
Tic-tac-toe, noughts and crosses, or Xs and Os is a paper-and-pencil game for two players who take turns marking the spaces in a three-by-three grid with X or O. The player who succeeds in placing three of their marks in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row is the winner. It is a solved game, with a forced draw assuming best play from both players.

3D tic-tac-toe, also known by the trade name Qubic, is an abstract strategy board game, generally for two players. It is similar in concept to traditional tic-tac-toe but is played in a cubical array of cells, usually 4×4×4. Players take turns placing their markers in blank cells in the array. The first player to achieve four of their own markers in a row wins. The winning row can be horizontal, vertical, or diagonal on a single board as in regular tic-tac-toe, or vertically in a column, or a diagonal line through four boards.
In mathematics, the Hales–Jewett theorem is a fundamental combinatorial result of Ramsey theory named after Alfred W. Hales and Robert I. Jewett, concerning the degree to which high-dimensional objects must necessarily exhibit some combinatorial structure.

OXO is a video game developed by A S Douglas in 1952 which simulates a game of noughts and crosses (tic-tac-toe). It was one of the first games developed in the early history of video games. Douglas programmed the game as part of a thesis on human-computer interaction at the University of Cambridge.
A toe is a digit of the foot of a human or animal.

"Mope" is a song by American comedy rock band Bloodhound Gang, released in September 2000 as the fourth single from their third studio album Hooray for Boobies. The song contains numerous samples such as "Rock Me Amadeus" by Falco, "Relax" by Frankie Goes to Hollywood, "For Whom the Bell Tolls" by Metallica, the Pac-Man theme song, and Homer Simpson shouting "holy macaroni" from the "Treehouse of Horror VI" episode of The Simpsons. A music video for the single was released in June 2000.

Quantum tic-tac-toe is a "quantum generalization" of tic-tac-toe in which the players' moves are "superpositions" of plays in the classical game. The game was invented by Allan Goff of Novatia Labs, who describes it as "a way of introducing quantum physics without mathematics", and offering "a conceptual foundation for understanding the meaning of quantum mechanics".

Waco was a Japanese toy manufacturer. It was known for manufacturing the handheld game Electro Tic-Tac-Toe. Released in 1972, the game is commonly cited as the first commercially available handheld electronic game. However some sources do not consider the Electro Tic-Tac-Toe to be the first handheld electronic game.

"Warum?" is a song by German female pop-rap group Tic Tac Toe. The song was written by Thorsten Börger and tells about a close friend of the group members, Melanie, who had developed an addiction to drugs and died as a result of overdose. "Warum?" was released as the lead single from their second album, Klappe die 2te (1997), on 24 February 1997 and was met with commercial success, reaching number one in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland as well as number four in the Netherlands. The single sold 700,000 copies in less than two months and remains Tic Tac Toe's biggest hit.
Tic Tac is a brand of small, hard mint.
X's and O's, Exes and Ohs, Ex's and Oh's, and other variants in spelling of that phrase may refer to:
Noughts and Crosses is an alternative name for the game of Tic-tac-toe.
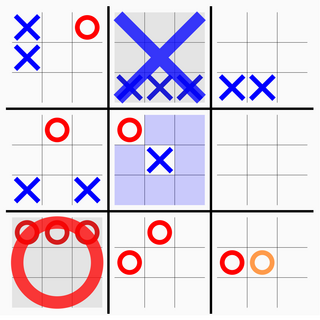
Ultimate tic-tac-toe is a board game composed of nine tic-tac-toe boards arranged in a 3 × 3 grid. Players take turns playing on the smaller tic-tac-toe boards until one of them wins on the larger board. Compared to traditional tic-tac-toe, strategy in this game is conceptually more difficult and has proven more challenging for computers.

Notakto is a tic-tac-toe variant, also known as neutral or impartial tic-tac-toe. The game is a combination of the games tic-tac-toe and Nim, played across one or several boards with both of the players playing the same piece. The game ends when all the boards contain a three-in-a-row of Xs, at which point the player to have made the last move loses the game. However, in this game, unlike tic-tac-toe, there will always be a player who wins any game of Notakto.
Number Scrabble is a mathematical game where players take turns to select numbers from 1 to 9 without repeating any numbers previously used, and the first player with a sum of exactly 15 using any three of their number selections wins the game. The game is isomorphic to tic-tac-toe, as can be seen if the game is mapped onto a magic square.

Tic-tac-toe is an instance of an m,n,k-game, where two players alternate taking turns on an m×n board until one of them gets k in a row. Harary's generalized tic-tac-toe is an even broader generalization. The game can also be generalized as a nd game. The game can be generalised even further from the above variants by playing on an arbitrary hypergraph where rows are hyperedges and cells are vertices.

The Matchbox Educable Noughts and Crosses Engine was a mechanical computer made from 304 matchboxes designed and built by artificial intelligence researcher Donald Michie in 1961. It was designed to play human opponents in games of noughts and crosses (tic-tac-toe) by returning a move for any given state of play and to refine its strategy through reinforcement learning.

The System Source Computer Museum, located in Hunt Valley, Maryland, USA, exhibits notable computing devices from ancient times until the present. Over 5,000 objects are on display and many of the computation devices are operational. STEM activities are offered to organized tour groups. Admission is $15 for adults, $10 for students, children, veterans, and first responders. The museum is open weekdays from 9:00am until 6:00pm by appointment. Museum docents are available to lead tours.










