
Sears, Roebuck and Co., commonly known as Sears, is an American chain of department stores founded in 1892 by Richard Warren Sears and Alvah Curtis Roebuck and reincorporated in 1906 by Richard Sears and Julius Rosenwald, with what began as a mail ordering catalog company migrating to opening retail locations in 1925, the first in Chicago. In 2005, the company was bought by the management of the American big box discount chain Kmart, which upon completion of the merger, formed Sears Holdings. Through the 1980s, Sears was the largest retailer in the United States. In 2018, it was the 31st-largest. After several years of declining sales, Sears's parent company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy on October 15, 2018. It announced on January 16, 2019, that it had won its bankruptcy auction, and that a reduced number of 425 stores would remain open, including 223 Sears stores.

Sears Canada Inc. was a publicly-traded Canadian company affiliated with the American-based Sears department store chain. In operation from 1952 until January 14, 2018, and headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, the company began as Simpsons-Sears—a joint venture between the Canadian Simpsons department store chain and the American Sears chain—which operated a national mail order business and co-branded Simpsons-Sears stores modelled after those of Sears in the U.S. After the Hudson's Bay Company purchased Simpsons in 1978, the joint venture was dismantled and Hudson's Bay sold its shares in the joint venture to Sears; with Sears now fully owning the company, it was renamed Sears Canada Inc. in 1984. In 1999, Sears Canada acquired the remaining assets and locations of the historic Canadian chain Eaton's. From 2014, Sears Holdings owned a 10% share in the company. ESL Investments was the largest shareholder of Sears Canada.

Julius Rosenwald was an American businessman and philanthropist. He is best known as a part-owner and leader of Sears, Roebuck and Company, and for establishing the Rosenwald Fund, which donated millions in matching funds to promote vocational or technical education. In 1919 he was appointed to the Chicago Commission on Race Relations. He was also the principal founder and backer for the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago, to which he gave more than $5 million and served as president from 1927 to 1932.

The Allstate is an American automobile that was offered for sale through Sears, Roebuck and Co. during the 1952 and 1953 model years. It was a rebadged version of the Henry J, an automobile manufactured by the Kaiser-Frazer company from 1950 through 1954.

Western Auto Supply Company—known more widely as Western Auto—was a specialty retail chain of stores that supplied automobile parts and accessories operating approximately 1,200 stores across the United States.
Craftsman is a line of tools, lawn and garden equipment, and work wear. Originally a house brand established by Sears, the brand is now owned by Stanley Black & Decker.

Richard Warren Sears was an American company manager, retail businessman and the co-founder of department store Sears, Roebuck and Company with his partner Alvah Curtis Roebuck.

Sears Modern Homes were houses sold primarily through mail order catalog by Sears, Roebuck and Co., an American retailer.

Mail order is the buying of goods or services by mail delivery. The buyer places an order for the desired products with the merchant through some remote methods such as:

Alvah Curtis Roebuck was an American retail businessman, who was one of the co-founders of department store Sears, Roebuck and Company with his partner Richard Warren Sears.

Silvertone Records was a record label manufactured for Sears, Roebuck and Co. for sale originally in their mail order catalog and later in their chain of department stores.

Challenge Records was a record label sold by the Sears-Roebuck Company. Releases were drawn from other recordings on other labels in the late 1920s, such as Banner, Gennett, Paramount Records and others. Sears also had the Silvertone label and the same recording of "Black Bottom" by Joe Candullo & his Everglades Orchestra was released on both labels. Around 1929 Sears did away with Challenge and Silvertone, replacing them with Conqueror Records. Challenge discs generally sold for less than Silvertone ones because they seldom used songs requiring royalty payments and the label generally assigned pseudonyms to the artists. Introduced in the Spring 1927 catalog for just 24¢ per disc, Challenge bore the frank disclaimer, "If you want the best, we recommend the Silvertone." The last issues appeared in Sears’ Spring 1931 catalog.
Tressy was an American fashion doll with a feature to adjust the length of its hair. Tressy was first produced by American Character Doll Company in the 1960s and later by Ideal Toy Company in the 1970s. The doll was invented and patented by modern furniture designer Jesse Dean and his wife, Diana.
Toughskins are a line of clothing sold by Sears, Roebuck and Co. which were primarily marketed for their durability. When launched, the line consisted of children's jeans which were sold with the guarantee that children would grow out of them before the pants wore out.

