Related Research Articles

Cambridgeshire is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the west. The largest settlement is the city of Peterborough, and the city of Cambridge is the county town.

The Fens or Fenlands in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a system of drainage channels and man-made rivers and automated pumping stations. There have been unintended consequences to this reclamation, as the land level has continued to sink and the dykes have been built higher to protect it from flooding.

Wisbech is a market town, inland port and civil parish in the Fenland district in Cambridgeshire, England. In 2011 it had a population of 31,573. The town lies in the far north-east of Cambridgeshire, bordering Norfolk and only 5 miles (8 km) south of Lincolnshire. The tidal River Nene running through the town is spanned by two road bridges. Wisbech is in the Isle of Ely and has been described as "the Capital of The Fens".

The Isle of Ely is a historic region around the city of Ely in Cambridgeshire, England. Between 1889 and 1965, it formed an administrative county.

Soham is a town and civil parish in the district of East Cambridgeshire, in Cambridgeshire, England, just off the A142 between Ely and Newmarket. Its population was 12,336 at the 2021 census.

Ramsey is a market town and civil parish in the Huntingdonshire district of Cambridgeshire, England. The town is about 9 miles (14 km) north of Huntingdon. Ramsey parish includes the settlements of Ramsey Forty Foot, Ramsey Heights, Ramsey Mereside, Ramsey Hollow and Ramsey St Mary's.

South Cambridgeshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, England, with a population of 162,119 at the 2021 census. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of Chesterton Rural District and South Cambridgeshire Rural District. It completely surrounds the city of Cambridge, which is administered separately from the district by Cambridge City Council.

East Cambridgeshire is a local government district in Cambridgeshire, England. Its council is based in the city of Ely. The district also contains the towns of Littleport and Soham and surrounding rural areas, including parts of the Fens.

Fenland is a local government district in Cambridgeshire, England. It was historically part of the Isle of Ely. The district covers around 500 square kilometres (190 sq mi) of mostly agricultural land in the extremely flat Fens. The council is based in March. Other towns include Chatteris, Whittlesey and Wisbech.

Wicken is a small village on the edge of The Fens near Soham in East Cambridgeshire, ten miles north east of Cambridge and five miles south of Ely. It is the site of Wicken Fen National Nature Reserve.
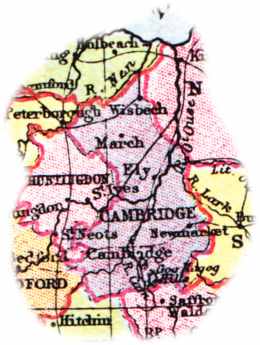
The English county of Cambridgeshire has a long history.

Cottenham is a village in Cambridgeshire, England. Cottenham is one of the larger villages surrounding the city of Cambridge, located around five miles north of the city. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 Census was 6,095. Cottenham is one of a number of villages that make up the historical Fen Edge region in between Cambridge and Ely, which were originally settlements on the shore of the marshes close to the city of Cambridge, then an inland port.

Wicken Fen is a 254.5-hectare (629-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest west of Wicken in Cambridgeshire. It is also a National Nature Reserve, and a Nature Conservation Review site. It is protected by international designations as a Ramsar wetland site of international importance, and part of the Fenland Special Area of Conservation under the Habitats Directive.
Holme is a village and civil parish in Cambridgeshire, England. Holme lies approximately 7 miles (11 km) south of Peterborough, near Conington and Yaxley. Holme is situated within Huntingdonshire which is a non-metropolitan district of Cambridgeshire as well as being a historic county of England. The parish contains the lowest point in Great Britain, 2.75 metres (9.0 ft) below sea level.

Chittering is a hamlet about 8 miles (13 km) north of Cambridge in Cambridgeshire, England. For administrative purposes it is part of the parish of Waterbeach. The population of the hamlet was included in the civil parish of Bottisham at the 2011 Census.

Stonea Camp is an Iron Age multivallate hill fort located at Stonea near March in the Cambridgeshire Fens. Situated on a gravel bank just 2 metres above sea-level, it is the lowest hill fort in Britain. Around 500 BC, when fortification is thought to have begun at this site, this "hill" would have provided a significant area of habitable land amidst the flooded marshes of the fens. The site exhibits at least two phases of development over several hundred years of settlement, with a D-shaped set of earth banks surrounded by a larger, more formal set of banks and ditches.
Rampton is a village in Cambridgeshire, England, situated on the edge of The Fens six miles to the north of Cambridge.

The Cambridgeshire Lodes are a series of man-made waterways, believed to be Roman in origin, located in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. Bottisham, Swaffham Bulbeck, Reach, Burwell, Wicken and Monks Lodes all connect to the River Cam, while Soham and Cottenham Lodes connect to the River Great Ouse. All have been navigable historically, but some are no longer officially navigable.

Ely is a cathedral city and civil parish in the East Cambridgeshire district of Cambridgeshire, England, about 14 miles (23 km) north-northeast of Cambridge, 24 miles (39 km) south east of Peterborough and 80 miles (130 km) from London. As of the 2021 census, Ely is recorded as having a population of 19,200.

Enid Mary Porter was a collector of folklore in Cambridgeshire and the longest serving curator of the Cambridge & County Folk Museum, now the Museum of Cambridge, working from 1947 to 1976. Her work was invaluable in recording the cultural and social practices of people in Cambridgeshire; she was innovative in the discipline of social history collection, employing working practices such as oral history, and engaging with people in areas that had previously been overlooked by folklorists. Her notebooks, now in possession of the Museum of Cambridge, hold a treasure-trove of information about Cambridgeshire customs, stories and songs.
References
- 1 2 Codd, Daniel (2010), "Supernatural Evil: Necromancers, Wisemen and Toad-men", Mysterious Cambridgeshire, JMD Media, ISBN 9781859838082
- 1 2 James, Maureen (2014), "Of the Fens and Farming: Elijah's Ghost (A Tale of a Toadman)", Cambridgeshire Folk Tales, History Press, ISBN 9780752466286