
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, and these are known as the Gulf States.
Ghana is a West African country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea.

The term "United States," when used in the geographical sense, refers to the contiguous United States, Alaska, Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions. The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, The Bahamas, and many other countries, mainly in the Caribbeanin addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world's longest bi-national land border.
The Geography of Guyana comprises the physical characteristics of the country in Northern South America and part of Caribbean South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Suriname and Venezuela, with a land area of approximately 214,969 square km. The country is situated between 1 and 9 north latitude and between 56 and 62 west longitude. With a 459 km (285 mi)-long Atlantic coastline on the northeast, Guyana is bounded by Venezuela on the west, Brazil on the west and south, and Suriname on the east.

The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the region encompassing the coastline where the Eastern United States meets the Atlantic Ocean. The Thirteen Colonies, which formed the United States in 1776 were located on this coast, and it has played an important role in the development of the United States.

"Tidewater" is a term for the north Atlantic Plain region of the United States, located east of the Piedmont. It includes Delaware, the remainder of the Delmarva Peninsula, the Chesapeake Bay area of Southern Maryland, Washington, D.C., Eastern Virginia, and Eastern North Carolina.

A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air hallway or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure.

American colonial architecture includes several building design styles associated with the colonial period of the United States, including First Period English (late-medieval), Spanish Colonial, French Colonial, Dutch Colonial, and Georgian. These styles are associated with the houses, churches and government buildings of the period from about 1600 through the 19th century.

Hurricane Bertha was an intense and early-forming major hurricane that affected areas from the Leeward Islands to the United States in July of the 1996 Atlantic hurricane season. The second named storm, first hurricane, and first major hurricane during the season, Bertha originated from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa in early July. Steadily organizing while moving generally towards the west, the disturbance was designated as a tropical depression at 0000 UTC on July 5, and was further upgraded to a tropical storm by 1200 UTC later that day. Over the next few days, continued intensification occurred, and Bertha became a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale, the first hurricane of the season, prior to moving through the northern Leeward Islands. Late on July 8, a period of rapid intensification began, and at 0600 UTC on July 9, Bertha reached its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) with a minimum barometric pressure of 960 mbar (28 inHg). Moving around the western periphery of the subtropical ridge, Bertha passed north of the Bahamas as a weakening hurricane before turning towards the north-northeast and undergoing another period of rapid intensification. Late on July 12, Bertha made landfall between Wrightsville Beach and Topsail Beach, North Carolina with winds of 105 mph (169 km/h). Gradual weakening ensued the following day as Bertha moved up the Mid-Atlantic and into New England before becoming an extratropical cyclone on July 14. The storm's remnants persisted for another several days, before dissipating on July 18.

California bungalow is an alternative name for the American Craftsman style of residential architecture, when it was applied to small-to-medium-sized homes rather than the large "ultimate bungalow" houses of designers like Greene and Greene. California bungalows became popular in suburban neighborhoods across the United States, and to varying extents elsewhere, from around 1910 to 1939.

Florida cracker architecture or Southern plantation style is a style of vernacular architecture typified by a low slung, wood-frame house, with a large porch. It was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century. Some elements of the style are still popular as a source of design themes. The name refers to colonial-era English and French pioneer settlers and their descendants. These homes were often designed with outdoor porches and large windows to help try to cool homes during the long hot season in these low latitude subtropical climates.

The Christmas 1994 nor'easter was an intense cyclone along the East Coast of the United States and Atlantic Canada. It developed from an area of low pressure in the southeast Gulf of Mexico near the Florida Keys, and moved across the state of Florida. As it entered the warm waters of the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean, it began to rapidly intensify, exhibiting traits of a tropical system, including the formation of an eye. It attained a pressure of 970 millibars on December 23 and 24, and after moving northward, it came ashore near New York City on Christmas Eve. Because of the uncertain nature of the storm, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) did not classify it as a tropical cyclone.
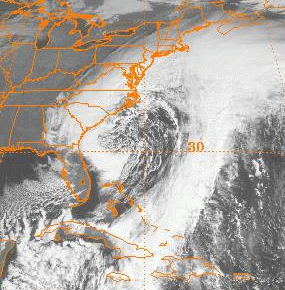
The November 2006 nor'easter was a powerful extratropical cyclone that formed offshore of the Southeastern United States on November 20, bringing heavy rains, high winds, beach erosion, and coastal flooding to the Carolinas and southern New England. In addition, the earliest snowfall ever noted in both Charleston, South Carolina and Savannah, Georgia occurred on the southwest side of this cyclone. Over 10,000 were without power during the storm. No longer a nor'easter, the extratropical cyclone accelerated rapidly across the North Atlantic while rapidly strengthening, becoming a cyclonic storm again by November 25, but this time with hurricane-force sustained winds. The intense low made a cyclonic loop west of Iceland, before being absorbed by another strengthening extratropical cyclone to the west of Great Britain, late on December 1.

Creole architecture in the United States is present in buildings in Louisiana and elsewhere in the South, and also in the U.S. associated territories of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands. A variant is Ponce Creole style.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the farther south one travels, and drier the farther west, until one reaches the West Coast.

A Dutch gable roof or gablet roof is a roof with a small gable at the top of a hip roof. The term Dutch gable is also used to mean a gable with parapets. Some sources refer to this as a gable-on-hip roof.

Queen Anne style architecture was one of a number of popular Victorian architectural styles that emerged in the United States during the period from roughly 1880 to 1910. It is sometimes grouped as New World Queen Anne Revival architecture. Popular there during this time, it followed the Second Empire and Stick styles and preceded the Richardsonian Romanesque and Shingle styles. Sub-movements of Queen Anne include the Eastlake movement.

The December 1969 nor'easter was a strong winter storm that mainly affected the Northeastern United States and southern Quebec between December 25 and December 28, 1969. The multi-faceted storm system included a tornado outbreak, record snow accumulations, a damaging ice storm, and flooding rains.

A porch is a room or gallery located in front of an entrance of a building. A porch is placed in front of the façade of a building it commands, and forms a low front. Alternatively, it may be a vestibule, or a projecting building that houses the entrance door of a building.

In the New World, Queen Anne Revival was a historicist architectural style of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was popular in the United States, Canada, Australia, and other countries. In Australia, it is also called Federation architecture.



















