Related Research Articles
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.
Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a method of planning and managing projects that emphasizes the resources required to execute project tasks. It was developed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt. It differs from more traditional methods that derive from critical path and PERT algorithms, which emphasize task order and rigid scheduling. A critical chain project network strives to keep resources levelled, and requires that they be flexible in start times.

Eliyahu Moshe Goldratt was an Israeli business management guru. He was the originator of the Optimized Production Technique, the Theory of Constraints (TOC), the Thinking Processes, Drum-Buffer-Rope, Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) and other TOC derived tools.

The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The body of knowledge evolves over time and is presented in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a book whose seventh edition was released in 2021. This document results from work overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers the CAPM and PMP certifications.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing process to identify the constraint and restructure the rest of the organization around it. TOC adopts the common idiom "a chain is no stronger than its weakest link". That means that organizations and processes are vulnerable because the weakest person or part can always damage or break them, or at least adversely affect the outcome.
Project management software are computer programs that help plan, organize, and manage resources.
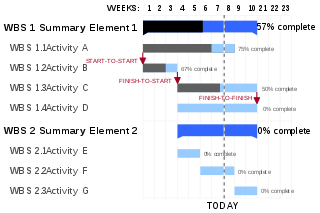
A Gantt chart is a bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. It was designed and popularized by Henry Gantt around the years 1910–1915. Modern Gantt charts also show the dependency relationships between activities and the current schedule status.
A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined start and a defined finish; regardless of industry. Project managers are first point of contact for any issues or discrepancies arising from within the heads of various departments in an organization before the problem escalates to higher authorities, as project representative.

The Goal is a management-oriented novel by Eliyahu M. Goldratt, a business consultant known for his theory of constraints, and Jeff Cox, the author of several management-oriented novels. The Goal was originally published in 1984 and has since been revised and republished. This describes a case study in operations management, focusing on the theory of constraints, and bottlenecks and how to alleviate them. In 2011, Time Magazine listed the book as one of "the 25 most influential business management books".

PRINCE2 is a structured project management method and practitioner certification programme. PRINCE2 emphasises dividing projects into manageable and controllable stages.

Henry Laurence Gantt was an American mechanical engineer and management consultant who is best known for his work in the development of scientific management. He created the Gantt chart in the 1910s.
Project Management Professional (PMP) is an internationally recognized professional designation offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). As of 31 July 2020, there are 1,036,368 active PMP-certified individuals and 314 chartered chapters across 214 countries and territories worldwide.
A project management office is a group or department within a business, government agency, or enterprise that defines and maintains standards for project management within the organization. The PMO strives to standardize and introduce economies of repetition in the execution of projects. The PMO is the source of documentation, guidance, and metrics on the practice of project management and execution.

Isambard Kingdom Brunel was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engineering giants", and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, [who] changed the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions". Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first purpose-built transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering.

The Hilton London Paddington, formerly the Great Western Royal Hotel, is a hotel that forms part of the Paddington Station complex in London, England. The hotel was originally the idea of Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who was the hotel's first managing director. The funding came in large part from the Directors of the Great Western Railway Company, who were persuaded by Brunel to buy shares in the project. The hotel was built on Praed Street in the early 1850s and opened on 9 June 1854 by H.R.H. The Prince Albert, Prince Consort, having taken 14 months to build. The hotel was designed by architect Philip Charles Hardwick, costing approximately £60,000 including all furnishing and fittings - a building which was 'to rival the facilities of the great hotels on the Continent'. The building effectively forms the main façade of the station, closing off the end of the train shed at the head of the terminal platforms. It was built by Messrs Holland Hannen & Cubitts, the building firm founded by Thomas Cubitt.
The Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) was a UK government agency providing computer and telecoms support to government departments.
Cost engineering is "the engineering practice devoted to the management of project cost, involving such activities as estimating, cost control, cost forecasting, investment appraisal and risk analysis". "Cost Engineers budget, plan and monitor investment projects. They seek the optimum balance between cost, quality and time requirements."
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
A project management information system (PMIS) is the logical organization of the information required for an organization to execute projects successfully. A PMIS is typically one or more software applications and a methodical process for collecting and using project information. These electronic systems "help [to] plan, execute, and close project management goals." PMIS systems differ in scope, design and features depending upon an organisation's operational requirements.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
References
- ↑ Dennis Lock (2007) Project management (9e ed.) Gower Publishing, Ltd., 2007. ISBN 0-566-08772-3
- ↑ Young-Hoon Kwak (2005). "A brief history of Project Management". In: The story of managing projects. Elias G. Carayannis et al. 9eds, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005. ISBN 1-56720-506-2
- ↑ "PROMPT | Simpact Systems 1975". projectmanagementhistory.com. Retrieved 2016-03-04.