
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.

Trunk Bay is a body of water and a beach on St. John in the United States Virgin Islands. Trunk Bay is part of the Virgin Islands National Park. Trunk Bay is named for the Leatherback turtle, which is endemic to the USVI and are locally known as trunks. The beach area is divided into two halves, the main Trunk Bay beach and swim area and Burgesman Cove which is located on the west end of Trunk Bay near Jumby Bay. Its amenities include a snack bar, showers and restrooms, a lifeguard, and an underwater trail for snorkeling its coral reef. Trunk Bay has consistently been voted one of the top beaches in the world.

Southampton Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named for Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton (1573-1624).

Warwick Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick (1587-1658).
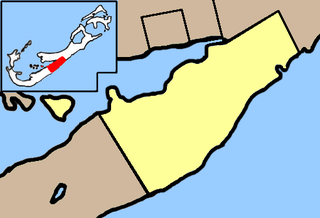
Paget Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named for William Paget, 4th Baron Paget de Beaudesert (1572–1629).
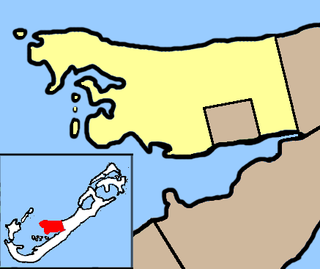
Pembroke Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after English aristocrat William Herbert, 3rd Earl of Pembroke (1580–1630).

Devonshire Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. Originally named Cavendish Tribe and later Devonshire Tribe, for William Cavendish, 1st Earl of Devonshire (1552–1626). Devonshire Redoubt, on Castle Island, one of the Castle Harbour fortifications of St. George's Parish, was also named after him.

Hamilton Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It was renamed for Scottish aristocrat James Hamilton, 2nd Marquess of Hamilton (1589–1625) when he purchased the shares originally held in the Virginia Company by Lucy Russell, Countess of Bedford.
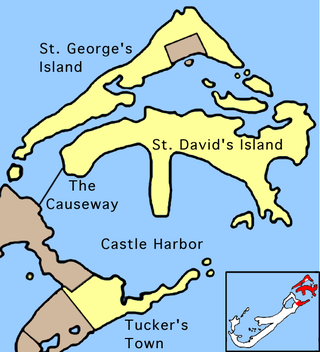
St. George's Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after the founder of the Bermuda colony, Admiral Sir George Somers.

Horseshoe Bay is a well-known beach in Bermuda. As a tourist spot, it lies on the main island's south coast, in the parish of Southampton. It is one of two beaches of the same name in Bermuda, with the other located at Tucker's Island: since the 1940s part of a peninsula that housed the former US Naval Operating Base, and is now called Morgan's Point.

The Causeway is a narrow strip of reclaimed land and bridges in the north of Bermuda linking Hamilton Parish on the mainland in the southwest and Bermuda International Airport on St. David's Island in St. George's Parish in the northeast, which are otherwise divided by Castle Harbour.

Cooper's Island is part of the chain which makes up Bermuda. It is located in St. George's Parish, in the northeast of the territory.

St. David's Island is one of the main islands of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is located in the far north of the territory, one of the two similarly sized islands that make up the majority of St. George's Parish.
Annie's Bay is a picturesque bay in the northeast of Bermuda. It occupies much of the east coast of Cooper's Island, in St. George's Parish.
The following is a list of places of interest in Bermuda.

HMS Vixen was an armoured composite gunboat, the only ship of her class, and the third ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name. She was the first Royal Navy vessel to have twin propellers.
Church Bay is a bay with an accompanying beach in Southampton Parish, Bermuda. It serves as a popular snorkelling destination for locals.
Montana was a paddle steamer that was wrecked off the north coast of Bermuda on 30 December 1863.

Lovango Cay is a private island in the district of St. John, in the United States Virgin Islands.

Admiralty House, Bermuda, was the official residence and offices for the senior officer of the Royal Navy in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda, originally the Commander-in-Chief of the North America and West Indies Station.


















