
The Bahamas, known officially as the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is a country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 700 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the US state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus Swietenia, indigenous to the Americas and part of the pantropical chinaberry family, Meliaceae.

Andros Island is an archipelago within the Bahamas, the largest of the Bahamian Islands. Politically considered a single island, Andros in total has an area greater than all the other 700 Bahamian islands combined. The land area of Andros consists of hundreds of small islets and cays connected by mangrove estuaries and tidal swamplands, together with three major islands: North Andros, Mangrove Cay, and South Andros. The three main islands are separated by "bights", estuaries that trifurcate the island, connecting the island's east and west coasts. It is 167 kilometres (104 mi) long by 64 km (40 mi) wide at the widest point.

Eleuthera refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of The Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incorporates the smaller Harbour Island. "Eleuthera" derives from the feminine form of the Greek adjective ἐλεύθερος (eleútheros), meaning "free". Known in the 17th century as Cigateo, it lies 80 km east of Nassau. It is long and thin—180 km long and in places little more than 1.6 km wide. Its eastern side faces the Atlantic Ocean, and its western side faces the Great Bahama Bank. The topography of the island varies from wide rolling pink sand beaches to large outcrops of ancient coral reefs, and its population is approximately 11,000. The principal economy of the island is tourism.

Cat Island is located in central Bahamas, and is one of its districts. Cat Island also has the nation's highest point, Mount Alvernia. It rises to 206 feet (63 m) and is topped by a monastery called The Hermitage. This assembly of buildings was erected by the Franciscan "Brother Jerome".

Freeport is a city, district and free trade zone on the island of Grand Bahama of the northwest Bahamas. In 1955, Wallace Groves, a Virginian financier with lumber interests in Grand Bahama, was granted 20,000 hectares of pineyard with substantial areas of swamp and scrubland by the Bahamian government with a mandate to economically develop the area. Freeport has grown to become the second most populous city in the Bahamas.

North Andros is one of the 31 districts of the Bahamas. It is also the largest district in the country. It has some of the largest settlements on Andros Island and many churches as well. The population is 3,898.

Timber Creek Regional High School is a four-year comprehensive community public high school for students in ninth through twelfth grades located in the Erial section in southern Gloucester Township in Camden County, New Jersey, United States, operating as one of the three secondary schools of the Black Horse Pike Regional School District. When the school opened in 2001, attendance zones were realigned to relieve overcrowding conditions at Highland and Triton high schools. Timber Creek serves students from the southern portion of Gloucester Township.
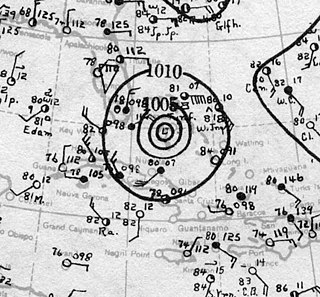
The 1929 Bahamas hurricane was a high-end Category 4 tropical cyclone whose intensity and slow forward speed led to catastrophic damage in the Bahamas in September 1929, particularly on Andros and New Providence islands. Its erratic path and a lack of nearby weather observations made the hurricane difficult to locate and forecast. The storm later made two landfalls in Florida, killing eleven but causing comparatively light damage. Moisture from the storm led to extensive flooding over the Southeastern United States, particularly along the Savannah River. Across its path from the Bahamas to the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River, the hurricane killed 155 people.

The Belmont Anti-Tank Ditch was an anti-tank trench constructed in 1942 as part of the southern perimeter defensive system of the Port of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia, as part of Fortress Newcastle during World War II. The anti-tank ditch was located 12 kilometres south of Newcastle, south of the town of Belmont.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.
Timber Creek may refer to:
Timber Creek High School is a public high school located in the city of Fort Worth, Texas which is served by the Keller Independent School District. The campus opened its doors in the fall of 2009 and was Keller ISD's fourth high school. Its first graduating class was in the spring of 2012. In 2015, the school was rated "Met Standard" by the Texas Education Agency.

Timber Creek Lodge is an American reality television series that premiered on the Bravo cable network, on December 5, 2016. The show follows a group of staff members serving "a slew of elite clientele at an ultra-luxurious" ski lodge located near the village of Whistler, British Columbia, Canada.

The Ingalara Creek railway bridge is a heritage-listed former railway bridge that carried the Bombala railway line across Ingalara Creek at Michelago in the Snowy Monaro Regional Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by John Whitton in his capacity as Engineer-in-Chief for Railways and built in 1889. It is also known as the Michelago Rail Bridge over Ingalara Creek and the Ingalara Creek Railway Viaduct. The property is owned by RailCorp, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. On 1 December 2020, changes were made to exemptions relating to the bridge's heritage status.
The Manilla railway underbridges are two heritage-listed railway bridges located on the Tamworth-Barraba railway line in the town of Manilla in the Tamworth Regional Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The underbridges are owned by RailCorp, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. The two sites were added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.
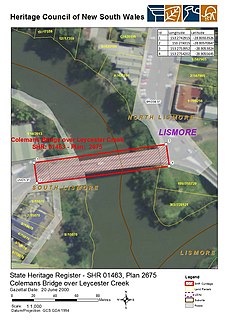
The Colemans Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries Union Street across the Leycester Creek in Lismore, City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Harvey Dare and built in 1907 by W. F. Oakes. The property is owned by Roads and Maritime Services, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Beckers Bridge over Webbers Creek is a heritage-listed timber truss road bridge that carries Main Road across Webbers Creek, located in Glendon Brook, Singleton Council, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Ernest de Burgh. The property is owned by Roads and Maritime Services, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.
The Glennies Creek Bridge is a heritage-listed road bridge that carries the Rixs Creek-Falbrook Road across the Glennies Creek, located at Middle Falbrook, in the Singleton Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by Ernest de Burgh and built in 1902-03 by William Murphy and James Taylor. The property is owned by Roads and Maritime Services, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. The bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 20 June 2000.














