera, the western honey bee, and Apis cerana, the Asian honey bee. Due to very similar physical characteristics, this species was thought to be the closely related Varroa jacobsoni prior to 2000, but they were found to be two separate species after DNA analysis.

Varroa jacobsoni is a species of mite that parasitises Apis cerana. The more damaging Varroa destructor was previously included under the name V. jacobsoni, but the two species can be separated on the basis of the DNA sequence of the cytochrome oxidase I gene in the mitochondrial DNA.

Deformed wing virus (DWV) is an RNA virus, one of 22 known viruses affecting honey bees. While most commonly infecting the honey bee, Apis mellifera, it has also been documented in other bee species, like Bombus terrestris, thus, indicating it may have a wider host specificity than previously anticipated. The virus was first isolated from a sample of symptomatic honeybees from Japan in the early 1980s and is currently distributed worldwide. It is found also in pollen baskets and commercially reared bumblebees. Its main vector in A. mellifera is the Varroa mite. It is named after what is usually the most obvious deformity it induces in the development of a honeybee pupa, which is shrunken and deformed wings, but other developmental deformities are often present.

The western honey bee or European honey bee is the most common of the 7–12 species of honey bees worldwide. The genus name Apis is Latin for "bee", and mellifera is the Latin for "honey-bearing" or "honey carrying", referring to the species' production of honey.

Fluvalinate is a synthetic pyrethroid chemical compound contained as an active agent in the products Apistan, Klartan, and Minadox, that is an acaricide, commonly used to control Varroa mites in honey bee colonies, infestations that constitute a significant disease of such insects.

Commercial Beekeeping in the United States dates back to the 1860s.

Beekeeping in New Zealand is reported to have commenced in 1839 with the importing of two skep hives by Mary Bumby, a missionary. It has since become an established industry as well a hobby activity.

Colony collapse disorder (CCD) is an abnormal phenomenon that occurs when the majority of worker bees in a honey bee colony disappear, leaving behind a queen, plenty of food, and a few nurse bees to care for the remaining immature bees. While such disappearances have occurred sporadically throughout the history of apiculture, and have been known by various names, the syndrome was renamed colony collapse disorder in early 2007 in conjunction with a drastic rise in reports of disappearances of western honey bee colonies in North America. Beekeepers in most European countries had observed a similar phenomenon since 1998, especially in Southern and Western Europe; the Northern Ireland Assembly received reports of a decline greater than 50%. The phenomenon became more global when it affected some Asian and African countries as well. From 1990 to 2021, the United Nation’s FAO calculated that the worldwide number of honeybee colonies increased 47%, reaching 102 million.
Varroa sensitive hygiene (VSH) is a behavioral trait of honey bees (Apis mellifera) in which bees detect and remove bee pupae that are infested by the parasitic mite Varroa destructor. V. destructor is considered to be the most dangerous pest problem for honey bees worldwide. VSH activity results in significant resistance to the mites.
Beekeeping is first recorded in Ireland in the seventh century. It has seen a surge in popularity in modern times, with the membership of beekeeping associations exceeding 4,500. The median average number of hives per beekeeper is three hives, while the average honey output per hive is 11.4 kg. The growth in the practice has occurred despite increased pressures on bees and beekeepers due to parasites, diseases and habitat loss.

Beekeeping in Australia is a commercial industry with around 25,000 registered beekeepers owning over 670,000 hives in 2018. Most are found in the eastern states of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania as well as the south-west of Western Australia.
Apis mellifera adansonii(Western African bee) is a subspecies of the Western honey bee with probably the largest range of Apis mellifera in Africa, belonging to the A (Africa) Lineage of honey bees. Originally identified by Michael Adansonin in his Histoire naturelle du Seneegal in 1757. Initially the name adsansonii was misapplied to A. m. scutelleta and in particular to the Africanised bees of South America.
















