
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster in London. Parliament possesses legislative supremacy and thereby holds ultimate power over all other political bodies in the United Kingdom and the Overseas Territories. While Parliament is bicameral, it has three parts: the sovereign, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The three parts acting together to legislate may be described as the King-in-Parliament. The Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation.

Ireland, also known as the Republic of Ireland, is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland, with a population of about 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island, with a population of about 1.5 million. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the Oireachtas, consists of a lower house, Dáil Éireann; an upper house, Seanad Éireann; and an elected president who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the Taoiseach, elected by the Dáil and appointed by the president, who appoints other government ministers.

The counties of Ireland are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number.

Northern Ireland is a part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland that is variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares an open border to the south and west with the Republic of Ireland. At the 2021 census, its population was 1,903,175, making up around 3% of the UK's population and 27% of the population on the island of Ireland. The Northern Ireland Assembly, established by the Northern Ireland Act 1998, holds responsibility for a range of devolved policy matters, while other areas are reserved for the UK Government. The government of Northern Ireland cooperates with the government of Ireland in several areas under the terms of the Belfast Agreement. The Republic of Ireland also has a consultative role on non-devolved governmental matters through the British–Irish Governmental Conference (BIIG).

The president of Ireland is the head of state of Ireland and the supreme commander of the Irish Defence Forces.
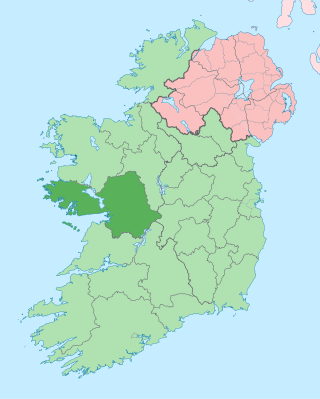
County Galway is a county in Ireland. It is in the Northern and Western Region, taking up the south of the province of Connacht. The county population was 276,451 at the 2022 census.

The Acts of Union 1800 were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The acts came into force between 31 December 1800 and 1 January 1801, and the merged Parliament of the United Kingdom had its first meeting on 22 January 1801.
The Peerage of Ireland consists of those titles of nobility created by the English monarchs in their capacity as Lord or King of Ireland, or later by monarchs of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It is one of the five divisions of Peerages in the United Kingdom. The creation of such titles came to an end in the 19th century. The ranks of the Irish peerage are duke, marquess, earl, viscount and baron. As of 2016, there were 135 titles in the Peerage of Ireland extant: two dukedoms, ten marquessates, 43 earldoms, 28 viscountcies, and 52 baronies. However, these titles have no official recognition in Ireland, with Article 40.2 of the Constitution of Ireland forbidding the state conferring titles of nobility and stating that an Irish citizen may not accept titles of nobility or honour except with the prior approval of the Irish government.
An alderman is a member of a municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law with similar officials existing in the Netherlands (wethouder) and Belgium (schepen). The term may be titular, denoting a high-ranking member of a borough or county council, a council member chosen by the elected members themselves rather than by popular vote, or a council member elected by voters.
The Northern Ireland Assembly, often referred to by the metonym Stormont, is the devolved legislature of Northern Ireland. It has power to legislate in a wide range of areas that are not explicitly reserved to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, and to appoint the Northern Ireland Executive. It sits at Parliament Buildings at Stormont in Belfast.
Municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally owned corporations.

In the United Kingdom, a member of Parliament (MP) is an individual elected to serve in the House of Commons, the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
The law of Northern Ireland is the legal system of statute and common law operating in Northern Ireland since the partition of Ireland established Northern Ireland as a distinct jurisdiction in 1921. Before 1921, Northern Ireland was part of the same legal system as the rest of Ireland.

Since 1922, the United Kingdom has been made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom.

Ireland uses Irish Standard Time in the summer months and Greenwich Mean Time in the winter period.

Dáil Éireann is the lower house and principal chamber of the Oireachtas, which also includes the president of Ireland and a senate called Seanad Éireann. It consists of 160 members, each known as a Teachta Dála. TDs represent 39 constituencies and are directly elected for terms not exceeding five years, on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). Its powers are similar to those of lower houses under many other bicameral parliamentary systems and it is by far the dominant branch of the Oireachtas. Subject to the limits imposed by the Constitution of Ireland, it has power to pass any law it wishes, and to nominate and remove the Taoiseach. Since 1922, it has met in Leinster House in Dublin.