Kit houses, also known as mill-cut houses, pre-cut houses, ready-cut houses,mail order homes, or catalog homes, were a type of housing that was popular in the United States, Canada, and elsewhere in the first half of the 20th century. Kit house manufacturers sold houses in many different plans and styles, from simple bungalows to imposing Colonials, and supplied at a fixed price all materials needed for construction of a particular house, but typically excluding brick, concrete, or masonry. Some house styles, like log cabins and geodesic dome homes, are still sometimes sold in kit form.

The Sears, Roebuck and Company Complex is a building complex in the community area of North Lawndale in Chicago, Illinois. The complex hosted most of department-store chain Sears' mail order operations between 1906 and 1993, and it also served as Sears' corporate headquarters until 1973, when the Sears Tower was completed. Of its original 40-acre (16 ha) complex, only three buildings survive and have been adaptively rehabilitated to other uses. The complex was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1978, at which time it still included the 3,000,000-square-foot mail order plant, the world's largest commercial building when it was completed. That building has been demolished, its site taken up by the Homan Square redevelopment project.
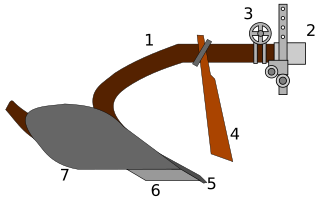
A (US:) colter / (British:) coulter is a vertically mounted component of many ploughs that cuts an edge about 7 inches (18 cm) deep ahead of a plowshare. Its most effective depth is determined by soil conditions.
Sears, Roebuck & Co. v. Stiffel Co., 376 U.S. 225 (1964), was a United States Supreme Court case that limited state law on unfair competition when it prevents the copying of an item that is not covered by a patent.

Ponce City Market is a mixed-use development located in a former Sears catalogue facility in Atlanta, with national and local retail anchors, restaurants, a food hall, boutiques and offices, and residential units. It is located adjacent to the intersection of the BeltLine with Ponce de Leon Avenue in the Old Fourth Ward near Virginia Highland, Poncey-Highland and Midtown neighborhoods. The 2.1-million-square-foot (200,000 m2) building, one of the largest by volume in the Southeast United States, was used by Sears, Roebuck and Co. from 1926 to 1987 and later by the City of Atlanta as "City Hall East". The building's lot covers 16 acres (65,000 m2). Ponce City Market officially opened on August 25, 2014. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2016.
The Stevens Model 520 was a pump-action shotgun developed by John Browning and originally manufactured by the J Stevens Arms & Tool Company between 1909 and 1916. Stevens was sold to New England Westinghouse on 28 May 1915 and production of civilian firearms was greatly reduced. The company was renamed the "J Stevens Arms Company" on 1 July 1916 and New England Westinghouse used their manufacturing facility in Chicopee Falls, MA to produce Mosin-Nagant rifles under contract for the Russian Czar during World War I. After the war, Stevens was sold to Savage Arms on 1 April 1920 and full production of civilian firearms resumed. Under Savage ownership, Model 520 production continued until 1939 when it was replaced by the Model 520A which ended production in 1948. Stevens also further modified the design when they introduced the streamlined Model 620 in 1927. The Model 620 was internally similar to the Model 520 and was produced until 1939 when it was replaced by the Model 620A which ended production in 1955. This shotgun is a hammerless, pump action, take-down design with a tubular magazine which holds 5 shells. All models can also be slam fired: the shotgun has no trigger disconnector and shells can be fired one after the other simply by working the slide if the trigger is held down.















